Abstract
Purpose
Advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common and lethal malignancy that has rarely benefited from chemotherapy. Erlotinib is highly effective in NSCLC patients selected by clinical characteristics and/or the presence of epidermal growth factor receptor-sensitizing mutations. However, the way to delay or bypass erlotinib resistance is not systematically addressed. Different erlotinib-failure modes have been reported in NSCLC, and strategies to prolong erlotinib efficacy are perhaps adaptable to them. We report the feasibility and efficacy of continued erlotinib maintenance and local salvage radiation to overcome erlotinib resistances in selected NSCLC patients.
Patients and methods
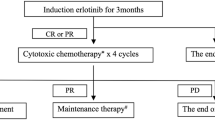
Thirty of 52 consecutive erlotinib-treated advanced NSCLC from the NYU Langone Medical Center and the Arnau de Vilanova Hospital of Lleida responded initially to erlotinib. Twenty-six patients eventually showed a generalized-progression to erlotinib, and four progressed in solitary tumor sites. These four patients were treated with continued erlotinib maintenance and local salvage radiation.
Results
The progression-free survival (PFS) was statistically similar in patients with oligo or generalized-progression to erlotinib. However, all four cases with solitary-progression did benefit from continued erlotinib maintenance and salvage radiation with 41–140 % prolongation of PFS. It was reflected in an improved overall survival when they were compared with patients with generalized-progression (76.4 vs. 19.9 months; p = 0.018).
Conclusion
Continued erlotinib maintenance and local salvage radiation is feasible and could contribute to a better outcome in selected NSCLC patients with solitary-progression to erlotinib. Prospective randomized trials of this strategy are warranted.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–917.
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(2):123–32.
Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, von Pawel J, et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet. 2005;366(9496):1527–37.
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–46.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57.
Yang JJ, Chen HJ, Yan HH, Zhang XC, Zhou Q, Su Q, et al. Clinical modes of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure and subsequent management in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2013;79(1):33–9.
Weickhardt AJ, Scheier B, Burke JM, Gan G, Lu X, Bunn PA, et al. Local ablative therapy of oligoprogressive disease prolongs disease control by tyrosine kinase inhibitors in oncogene-addicted non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(12):1807–14.
Yu HA, Sima CS, Dela Cruz Drilon AE, Varghese AM, Pietanza MC, Azzoli CG, et al. Local therapy as a treatment strategy in EGFR-mutant advanced lung cancers that have developed acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(suppl):7527.
Brower V. Radiologists urge FDA to accept PET-based tumor response criteria in clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:622–4.
Bengtsson T, Hicks RJ, Peterson A, Port RE. 18F-FDG PET as a surrogate biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib: newly identified lesions are more informative than standardized uptake value. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(4):530–7.
Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, Fujita S, Kunimasa K, Nanjo S, et al. Erlotinib after gefitinib failure in relapsed non-small cell lung cancer: clinical benefit with optimal patient selection. Lung Cancer. 2011;74(2):268–73.
Watanabe S, Tanaka J, Ota T, Kondo R, Tanaka H, Kagamu H, et al. Clinical responses to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor retreatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients who benefited from prior effective gefitinib therapy: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:1.
Oh IJ, Ban HJ, Kim KS, Kim YC. Retreatment of gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who previously controlled to gefitinib: a single-arm, open-label, phase II study. Lung Cancer. 2012;77(1):121–7.
Horiike A, Kudo K, Miyauchi E, Ohyanagi F, Kasahara K, Horai T, Nishio M. Phase I study of irinotecan and gefitinib in patients with gefitinib treatment failure for non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(8):1131–6.
Takeuchi S, Wang W, Li Q, Yamada T, Kita K, Donev IS, et al. Dual inhibition of met kinase and angiogenesis to overcome HGF-induced EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(3):1034–43.
Inomata M, Shukuya T, Takahashi T, Ono A, Nakamura Y, Tsuya A, et al. Continuous administration of EGFR-TKIs following radiotherapy after disease progression in bone lesions for non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011;31:4519–23.
Chang CC, Chi KH, Kao SJ, Hsu PS, Tsang YW, Chang HJ, et al. Upfront gefitinib/erlotinib treatment followed by concomitant radiotherapy for advanced lung cancer: a mono-institutional experience. Lung Cancer. 2011;73(2):189–94.
Shukuya T, Takahashi T, Naito T, Kaira R, Ono A, Nakamura Y, et al. Continuous EGFR-TKI administration following radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer patients with isolated CNS failure. Lung Cancer. 2011;74(3):457–61.
Wu CC, Hsu HY, Liu HP, Chang JW, Chen YT, Hsieh WY, et al. Reversed mutation rates of KRAS and EGFR genes in adenocarcinoma of the lung in Taiwan and their implications. Cancer. 2008;113(11):3199–208.
Cappuzzo F, Jänne PA, Skokan M, Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Ligorio C, et al. MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(2):298–304.
Gow CH, Chang YL, Hsu YC, Tsai MF, Wu CT, Yu CJ, et al. Comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations between primary and corresponding metastatic tumors in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(4):696–702.
Kalikaki A, Koutsopoulos A, Trypaki M, Souglakos J, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, et al. Comparison of EGFR and K-RAS gene status between primary tumours and corresponding metastases in NSCLC. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(6):923–9.
Bozzetti C, Tiseo M, Lagrasta C, Nizzoli R, Guazzi A, Leonardi F, et al. Comparison between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene expression in primary non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and in fine-needle aspirates from distant metastatic sites. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3(1):18–22.
Rosell R, Molina MA, Costa C, Simonetti S, Gimenez-Capitan A, Bertran-Alamillo J, et al. Pre-treatment EGFR T790M mutation and BRCA1 mRNA expression in erlotinib-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(5):1160–8.
Chaft JE, Oxnard GR, Sima CS, Kris MG, Miller VA, Riely GJ. Disease flare after tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer and acquired resistance to erlotinib or gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(19):6298–303.
Salah S, Tanvetyanon T, Abbasi S. Metastatectomy for extra-cranial extra-adrenal non-small cell lung cancer solitary metastases: systematic review and analysis of reported cases. Lung Cancer. 2012;75(1):9–14.
Jamal-Hanjani M, Spicer J. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer metastatic to the brain. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:938–44.
Park SJ, Kim HT, Lee DH, Kim KP, Kim SW, Suh C, et al. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer. 2012;77(3):556–60.
Porta R, Massuti B, Paz-Ares L, Massutí B, Reguart N, Mayo C, et al. Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: the importance of EGFR mutation. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(3):624–31.
Liu M, Jiang G, He W, Zhang P, Song N. Surgical resection of locally advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma after gefitinib therapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:e11–2.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marquez-Medina, D., Chachoua, A., Martin-Marco, A. et al. Continued erlotinib maintenance and salvage radiation for solitary areas of disease progression: a useful strategy in selected non-small cell lung cancers?. Clin Transl Oncol 15, 959–964 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1035-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1035-z