Abstract
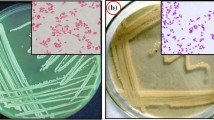
A Gram-negative, short-rod, non-motile, facultatively anaerobic, potassium-solubilizing bacterium MR1 (Mine Rhizosphere) was isolated from rhizospheric soil of an open-cast coal mine of Jharia, Jharkhand, India. Isolate MR1 can grow in a broad range of temperature, pH, and NaCl concentrations. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of the strain showed 99.24% similarity with Pantoea septica LMG 5345T. However, maximum-likelihood tree constructed using 16S rRNA gene sequence, multilocus sequence analysis using concatenated sequences of ten housekeeping genes, whole-genome based phylogenetic reconstruction, digital DNA–DNA hybridization, and average nucleotide identity (ANIm and ANIb) values indicated segregation of MR1 from its closest relatives. Fatty acid profile of MR1 also suggested the same, with clear variation in major and minor fatty acid contents, having C13:0 anteiso (10-Methyldodecanoic acid) as the unique one. Thus, considering all polyphasic data, strain MR1T (= MTCC 13265T, where ‘T’ stands for Type strain) is presented as a novel species of the genus Pantoea, for which the name Pantoea tagorei sp. nov. is proposed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Whole Genome sequence has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the Bioproject accession PRJNA892926.
Abbreviations
- WGS:
-
Whole-genome sequencing
- MLSA:
-
Multilocus sequence analysis
- TYGS:
-
Type Strain Genome Server
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA–DNA hybridization
- FAME:
-
Fatty acid methyl ester
References
Gavini F, Mergaert J, Beji A, Mielcarek C, Izard D, Kersters K, De Ley J (1989) Transfer of Enterobacter agglomerans (Beijerinck 1888) Ewing and Fife 1972 to Pantoea gen. nov. as Pantoea agglomerans comb. nov. and Description of Pantoea dispersa sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 39:337–345
Cruz AT, Cazacu AC, Allen CH (2007) Pantoea agglomerans, a plant pathogen causing human disease. J Clin Microbiol 45:1989–1992
Prakash O, Nimonkar Y, Vaishampayan A, Mishra M, Kumbhare S, Josef N, Shouche YS (2015) Pantoea intestinalis sp. nov., isolated from the human gut. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3352–3358
Bomfeti CA, Souza-Paccola EA, Massola Júnior NS, Marriel IE, Meirelles WF, Casela CR, Paccola-Meirelles LD (2008) Localization of Pantoea ananatis inside lesions of maize white spot disease using transmission electron microscopy and molecular techniques. Trop Plant Pathol 33:63–66
Abidin N, Ismail SI, Vadamalai G, Yusof MT, Hakiman M, Karam DS, Ismail-Suhaimy NW, Ibrahim R, Zulperi D (2020) Genetic diversity of Pantoea stewartii subspecies stewartii causing jackfruit-bronzing disease in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 15:1–18
Merbach W, Ruppel S, Schulze J (1998) Dinitrogen fixation of microbe-plant associations as affected by nitrate and ammonium supply. Isot Environ Health Stud 34:67–73
Prasad P, Kalam S, Sharma NK, Podile AR, Das SNJFiA. (2022) Phosphate Solubilization and Plant Growth Promotion by Two Pantoea Strains Isolated from the Flower of Hedychium coronarium L. Front agron 990869:86
Feng Y, Shen D, Song W (2006) Rice endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19 promotes host plant growth and affects allocations of host photosynthates. J Appl Microbiol 100:938–945
Lim J-A, Lee DH, Kim B-Y, Heu S (2014) Draft genome sequence of Pantoea agglomerans R190, a producer of antibiotics against phytopathogens and foodborne pathogens. J Biotechnol 188:7–8
Mishra A, Chauhan PS, Chaudhry V, Tripathi M, Nautiyal CS (2011) Rhizosphere competent Pantoea agglomerans enhances maize (Zea mays) and chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) growth, without altering the rhizosphere functional diversity. Anton Leeuw Int J G 100:405–413
Remus-Emsermann MN, Kim EB, Marco ML, Tecon R, Leveau JH (2013) Draft genome sequence of the phyllosphere model bacterium Pantoea agglomerans 299R. Genome Announc 1:e00036-e113
Houba V, Temminghoff E, Gaikhorst G, Van Vark W (2000) Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1299–1396
Dahal RH, Chaudhary DK, Kim J (2017) Acinetobacter halotolerans sp. nov., a novel halotolerant, alkalitolerant, and hydrocarbon degrading bacterium, isolated from soil. Arch Microbiol 199:701–710
Banerjee S, Misra A, Chaudhury S, Dam B (2019) A Bacillus strain TCL isolated from Jharia coalmine with remarkable stress responses, chromium reduction capability and bioremediation potential. J Hazard Mater 367:215–223
