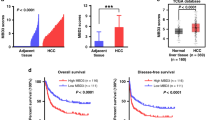
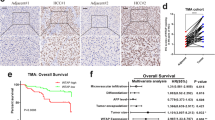
Abstract
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is frequently activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A number of studies have focused on the aberrant hypermethylation of the DKK family proteins and its role in regulating the activation of specific signaling pathways. However, the exact way by which DKK regulates the signaling pathway caused by Core protein of HCV has not been reported. In the present study, we evaluated the expression level of DKK and its aberrant promoter methylation to investigate the involvement of epigenetic regulation in hepatoma cell lines. The transcription and protein expression of DKK1 was significantly increased, whereas the transcription and protein expression levels of DKK2, DKK3, and DKK4 were significantly decreased following overexpression of Core protein. Pyrosequencing indicated that hypermethylation of DKK3 was increased. This was associated with increased expression of Dnmt1. The investigation of the molecular mechanism indicated that HCV Core protein interacted with Dnmt1, which combined with the promoter of DKK3, leading to methylation of DKK3. Functional studies indicated that Core protein promoted the growth, migration and invasion of cancer cells. However, upregulation of the expression of DKK3 and/or the knockdown of the expression of Dnmt1 inhibited the growth, migration and invasion of cancer cells. Taken together, the data indicated that epigenetic silencing of DKK3 caused by Dnmt1 activated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in HCV Core-mediated HCC. Therefore, DKK3 may be a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for HCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnolfo P. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) related hepatocellular carcinoma. Open Virol J. 2018;12:26–32.
Chao J, Zhao S, Sun H. Dedifferentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:2099–109.
Liu L. Clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis B virus among patients on Nucleos(t)ide analog therapy. Infect Agent Cancer. 2020;15:8.
Busceti CL, Di Menna L, Bianchi F, Mastroiacovo F, Di Pietro P, Traficante A, Bozza G, Niehrs C, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Fornai F, Volpe M, Rubattu S, Nicoletti F. Dickkopf-3 causes neuroprotection by inducing vascular endothelial growth factor. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:292.
Hoang BH, Kubo T, Healey JH, Yang R, Nathan SS, Kolb EA, Mazza B, Meyers PA, Gorlick R. Dickkopf 3 inhibits invasion and motility of Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells by modulating the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2734–9.
Kong D, Zhao L, Sun L, Fan S, Li H, Zhao Y, Guo Z, Lin L, Cui L, Wang K, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Li Y. MYCN is a novel oncogenic target in adult B-ALL that activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by suppressing DKK3. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:3627–37.
Liu D, Zou Z, Li G, Pan P, Liang G. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis of glioma cells via downregulating MiR-92b. Cancer Control. 2020;27:1073274819897977.
Katase N, Nagano K, Fujita S. DKK3 expression and function in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and other cancers. J Oral Biosci. 2020;62:9–15.
Abarzua F. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of REIC/Dkk-3 selectively induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through activation of c-Jun-NH2-kinase. Can Res. 2005;65:9617–22.
Yu J, Tao Q, Cheng YY, Lee KY, Ng SS, Cheung KF, Tian L, Rha SY, Neumann U, Röcken C, Ebert MP, Chan FK, Sung JJ. Promoter methylation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling antagonist Dkk-3 is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:49–60.
Hardy T, Mann DA. Epigenetics in liver disease: from biology to therapeutics. Gut. 2016;65:1895–905.
Kulis M, Esteller M. DNA methylation and cancer. Adv Genet. 2010;70:27–56.
Xie CR, Sun H, Wang FQ, Li Z, Yin YR, Fang QL, Sun Y, Zhao WX, Zhang S, Zhao WX, Wang XM, Yin ZY. Integrated analysis of gene expression and DNA methylation changes induced by hepatocyte growth factor in human hepatocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:4250–8.
Lim SO, Gu JM, Kim MS, Kim HS, Park YN, Park CK, Cho JW, Park YM, Jung G. Epigenetic changes induced by reactive oxygen species in hepatocellular carcinoma: methylation of the E-cadherin promoter. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:2128–40.
Ying J, Li H, Seng TJ, Langford C, Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Putti T, Murray P, Chan AT, Tao Q. Functional epigenetics identifies a protocadherin PCDH10 as a candidate tumor suppressor for nasopharyngeal, esophageal and multiple other carcinomas with frequent methylation. Oncogene. 2006;25:1070–80.
Hamdane N, Jühling F, Crouchet E, El Saghire H, Thumann C, Oudot MA, Bandiera S, Saviano A, Ponsolles C, Roca Suarez AA, Li S, Fujiwara N, Ono A, Davidson I, Bardeesy N, Schmidl C, Bock C, Schuster C, Lupberger J, Habersetzer F, Doffoël M, Piardi T, Sommacale D, Imamura M, Uchida T, Ohdan H, Aikata H, Chayama K, Boldanova T, Pessaux P, Fuchs BC, Hoshida Y, Zeisel MB, Duong FHT, Baumert TF. HCV-induced epigenetic changes associated with liver cancer risk persist after sustained virologic response. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:2313–29.
