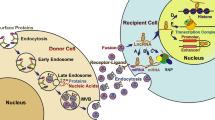
Abstract
Exosomes are small membrane-enclosed vesicles that are released by most living cells and harbor a diverse array of proteins, nucleic acids, and lipid cargos. These exosomes offer valuable biomarkers that may offer insights regarding as a range of physiological and pathological processes, including immune responses, cancer development, pregnancy, and diseases of the central nervous system. With the development of high-throughput technologies, the vital functions of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been gradually entered people’s vision and become new research hotspots. Nowadays, lncRNAs can play important roles in cancer progression by combining with miRNAs, activating molecular targets and other ways, and are also related to the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis for cancer, such as prostate cancer. Current review focused on the summary of diagnostic roles and mechanistic functions about exosomal lncRNAs in prostate cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESCRT:
-
Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular bodies
- PCA3:
-
PCa antibody 3
- NEAT1:
-
Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1
- PCSEAT:
-
PCa specific expression and EZH2-associated transcript
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1
- CXCL14:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand-14
- EZH2:
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- RUNX2:
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2
- SFPQ:
-
Splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich
- PTBP2:
-
Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 2
- FOXM1:
-
Forkhead box M1
- ATG4a:
-
Autophagy-related protein 4 homolog A
References
Culp MB, Soerjomataram I, Efstathiou JA, Bray F, Jemal A. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2020;77(1):38–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.005.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708.
Zhu Y, Mo M, Wei Y, Wu J, Pan J, Freedland SJ, et al. Epidemiology and genomics of prostate cancer in Asian men. Nat Rev Urol. 2021;18(5):282–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-021-00442-8.
Hoffman RM. Clinical practice. Screening for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(21):2013–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1103642.
Marar C, Starich B, Wirtz D. Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5):560–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-00899-0.
Shah R, Patel T, Freedman JE. Circulating extracellular vesicles in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(10):958–66. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1704286.
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487–514. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902.
Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977.
Sun Z, Yang S, Zhou Q, Wang G, Song J, Li Z, et al. Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0831-z.
St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C, Kapranov P. The landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet. 2015;31(5):239–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2015.03.007.
Zeuschner P, Linxweiler J, Junker K. Non-coding RNAs as biomarkers in liquid biopsies with a special emphasis on extracellular vesicles in urological malignancies. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020;20(2):151–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2019.1665998.
Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172(3):393–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011.
Noh JH, Kim KM, McClusky WG, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. Cytoplasmic functions of long noncoding RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018;9(3): e1471. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1471.
Robert Finestra T, Gribnau J. X chromosome inactivation: silencing, topology and reactivation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017;46:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2017.01.007.
Mitchell P, Tollervey D. mRNA turnover. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(3):320–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00214-3.
Gong C, Maquat LE. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3’ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature. 2011;470(7333):284–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09701.
Loewer S, Cabili MN, Guttman M, Loh YH, Thomas K, Park IH, et al. Large intergenic non-coding RNA-RoR modulates reprogramming of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Genet. 2010;42(12):1113–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.710.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-2634.
Cheng W, Zhang Z, Wang J. Long noncoding RNAs: new players in prostate cancer. Cancer. 2013;339(1):8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.008.
Ferrè F, Colantoni A, Helmer-Citterich M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17(1):106–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbv031.
Schmitz SU, Grote P, Herrmann BG. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(13):2491–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2174-5.
Boon RA, Jaé N, Holdt L, Dimmeler S. Long noncoding RNAs: from clinical genetics to therapeutic targets? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(10):1214–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.12.051.
Choi SW, Kim HW, Nam JW. The small peptide world in long noncoding RNAs. Brief Bioinform. 2019;20(5):1853–64. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bby055.
Wang X, Xu Y, Wang X, Jiang C, Han S, Dong K, et al. LincRNA-p21 suppresses development of human prostate cancer through inhibition of PKM2. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(6): e12395. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12395.
Rathinasamy B, Velmurugan BK. Role of lncRNAs in the cancer development and progression and their regulation by various phytochemicals. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:242–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.077.
McCabe EM, Rasmussen TP. lncRNA involvement in cancer stem cell function and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;75:38–48.
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M, et al. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(4):466–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074.
Casanova-Salas I, Athie A, Boutros PC, Del Re M, Miyamoto DT, Pienta KJ, et al. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of blood-based liquid biopsies to inform clinical decision-making in prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2021;79(6):762–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.037.
Prensner JR, Zhao S, Erho N, Schipper M, Iyer MK, Dhanasekaran SM, et al. RNA biomarkers associated with metastatic progression in prostate cancer: a multi-institutional high-throughput analysis of SChLAP1. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(13):1469–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71113-1.
Wang YH, Ji J, Wang BC, Chen H, Yang ZH, Wang K, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal long noncoding RNAs as promising diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):532–45. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488620.
Luo J, Wang K, Yeh S, Sun Y, Liang L, Xiao Y, et al. LncRNA-p21 alters the antiandrogen enzalutamide-induced prostate cancer neuroendocrine differentiation via modulating the EZH2/STAT3 signaling. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2571. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09784-9.
