Abstract
Objective
Recent studies have identified Engrailed-2 (EN-2), a homeobox-containing transcription factor, as a candidate oncogene in prostate cancer (PC). Therapeutic targeting on EN-2, however, is limited because the mechanism underlying EN-2 overexpression in prostatic cancer cells is unknown. This study was to investigate the potential regulatory role of miR-33a on EN-2 expression and explore this signaling axis in ability of prostate cancer survival and metastasis.
Methods
The relative expression of miR-33a and EN-2 in paired prostate cancer tissue and adjacent normal tissue as well as in prostate cancer cell lines, PC3 and DU145, was determined using quantitative real-time PCR or western blot, respectively. Cells survival, migration and invasion were evaluated by assays of MTT, TUNEL and Boyden chamber assays, respectively. Direct regulation of EN-2 by miR-33a was examined by luciferase reporter assay.
Results
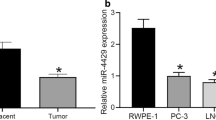
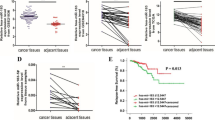
The data showed that miR-33a was upregulated and EN-2 was downregulated in both prostate cancer tissue and prostate cancer cells. miR-33a overexpression suppresses prostate cancer cell survival and metastasis. miR-33a can directly act on EN-2 expression by binding to 3′UTR of its mRNA. Also, miR-33a negatively regulated EN-2 mRNA and protein expression. In pcDNA-EN-2 and miR-33a mimic co-transfected PC3 and DU145 cells, EN-2 overexpression reverses the anti-cell survival and metastasis actions of miR-33a overexpression. The pivotal role of miR-33a in inhibiting prostate tumor growth was confirmed in xenograft models of prostate cancer.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that the functional interaction of miR-33a and EN-2 is involved in tumorigenesis of prostate cancer. Also in this process EN-2 serves as a negative responder for miR-33a.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaudreau PO, Stagg J, Soulieres D, Saad F. The Present and Future of Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer: Proteomics, Genomics, and Immunology Advancements. Biomark Cancer. 2016;8(Suppl 2):15–33. doi:10.4137/BIC.S31802.
Yegnasubramanian S. Prostate cancer epigenetics and its clinical implications. Asian J Androl. 2016;. doi:10.4103/1008-682X.179859.
Sharma S, Kelly TK, Jones PA. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31(1):27–36. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp220.
Chen Y, Wang Y, Yu Y, Xu L, Zhang Y, Yu S, et al. Transcription Factor HBP1 Enhances Radiosensitivity by Inducing Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Anal Cell Pathol. 2016;2016:7015659. doi:10.1155/2016/7015659.
Patel D, Chinaranagari S, Chaudhary J. Basic helix loop helix (bHLH) transcription factor 3 (TCF3, E2A) is regulated by androgens in prostate cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(11):3407–21.
Jones D, Wade M, Nakjang S, Chaytor L, Grey J, Robson CN, et al. FOXA1 regulates androgen receptor variant activity in models of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(30):29782–94. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4927.
Morgan R, Boxall A, Bhatt A, Bailey M, Hindley R, Langley S, et al. Engrailed-2 (EN2): a tumor specific urinary biomarker for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2011;17(5):1090–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2410.
Bose SK, Bullard RS, Donald CD. Oncogenic role of engrailed-2 (en-2) in prostate cancer cell growth and survival. Trans Oncogenom. 2008;3:37–43.
Marszall MP, Sroka W, Adamowski M, Slupski P, Jarzemski P, Siodmiak J, et al. Engrailed-2 protein as a potential urinary prostate cancer biomarker: a comparison study before and after digital rectal examination. Eur J Cancer Prev Off J Eur Cancer Prev Organ. 2015;24(1):51–6. doi:10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000046.
McGrath SE, Michael A, Morgan R, Pandha H. EN2: a novel prostate cancer biomarker. Biomark Med. 2013;7(6):893–901. doi:10.2217/bmm.13.115.
Lv Y, Wang S, Meng F, Yang L, Wang Z, Wang J, et al. Identifying novel associations between small molecules and miRNAs based on integrated molecular networks. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(22):3638–44. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv417.