Xu M, Horrell J, Snitow M, Cui J, Gochnauer H, Syrett CM, Kallish S, Seykora JT, Liu F, Gaillard D, Katz JP, Kaestner KH, Levin B, Mansfield C, Douglas JE, Cowart BJ, Tordoff M, Liu F, Zhu X, Barlow LA, Rubin AI, McGrath JA, Morrisey EE, Chu EY, Millar SE. WNT10A mutation causes ectodermal dysplasia by impairing progenitor cell proliferation and KLF4-mediated differentiation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15397.
Ju J, Chen A, Deng Y, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Nie M, Wang C, Ding H, Yao B, Gui T, Li X, Xu Z, Ma C, Song Y, Kvansakul M, Zen K, Zhang CY, Luo C, Fang M, Huang DCS, Allis CD, Tan R, Zeng CK, Wei J, Zhao Q. NatD promotes lung cancer progression by preventing histone H4 serine phosphorylation to activate Slug expression. Nat Commun. 2017;8:928.
Shao S, Zhao X, Zhang X, Luo M, Zuo X, Huang S, Wang Y, Gu S, Zhao X. Notch1 signaling regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer in a Slug-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:28.
Su M, Xiao Y, Ma J, Tang Y, Tian B, Zhang Y, Li X, Wu Z, Yang D, Zhou Y, Wang H, Liao Q, Wang W. Circular RNAs in cancer: emerging functions in hallmarks, stemness, resistance and roles as potential biomarkers. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:90.
Zhang X, Yang Y, Liu X, Herman JG, Brock MV, Licchesi JD, Yue W, Pei X, Guo M. Epigenetic regulation of the Wnt signaling inhibitor DACT2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Epigenetics. 2013;8:373–82.
Xie Q, Chen L, Shan X, Shan X, Tang J, Zhou F, Chen Q, Quan H, Nie D, Zhang W, Huang AL, Tang N. Epigenetic silencing of SFRP1 and SFRP5 by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell tumorigenicity through Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:635–46.
Quan H, Zhou F, Nie D, Chen Q, Cai X, Shan X, Zhou Z, Chen K, Huang A, Li S, Tang N. Hepatitis C virus core protein epigenetically silences SFRP1 and enhances HCC aggressiveness by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2014;33:2826–35.
Kao CF, Chen SY, Chen JY, Wu Lee YH. Modulation of p53 transcription regulatory activity and post-translational modification by hepatitis C virus core protein. Oncogene. 2004;23:2472–83.
Paul C, Khera L, Kaul R. Hepatitis C virus core protein interacts with cellular metastasis suppressor Nm23-H1 and promotes cell migration and invasion. Arch Virol. 2019;164:1271–85.
Liu J, Ding X, Tang J, Cao Y, Hu P, Zhou F, Shan X, Cai X, Chen Q, Ling N, Zhang B, Bi Y, Chen K, Ren H, Huang A, He TC, Tang N. Enhancement of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity by HCV core protein promotes cell growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6: e27496.
Mukozu T, Nagai H, Matsui D, Kanekawa T, Sumino Y. Serum VEGF as a tumor marker in patients with HCV-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1013–21.
Dharancy S, Malapel M, Perlemuter G, Roskams T, Cheng Y, Dubuquoy L, Podevin P, Conti F, Canva V, Philippe D, Gambiez L, Mathurin P, Paris JC, Schoonjans K, Calmus Y, Pol S, Auwerx J, Desreumaux P. Impaired expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha during hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:334–42.
Pavio N, Battaglia S, Boucreux D, Arnulf B, Sobesky R, Hermine O, Brechot C. Hepatitis C virus core variants isolated from liver tumor but not from adjacent non-tumor tissue interact with Smad3 and inhibit the TGF-beta pathway. Oncogene. 2005;24:6119–32.
Jahan S, Ashfaq UA, Khaliq S, Samreen B, Afzal N. Dual behavior of HCV Core gene in regulation of apoptosis is important in progression of HCC. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:236–9.
Ripoli M, Barbano R, Balsamo T, Piccoli C, Brunetti V, Coco M, Mazzoccoli G, Vinciguerra M, Pazienza V. Hypermethylated levels of E-cadherin promoter in Huh-7 cells expressing HCV Core protein. Virus Res. 2011;160:74–81.
Zhu G, Song J, Chen W, Yuan D, Wang W, Chen X, Liu H, Su H, Zhu J. Expression and role of Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) in tumors: from the cells to the patients. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:659–75.
Lee J, Yoon YS, Chung JH. Epigenetic silencing of the WNT antagonist DICKKOPF-1 in cervical cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;109(2):270–4.
