Abstract
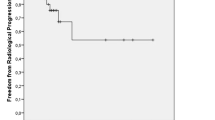
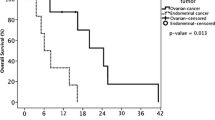
We present three patients with brain metastasis cases from ovarian carcinoma (BMOC) treated at William Beaumont Hospital with a median follwow-up of 77 months and a mean survival after brain involvement of 23.66 months (range 5–44). Clinical and physical aspects are presented. Between December 2006 and August 2008, three cases of BMOC were treated using Gamma Knife (GK) radiosurgery. All patients had FIGO Stage III primary disease at initial diagnosis. Treatment sequences and features are described. GK achieves excellent local control of BMOC. Other parameters could be considered as biologically effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posner JB (1995) Neurologic complications of cancer. FA Davis, Philadelphia
Knisely JP, Berkey B, Chakravarti A et al (2008) A phase III study of conventional radiation therapy plus thalidomide versus conventional radiation therapy for multiple brain metastases (RTOG 0118). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:79–86
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Pectasides D, Pectasides M, Economopoulos T (2006) Brain metastases from epithelian ovarian cancer: a review of literature. Oncologist 11:252–260
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW et al (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322: 494–500
Noordijk EM, Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H et al (1994) The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 29:711–717
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Young DF, Posner JB, Chu F et al (1974) Rapidcourse radiation therapy of cerebral metastasis: results and complications. Cancer 34:1069–1076
Hindo WA, DeTrana FA, Lee MS et al (1970) Large dose increment irradiation in treatment of cerebral metastasis. Cancer 26:138–141
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 39:789–796
Asai A, Matsutani M, Kohno T et al (1989) Subacute brain atrophy after radiation therapy for malignant brain tumor. Cancer 63:1962–1974
Cull A, Gregor A, Hopwood P et al (1994) Neurological and cognitive impairment in long-term survivors of small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 30A:1067–1074
Shibamoto Y, Baba F, Oda K et al (2008) Incidence of brain atrophy and decline in Mini-Mental State Examination Score after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastasis: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1168–1173.
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs sterotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Welzer G, Fleckenstein K, Schaefer J et al (2008) Memory function before and after whole brain radiotherapy in patients with and without brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1311–1318
Lee YK, Park NH, Kim JW (2008) Gamma-knife radiosurgery as an optimal treatment modality for brain metastases from epithelian ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 108:505–509
Monaco E 3rd, Kondziolka D, Mongia S et al (2008) Management of brain metastases from ovarian and endometrial carcinoma with stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer 113:2610–2614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro-Martín, A., Maitz, A., Manders, M. et al. Gamma Knife radiosurgery as a primary treatment option for solitary brain metastases from ovarian carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 11, 326–328 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-009-0362-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-009-0362-6