Abstract
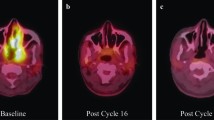
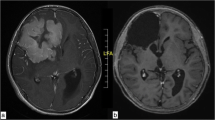
Primary brain lymphoma is a rare variant of extranodal non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma. In >90% of cases, this is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with CD20 expression and is confined to the brain, meninges, spinal cord, and eyes. It accounts for fewer than 7% of primary brain tumors. Its incidence has been rising in recent years in immunocompetent patients in their fifth and sixth decades. The rate of relapse after initial therapy based on high-dose methotrexate and/or total brain irradiation is high. There is no consensus for treating relapse, which ranges from retreatment with high doses of methotrexate, polychemotherapy, high doses of chemotherapy backed up by autologous stem-cell transplant to intrathecal chemotherapy, with widely differing results. Given the lack of consensus and poor results, new therapy options have appeared, including immunotherapy with rituximab. At a systemic level, alongside chemotherapy, its results are very modest and limited due to the low concentration it reaches in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). However, its intrathecal and intraventricular use, though only isolated cases have been reported, has provided promising results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swinnen LJ (2009) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: recent progress, many remaining questions. Curr Opin Oncol 5:393–396
Sierra del Rio M, Rousseau A, Soussain C et al (2009) Primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients. Oncologist 14:526–539
Hoang-Xuan K, Camilleri-Broët S, Soussain C (2004) Recent advances in primary CNS lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol 6:601–606
Montesinos-Rongen M, Siebert R, Deckert M (2009) Primary lymphoma of the central nervous system: just DLBCL or not? Blood 113:7–10
Uhm JE, Kim KH, Yi SY et al (2009) A retrospective study to compare two methotrexate-based regimens for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 50:1110–1118
Ekenel M, Iwamoto FM, Ben-Porat LS et al (2008) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: the role of consolidation treatment after a complete response to high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy. 113:1025–1031
Voloschin AD, Betensky R, Wen PY et al (2008) Topotecan as salvage therapy for relapsed or refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neurooncol 86:211–215
Morris PG, Abrey LE (2009) Therapeutic challenges in primary CNS lymphoma. Lancet Neurol 8:581–592
Algazi AP, Kadoch C, Rubenstein JL (2009) Biology and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurotherapeutics 3:587–597
Soussain C, Hoang-Xuan K, Taillandier L et al, for the Société Française de Greffe de Moëlle Osseuse-Thérapie Cellulaire (2008) Intensive chemotherapy followed by hematopoietic stem-cell rescue for refractory and recurrent primary CNS and intraocular lymphoma: Société Française de Greffe de Moëlle Osseuse-Thérapie Cellulaire. J Clin Oncol 26:2512–2518
Rubenstein JL, Combs D, Rosenberg J et al (2003) Rituximab therapy for CNS lymphomas: targeting the leptomeningeal compartment. Blood. 101:466–468
Jahnke K, Doolittle ND, Muldoon LL, Neuwelt EA (2006) Implications of the blood-brain barrier in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurosurg Focus 21:E11
Stapleton S, Blaney S (2006) New agents for intrathecal administration. Cancer Invest. 5:528–534.
Jaime-Pérez JC, Rodríguez-Romo LN, González-Llano O et al (2009) Effectiveness of intrathecal rituximab in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia relapsed to the CNS and resistant to conventional therapy. Br J Haematol 144:794–795
Rubenstein JL, Fridlyand J, Abrey L et al (2007) Phase I study of intraventricular administration of rituximab in patients with recurrent CNS and intraocular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 25:1350–1356
Schulz H, Pels H, Schmidt-Wolf I et al (2004) Intraventricular treatment of relapsed central nervous system lymphoma with the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab. Haematologica 89:753–754
Itty S, Pulido JS (2009) Rituximab for intraocular lymphoma. Retina 29:129–132
Antonini G, Cox MC, Montefusco E et al (2007) Intrathecal anti-CD20 antibody: an effective and safe treatment for leptomeningeal lymphoma. J Neurooncol 81:197–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso, C.M., Sánchez Ruiz, A.C., Sánchez de Ibargüen, B.C. et al. Ocular relapse of primary brain lymphoma in immunocompetent patient, treated with intrathecal rituximab. Clin Transl Oncol 12, 701–703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-010-0580-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-010-0580-y