Bertoli G, Cava C, Castiglioni I. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Theranostics in Prostate Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(3):421. doi:10.3390/ijms17030421.
Goto Y, Kojima S, Kurozumi A, Kato M, Okato A, Matsushita R, et al. Regulation of E3 ubiquitin ligase-1 (WWP1) by microRNA-452 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016;114(10):1135–44. doi:10.1038/bjc.2016.95.
Nam RK, Benatar T, Wallis CJ, Amemiya Y, Yang W, Garbens A, et al. MiR-301a regulates E-cadherin expression and is predictive of prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate. 2016;76(10):869–84. doi:10.1002/pros.23177.
Wolfe AR, Bambhroliya A, Reddy JP, Debeb BG, Huo L, Larson R, et al. MiR-33a Decreases High-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Radiation Sensitivity in Breast Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;95(2):791–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.01.025.
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Lin Y, Huang Z, Luo Q. MiR-33a suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting ADAM9 and ROS1. Protein Cell. 2015;6(12):881–9. doi:10.1007/s13238-015-0223-8.
Yang L, Yang J, Li J, Shen X, Le Y, Zhou C, et al. MircoRNA-33a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis and could be a prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13677. doi:10.1038/srep13677.
Nouraee N, Khazaei S, Vasei M, Razavipour SF, Sadeghizadeh M, Mowla SJ. MicroRNAs contribution in tumor microenvironment of esophageal cancer. Cancer Biomark Sect A Dis Mark. 2016;16(3):367–76. doi:10.3233/CBM-160575.
Zhou Y, Huang Z, Wu S, Zang X, Liu M, Shi J. miR-33a is up-regulated in chemoresistant osteosarcoma and promotes osteosarcoma cell resistance to cisplatin by down-regulating TWIST. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:12. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-12.
Rane JK, Scaravilli M, Ylipaa A, Pellacani D, Mann VM, Simms MS, et al. MicroRNA expression profile of primary prostate cancer stem cells as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Eur Urol. 2015;67(1):7–10. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.09.005.
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M, Grunweller A, Hartmann RK, Aigner A. MicroRNA replacement therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011;71(15):5214–24. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4645.
Liang C, Wang Z, Li YY, Yu BH, Zhang F, Li HY. miR-33a suppresses the nuclear translocation of beta-catenin to enhance gemcitabine sensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2015;36(12):9395–403. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3679-5.
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS, Hsu YL. MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(6):3756–66. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.022.
Langley RR, Fidler IJ. Tumor cell-organ microenvironment interactions in the pathogenesis of cancer metastasis. Endocr Rev. 2007;28(3):297–321. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0027.
Killick E, Morgan R, Launchbury F, Bancroft E, Page E, Castro E, et al. Role of Engrailed-2 (EN2) as a prostate cancer detection biomarker in genetically high risk men. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2059. doi:10.1038/srep02059.
Lee S, Jo H, Her J, Lee HY, Ban C. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of engrailed-2 based on homeodomain-specific DNA probe recognition for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;66:32–8. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.11.003.
Li Y, Liu H, Lai C, Su Z, Heng B, Gao S. Repression of engrailed 2 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of human bladder cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(5):2319–30. doi:10.3892/or.2015.3858.
Abollo-Jimenez F, Campos-Sanchez E, Toboso-Navasa A, Vicente-Duenas C, Gonzalez-Herrero I, Alonso-Escudero E, et al. Lineage-specific function of Engrailed-2 in the progression of chronic myelogenous leukemia to T-cell blast crisis. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(11):1717–26. doi:10.4161/cc.28629.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the key Scientific Research Program of Higher Education of Henan province (Grant No: 15A320072) and the Medical Science and Technique Foundation Project of Henan Province (Grant No: 201403017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential financial conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Ethics approval
This work was approved by the key Scientific Research Program of Higher Education of Henan province (Grant No: 15A320072) and the Medical Science and Technique Foundation Project of Henan Province (Grant No: 201403017).
Informed consent
Written informed consents were obtained from all cases.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Lu, S., Li, X. et al. Biological function and mechanism of miR-33a in prostate cancer survival and metastasis: via downregulating Engrailed-2. Clin Transl Oncol 19, 562–570 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-016-1564-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-016-1564-3