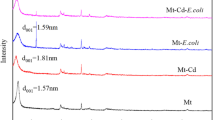
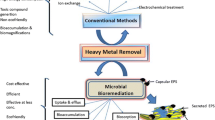
Abstract
Metal-resistant bacteria are recommended for metal removal applications due to their rapid multiplication and growth rates. To ensure safety replenishment in contaminated areas frequently hampered by heavy metal toxicity, it is crucial to comprehend their coping mechanisms under heavy metal stress. This study primarily examines the role of EPS (exopolysaccharide) in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Gram-negative, aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria, in response to Cd, as well as the binding behavior and biosorption mechanism between EPS and Cd, using SEM and FTIR. The studies showed that Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, can resist up to 150 μM of Cd due to the binding of Cd to EPS. SEM analysis showed significant morphological changes and FTIR was to identify main structural groups like carboxyl and hydroxyl which confirms the presence of EPS. The study will also describe the mechanism of cross-reactivity between exopolysaccharide and siderophore production in metal-tolerant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. This study proved that siderophore-mediated metal detoxification and effective absorption have been linked to metal chelation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yadav JS, Sharma RK, Yadav J, Tiwari S, Kumar U, Kumar P (2022) Isolation, identification and characterization of Cd resistant rhizobacterial isolates from long-term wastewater irrigated soils. J Sci Res. https://doi.org/10.37398/JSR.2022.660122
Lima E, Silva A (2012) Heavy metal tolerance (Cr, Ag and Hg) in bacteria isolated from sewage. Brazil J Microbiol 43:1620
Rouch DA, Lee BT, Morby AP (1995) Understanding cellular responses to toxic agents: a model for mechanism-choice in bacterial metal resistance. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 14(2):132–141
Qin W, Zhao J, Yu X, Liu X, Chu X, Tian J, Wu N (2019) Improving Cd resistance in Escherichia coli through continuous genome evolution. Front Microbiol 10:278
Kumar R, Chawla J, Kaur I (2015) Removal of Cd ion from wastewater by carbon-based nano sorbents: a review. J Water Health 13:18–33
Mathivanan K, Chandirika JU, Vinothkanna A, Yin H, Liu X, Meng D (2021) Bacterial adaptive strategies to cope with metal toxicity in the contaminated environment–A review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112863
Rajbanshi A (2008) Study on heavy metal resistant bacteria in Guheswori sewage treatment plant. Our nature 6:52–57
Rahman K, Menon U (2022) Removal of Cd by heavy metal–resistant bacteria isolated from Hussain Sagar Lake—Hyderabad. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery 12:1703–1713
Ivanieva OD (2009) Heavy metal resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Mikrobiol Z 71:54–65
Abbas SZ, Rafatullah M, Hossain K, Ismail N, Tajarudin HA, Abdul Khalil HPS (2018) A review on mechanism and future perspectives of Cd-resistant bacteria. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:243–262
Majumdar R, Mohandass R, Manickam R, Dharshini RS, & Sugumar S (2022). Isolation and genomic characterization of metal-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia SRM01 from the marine environment.
Pages D, Rose J, Conrod S, Cuine S, Carrier P, Heulin T, Achouak W (2008) Heavy metal tolerance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. PLoS ONE 3:e1539
Alonso A, Sanchez P, Martínez JL (2000) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia D457R contains a cluster of genes from gram-positive bacteria involved in antibiotic and heavy metal resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:1778–1782
Yu W, Chen X, Sheng Y, Hong Q (2018) Genomic analysis for heavy metal resistance in S. maltophilia. J BioRxiv 31:404954
Haroun AA, Kamaluddeen KK, Alhaji I, Magaji Y, Oaikhena EE (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal tolerance level (MIC) and bioremediation potentials of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Makera-Kakuri industrial drain in Kaduna. Nigeria Eur J Exper Biol 7:28
Zeng W, Li F, Wu C, Yu R, Wu X, Shen L, Li J (2020) Role of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) in toxicity response of soil bacteria Bacillus sp S3 to multiple heavy metals. Bioprocess biosystems Eng 43:153–167
Masuko T, Minami A, Iwasaki N, Majima T, Nishimura SI, Lee YC (2005) Carbohydrate analysis by a phenol–sulfuric acid method in microplate format. Anal Biochem 339:69–72
Kruger, N. J. (2009). The Bradford method for protein quantitation. The protein protocols handbook, 17–24.
Arora NK, Verma M (2017) Modified microplate method for rapid and efficient estimation of siderophore produced by bacteria. Biotech 7:1–9
Louden BC, Haarmann D, Lynne AM (2011) Use of blue agar CAS assay for siderophore detection. J Microbiol Biol Educat 12(1):51–53
Naik MM, Dubey SK (2011) Lead-enhanced siderophore production and alteration in cell morphology in a Pb-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 4EA. Curr Microbiol 62:409–414
Kaláb M, Yang AF, Chabot D (2008) Conventional scanning electron microscopy of bacteria. Infocus magazine 10:42–61
Liaquat, F., Munis, M. F. H., Arif, S., Haroon, U., Shengquan, C., & Qunlu, L. (2020). Cd-tolerant SY-2 strain of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: a potential PGPR, isolated from the Nanjing mining area in China. 3 Biotech, 10: 1–10.
Chakravarty R, Banerjee PC (2008) Morphological changes in an acidophilic bacterium induced by heavy metals. Extremophiles 12:279–284
Argudín MA, Hoefer A, Butaye P (2019) Heavy metal resistance in bacteria from animals. Res Vet Sci 122:132–147
Neethu CS, Mujeeb Rahiman KM, Saramma AV, Mohamed Hatha AA (2015) Heavy-metal resistance in Gram-negative bacteria isolated from Kongsfjord, Arctic. Can J Microbiol 61:429–435
Gupta P, Diwan B (2017) Bacterial exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: a review on biosynthesis, mechanism, and remediation strategies. Biotechnol Rep 13:58–71
Chellaiah ER (2018) Cd (heavy metals) bioremediation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a minireview. Appl Water Sci 8(6):1–10
Sinha S, Mukherjee SK (2008) Cd–induced siderophore production by a high Cd-resistant bacterial strain relieved Cd toxicity in plants through root colonization. Curr Microbiol 56:55–60
Schalk IJ, Hannauer M, Braud A (2011) New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ Microbiol 13(11):2844–2854
Park D, Yun YS, Park JM (2005) Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically-treated biomass of Ecklonia sp. Chemosphere 60(10):1356–1364
Mulik ANURADHA, Bhadekar RAMA (2018) Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) from Kocuria sp. BRI 36: A key component in heavy metal resistance. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 10:50–54
Khan Z, Rehman A, Hussain SZ, Nisar MA, Zulfiqar S, Shakoori AR (2016) Cd resistance and uptake by bacterium, Salmonella enterica 43C, isolated from industrial effluent. AMB Express 6:1–16
Vicentin, R. P., Santos, J. V. D., Labory, C. R. G., Costa, A. M. D., Moreira, F. M. D. S., & Alves, E. (2018). Tolerance to and Accumulation of Cd, Copper, and Zinc by Cupriavidus necator. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishnan, S., Muruganraj, T., Majumdar, R. et al. Study of Cadmium Metal Resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Indian J Microbiol 63, 91–99 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01066-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01066-9