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1994) MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers. Bioinformatics 10:189–191
Andrews S (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Retrieved 17 May 2018
Andrews S, Krueger F, Segonds-Pichon A, Biggins L, Virk B, Dalle-Pezze P, Wingett S, Saadeh H, Ahlfors H (2015) Trim Galore
Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE (2017) Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005595
Nikolenko SI, Korobeynikov AI, Alekseyev MA. BayesHammer: Bayesian clustering for error correction in single-cell sequencing. In: (ed). Springer, pp 1–11
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181–W184
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29:1072–1075
Guo Y, Zheng W, Rong X, Huang Y (2008) A multilocus phylogeny of the Streptomyces griseus 16S rRNA gene clade: use of multilocus sequence analysis for streptomycete systematics. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:149–159
Brady C, Cleenwerck I, Venter S, Vancanneyt M, Swings J, Coutinho T (2008) Phylogeny and identification of Pantoea species associated with plants, humans and the natural environment based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA). Syst Appl Microbiol 31:447–460
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M (2019) TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat Commun 10:1–10
Eriksson A, Manica A (2014) The doubly conditioned frequency spectrum does not distinguish between ancient population structure and hybridization. Mol Biol Evol 31:1618–1621
Farris JS (1972) Estimating phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Am Nat 106:645–668
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931
Kumar A, Kumar A, Thakur P, Patil S, Payal C, Kumar A, Sharma P (2012) Antibacterial activity of green tea (Camellia sinensis) extracts against various bacteria isolated from environmental sources. Recent Res Sci Technol 4:19–23
Priester JH, Horst AM, Van De Werfhorst LC, Saleta JL, Mertes LA, Holden PA (2007) Enhanced visualization of microbial biofilms by staining and environmental scanning electron microscopy. J Microbiol Methods 68:577–587
Suzuki Y, Kishigami T, Inoue K, Mizoguchi Y, Eto N, Takagi M, Abe S (1983) Bacillus thermoglucosidasius sp. nov., a new species of obligately thermophilic bacilli. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:487–495
Miskin A, Edberg SC (1978) Esculin hydrolysis reaction by Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 7:251–254
Mukherjee T, Banik A, Mukhopadhyay SK (2020) Plant growth-promoting traits of a thermophilic strain of the Klebsiella group with its effect on rice plant growth. Curr Microbiol 77:2613–2622
Oskay M (2011) Effects of some environmental conditions on biomass and antimicrobial metabolite production by Streptomyces sp., KGG32. Int J Agric Biol 13:317–324
Lateef A, Oloke J, Gueguim-Kana E (2004) Antimicrobial resistance of bacterial strains isolated from orange juice products. Afr J Biotechnol 3:334–338
Kunitsky C, Osterhout G, Sasser M (2006) Identification of microorganisms using fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) analysis and the MIDI sherlock microbial identification system. Encycl Rapid Microbiol Methods 3:1–18
Li C, Cano A, Acosta-Martinez V, Veum KS, Moore-Kucera J (2020) A comparison between fatty acid methyl ester profiling methods (PLFA and EL-FAME) as soil health indicators. Soil Sci Soc Am J 84:1153–1169
Brady CL, Venter SN, Cleenwerck I, Engelbeen K, Vancanneyt M, Swings J, Coutinho TA (2009) Pantoea vagans sp. nov., Pantoea eucalypti sp. nov., Pantoea deleyi sp. nov. and Pantoea anthophila sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2339–2345
Tanaka YK, Horie N, Mochida K, Yoshida Y, Okugawa E, Nanjo F (2015) Pantoea theicola sp. nov., isolated from black tea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3313–3319
Brady C, Cleenwerck I, Venter S, Coutinho T, De Vos P (2013) Taxonomic evaluation of the genus Enterobacter based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA): proposal to reclassify E. nimipressuralis and E. amnigenus into Lelliottia gen. nov. as Lelliottia nimipressuralis comb. nov. and Lelliottia amnigena comb. nov., respectively, E. gergoviae and E. pyrinus into Pluralibacter gen. nov. as Pluralibacter gergoviae comb. nov. and Pluralibacter pyrinus comb. nov., respectively, E. cowanii, E. radicincitans, E. oryzae and E. arachidis into Kosakonia gen. nov. as Kosakonia cowanii comb. nov., Kosakonia radicincitans comb. nov., Kosakonia oryzae comb. nov. and Kosakonia arachidis comb. nov., respectively, and E. turicensis, E. helveticus and E. pulveris into Cronobacter as Cronobacter zurichensis nom. nov., Cronobacter helveticus comb. nov. and Cronobacter pulveris comb. nov., respectively, and emended description of the genera Enterobacter and Cronobacter. Syst Appl Microbiol 36:309–319