Li L, Kou J, Zhong B. Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA AWPPH inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells via miR-203a/DKK2 axis. Hum Cell. 2019;32(4):495–503.
Lou X, Meng Y, Hou Y. A literature review on function and regulation mechanism of DKK4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(6):2786–94.
Hamzehzadeh L, Caraglia M, Atkin SL, Sahebkar A. Dickkopf homolog 3 (DKK3): A candidate for detection and treatment of cancers? J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:4595–605.
Guo Q, Qin W. DKK3 blocked translocation of β-catenin/EMT induced by hypoxia and improved gemcitabine therapeutic effect in pancreatic cancer Bxpc-3 cell. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19:2832–41.
Kamińska K, Białkowska A, Kowalewski J, Huang S, Lewandowska MA. Differential gene methylation patterns in cancerous and non-cancerous cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;42:43–54.
Gondkar K, Patel K, Patil Okaly GV, Nair B, Pandey A, Gowda H, Kumar P. Dickkopf Homolog 3 (DKK3) acts as a potential tumor suppressor in gallbladder cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1121.
Maehata T, Taniguchi H, Yamamoto H, Nosho K, Adachi Y, Miyamoto N, Miyamoto C, Akutsu N, Yamaoka S, Itoh F. Transcriptional silencing of Dickkopf gene family by CpG island hypermethylation in human gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2702–14.
Yue W, Sun Q, Dacic S, Landreneau RJ, Siegfried JM, Yu J, Zhang L. Downregulation of Dkk3 activates beta-catenin/TCF-4 signaling in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:84–92.
Lodygin D, Epanchintsev A, Menssen A, Diebold J, Hermeking H. Functional epigenomics identifies genes frequently silenced in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4218–27.
Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Agirre X, Castillejo JA, Navarro G, Barrios M, Andreu EJ, Prosper F, Heiniger A, Torres A. Transcriptional silencing of the Dickkopfs-3 (Dkk-3) gene by CpG hypermethylation in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:707–13.
Ding Z, Qian YB, Zhu LX, Xiong QR. Promoter methylation and mRNA expression of DKK-3 and WIF-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:2595–601.
Sawahara H, Shiraha H, Uchida D, Kato H, Kato R, Oyama A, Nagahara T, Iwamuro M, Horiguchi S, Tsutsumi K, Mandai M, Mimura T, Wada N, Takeuchi Y, Kuwaki K, Onishi H, Nakamura S, Watanabe M, Sakaguchi M, Takaki A, Nouso K, Yagi T, Nasu Y, Kumon H, Okada H. Promising therapeutic efficacy of a novel reduced expression in immortalized cells/dickkopf-3 expressing adenoviral vector for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:1769–77.
Oyama A, Uchida D, Shiraha H, Sawahara H, Kato R, Iwamuro M, Horiguchi S, Okada H. Serum REIC/Dickkopf-3 protein level predicts disease-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Med Okayama. 2020;74:237–43.
Jee BA, Choi JH, Rhee H, Yoon S, Kwon SM, Nahm JH, Yoo JE, Jeon Y, Choi GH, Woo HG, Park YN. Dynamics of genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic aberrations during stepwise hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2019;79:5500–12.
Dong B, Lee JS, Park YY, Yang F, Xu G, Huang W, Finegold MJ, Moore DD. Activating CAR and β-catenin induces uncontrolled liver growth and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:5944.
Lv Z, Fan H, Song B, Li G, Liu D, Guo Y. Supplementing genistein for breeder hens alters the fatty acid metabolism and growth performance of offsprings by epigenetic modification. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:9214209.
Qu Y, Yang Q, Liu J, Shi B, Ji M, Li G, Hou P. c-Myc is required for BRAFV600E-induced epigenetic silencing by H3K27me3 in tumorigenesis. Theranostics. 2017;7:2092–107.
Wahid B, Ali A, Rafique S, Idrees M. New insights into the epigenetics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1609575.
Gao X, Sheng Y, Yang J, Wang C, Zhang R, Zhu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang K, Yan S, Sun H, Wei J, Wang X, Yu X, Zhang Y, Luo Q, Zheng Y, Qiao P, Zhao Y, Dong Q, Qin L. Osteopontin alters DNA methylation through up-regulating DNMT1 and sensitizes CD133+/CD44+ cancer stem cells to 5 azacytidine in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:179.
Toh TB, Lim JJ, Chow EK. Epigenetics in cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:29.
Grzybkowska D, Nowak K, Gaj MD. Hypermethylation of auxin-responsive motifs in the promoters of the transcription factor genes accompanies the somatic embryogenesis induction in arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6849.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81602462, 81870414, 81601749).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiaoyan Wang and Yun Zhou are the first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, C. et al. HCV Core protein represses DKK3 expression via epigenetic silencing and activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway during the progression of HCC. Clin Transl Oncol 24, 1998–2009 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02859-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02859-y