Işın M, Uysaler E, Özgür E, Köseoğlu H, Şanlı Ö, Yücel ÖB, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-p21 levels may help to distinguish prostate cancer from benign disease. Front Genet. 2015;6:168. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00168.
Goyal B, Yadav SRM, Awasthee N, Gupta S, Kunnumakkara AB, Gupta SC. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1875(2): 188502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188502.
Li Y, Ji J, Lyu J, Jin X, He X, Mo S, et al. A novel urine exosomal lncRNA assay to improve the detection of prostate cancer at initial biopsy: a retrospective multicenter diagnostic feasibility study. Cancers. 2021;13(16):4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164075.
Hendriks RJ, Dijkstra S, Jannink SA, Steffens MG, van Oort IM, Mulders PF, et al. Comparative analysis of prostate cancer specific biomarkers PCA3 and ERG in whole urine, urinary sediments and exosomes. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2016;54(3):483–92. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2015-0599.
Zhang X. Interactions between cancer cells and bone microenvironment promote bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Cancer Commun. 2019;39(1):76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0425-1.
Guo Z, Lu X, Yang F, He C, Qin L, Yang N, et al. Exosomal LINC01213 plays a role in the transition of androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells into androgen-independent manners. J Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8058770.
Li Q, Hu J, Shi Y, Xiao M, Bi T, Wang C, et al. Exosomal lncAY927529 enhances prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion through regulating bone microenvironment. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(23):2531–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2021.1992853.
Yang X, Wang L, Li R, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Liu S, et al. The long non-coding RNA PCSEAT exhibits an oncogenic property in prostate cancer and functions as a competing endogenous RNA that associates with EZH2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502(2):262–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.157.
Wang J, Yang X, Li R, Wang L, Gu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA MYU promotes prostate cancer proliferation by mediating the miR-184/c-Myc axis. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(5):2814–25. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6661.
Jiang Y, Zhao H, Chen Y, Li K, Li T, Chen J, et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1 promotes prostate cancer metastasis via miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12):1129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04421-0.
Mo C, Huang B, Zhuang J, Jiang S, Guo S, Mao X. LncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 shuttled by prostate cancer cells-secreted exosomes initiates osteoblastic phenotypes in the bone metastatic microenvironment via miR-205-5p/runt-related transcription factor 2/splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich/polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 2 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(8): e493. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.493.
Xia W, Chen H, Xie C, Hou M. Long-noncoding RNA MALAT1 sponges microRNA-92a-3p to inhibit doxorubicin-induced cardiac senescence by targeting ATG4a. Aging. 2020;12(9):8241–60. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103136.
Ozgur E, Gezer U. Investigation of lncRNA H19 in prostate cancer cells and secreted exosomes upon androgen stimulation or androgen receptor blockage. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2020;121(5):362–5. https://doi.org/10.4149/bll_2020_058.
Cully M. Exosome-based candidates move into the clinic. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(1):6–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41573-020-00220-y.
Yang F, Liao X, Tian Y, Li G. Exosome separation using microfluidic systems: size-based, immunoaffinity-based and dynamic methodologies. Biotechnol J. 2017;12(4):1600699. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201600699.
Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Mahajan V, Deygen I, Klyachko NL, et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(3):655–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.10.012.
Barile L, Vassalli G. Exosomes: therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:63–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.020.
Wang J, Chen D, Ho EA. Challenges in the development and establishment of exosome-based drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2021;329:894–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.020.
Zhang M, Zang X, Wang M, Li Z, Qiao M, Hu H, et al. Exosome-based nanocarriers as bio-inspired and versatile vehicles for drug delivery: recent advances and challenges. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(15):2421–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb00170k.
Li W, Li C, Zhou T, Liu X, Liu X, Li X, et al. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8.
Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang X, Huang Z, He Z, Chen Y. Long non-coding RNA: a new player in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-6-37.
Mehra R, Shi Y, Udager AM, Prensner JR, Sahu A, Iyer MK, et al. A novel RNA in situ hybridization assay for the long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 predicts poor clinical outcome after radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 2014;16(12):1121–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2014.11.006.
Na XY, Liu ZY, Ren PP, Yu R, Shang XS. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 contributes to the progression of prostate cancer and regulates proliferation through KLF4-KRT6/13 signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):12609–16.
Shukla S, Zhang X, Niknafs YS, Xiao L, Mehra R, Cieślik M, et al. Identification and validation of PCAT14 as prognostic biomarker in prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 2016;18(8):489–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2016.07.001.
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81802576), Wuxi City Medical Young Talent (No. QNRC043), Wuxi Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. T202102, T202024, J202012, Z202011), the Science and Technology Development Fund of Wuxi (No. N20202021), and Jiangnan University Wuxi School of Medicine (No. 1286010242190070) and Talent plan of Taihu Lake in Wuxi (Double Hundred Medical Youth Professionals Program) from Health Committee of Wuxi (No. BJ2020061). Clinical trial of Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University (No. LCYJ202227), Research topic of Jiangsu Health Commission (Z2022047).
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approvalThe manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Informed consentInformed consent is not required for this type of study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Wan, H., Feng, Y. et al. The diagnostic role and mechanistic functions of exosomal lncRNAs in prostate cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 592–600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02982-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02982-w