Wei M, Wang P, Yang C, Gu L (2019) Molecular identification and phylogenetic relationships of clinical Nocardia isolates. Anton Leeuw Int J G 112:1755–1766
Tambong JT, Xu R, Gerdis S, Daniels GC, Chabot D, Hubbard K, Harding MW (2021) Molecular analysis of bacterial isolates from necrotic wheat leaf lesions caused by Xanthomonas translucens, and description of three putative novel species, Sphingomonas albertensis sp. nov., Pseudomonas triticumensis sp. nov. and Pseudomonas foliumensis sp. nov. Front Microbiol 12:666689
Pritchard L, Glover RH, Humphris S, Elphinstone JG, Toth IK (2016) Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal Methods 8:12–24
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PA, Kämpfer P, Maiden MC, Nesme X, Rosselló-Mora R, Swings J, Trüper HG (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Maiti PK, Mandal S (2021) Streptomyces himalayensis sp. nov. including Streptomyces himalayensis subsp. himalayensis subsp. nov. and Streptomyces himalayensis subsp. aureolus subsp. nov. isolated from Western Himalaya. Arch Microbiol 203:2325–2334
Fiedler G, Gieschler S, Kabisch J, Grimmler C, Brinks E, Wagner N, Hetzer B, Franz CM, Böhnlein C (2022) Pseudomonas rustica sp. nov., isolated from bulk tank raw milk at a German dairy farm. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 72:1–11
Brady CL, Cleenwerck I, Venter SN, Engelbeen K, De Vos P (2010) Emended description of the genus Pantoea, description of four species from human clinical samples, Pantoea septica sp. nov., Pantoea eucrina sp. nov., Pantoea brenneri sp. nov. and Pantoea conspicua sp. nov., and transfer of Pectobacterium cypripedii (Hori 1911) Brenner et al. 1973 emend. Hauben et al. 1998 to the genus as Pantoea cypripedii comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2430–2440
Chen C, Xin K, Liu H, Cheng J, Shen X, Wang Y, Zhang L (2017) Pantoea alhagi, a novel endophytic bacterium with ability to improve growth and drought tolerance in wheat. Sci Rep 7:1–14
Brady CL, Goszczynska T, Venter SN, Cleenwerck I, De Vos P, Gitaitis RD, Coutinho TA (2011) Pantoea allii sp. nov., isolated from onion plants and seed. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:932–937
UK C. 2014. Pantoea ananatis pv. ananatis ((Serrano, 1928) Mergaert et al., 1993), fruitlet rot of pineapple.[pest/pathogen].
Gao J-l, Xue J, Yan H, Tong S, Khan MS, Wang L-w, Mao X-j, Zhang X, Sun J-g (2019) Pantoea endophytica sp. nov., novel endophytic bacteria isolated from maize planting in different geographic regions of northern China. Syst Appl Microbiol 42:488–494
Popp A, Cleenwerck I, Iversen C, De Vos P, Stephan R (2010) Pantoea gaviniae sp. nov. and Pantoea calida sp. nov., isolated from infant formula and an infant formula production environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2786–2792
Brady CL, Cleenwerck I, Van der Westhuizen L, Venter SN, Coutinho TA, De Vos P (2012) Pantoea rodasii sp. nov., Pantoea rwandensis sp. nov. and Pantoea wallisii sp. nov., isolated from Eucalyptus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1457–1464
Pizzolante G, Durante M, Rizzo D, Di Salvo M, Tredici SM, Tufariello M, De Paolis A, Talà A, Mita G, Alifano P (2018) Characterization of two Pantoea strains isolated from extra-virgin olive oil. AMB Express 8:1–17
Lefort V, Desper R, Gascuel O (2015) FastME 2.0: a comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol Biol Evol 32:2798–2800
Acknowledgements
Raju Biswas, Abhinaba Chakraborty, and Puja Mukherjee, are grateful to WB-DST, SERB, and CSIR for their fellowships. Prof. Manoranjan Chowdhury (North Bengal University, India) is acknowledged for his suggestions in determining the taxonomic nomenclature of the novel species. Funding from DST-PURSE is acknowledged for FE-SEM imaging and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BD, RB, and AM designed the study. RB, and AM analyzed the data. RB, AM, SG, AC, PM, and BD wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict regarding financial or any academic interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, R., Misra, A., Ghosh, S. et al. Pantoea tagorei sp. nov., a Rhizospheric Bacteria with Plant Growth-Promoting Activities. Indian J Microbiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01147-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01147-9