Abstract
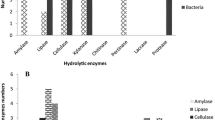
This research is a comparative study on the diversity of halophilic bacteria with hydrolytic activities in three significant hypersaline lakes; Urmia in the northwest and Howz-Soltan and Aran-Bidgol in the central desert in Iran. Isolated strains from these saline lakes were found to be halotolerant, moderately and extremely halophilic bacteria. The bacteria in each saline lake were able to produce different hydrolytic enzymes including amylase, protease, lipase, DNase, inulinase, xylanase, carboxy methyl cellulase, pectinase and pullulanase. 188, 302, 91 halophilic strains were isolated from Urmia Lake, Howz-Soltan and Aran-Bidgol playa, respectively. The numbers of Gram-positive strains were more than Gram-negatives, and among Gram-positive bacteria; spore-forming bacilli were most abundant. Due to the unique physico-chemical conditions of the lake environments, the hydrolytic activities of isolated strains were significantly different. For instance, isolated strains from Howz-Soltan playa did not produce pectinase, DNase, amylase, lipase and inulinase, while the isolates from Aran-Bidgol playa had a great ability to produce pectinase and DNase. The strains from Urmia Lake were also good producers of DNase but failed to show any chitinase activity. The diversity of halophilic bacteria from the mentioned three saline lakes was also determined using PCR-amplified 16S rRNA followed by phylogenetic analysis of the partial 16S rRNA sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oren A (2002) Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology and applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:56–63
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2008) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolases from Howz-Soltan Lake, Iran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:333–340
Makhdoumi KA, Amoozegar MA, Kazemi B, Pasic L, Ventosa A (2012) Prokaryotic diversity in Aran-Bidgol Salt Lake, the largest hypersaline playa in Iran. Microbes Environ 27:87–93
Babavalian H, Amoozegar MA, Pourbabaee AA, Moghaddam MM, Shakeri F (2013) Isolation and identification of moderately halophilic bacteria producing hydrolytic enzymes from the largest hypersaline playa in Iran. Microbiology 82:466–474
Eimanifar A, Mohebbi F (2007) Urmia Lake (northwest Iran): a brief review. Saline Syst 3:1–8
DasSarma S, DasSarma P (2012) Halophiles. In: eLS. Wiley, Chichester. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0000394.pub3
Lourdes MM, Perez D, Teresa GM, Mellado E (2013) Halophilic bacteria as a source of novel hydrolytic enzymes. Life 3:38–51
Amoozegar MA, Malekzadeh F, Malik KA (2003) Production of amylase by newly isolated moderate halophile Halobacillus sp. strain MA-2. J Microbiol Methods 52:353–359
Amoozegar MA, Fatemi AZ, Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Razavi MR (2007) Production of an extracellular alkaline metalloprotease from a newly isolated, moderately halophile, Salinivibrio sp. strain AF-2004. Microbiol Res 162:369–377
Amoozegar MA, Schumann P, Hajighasemi M, Fatemi AZ (2008) Salinivibrio proteolyticus sp. nov. a moderately halophilic and proteolytic species from a hypersaline lake in Iran. Int J Syst Microbiol 58:1159–1163
Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Amoozegar MA, Hajighasemi M, Ziaee AA, Ventosa A (2009) Production, optimization and purification of a novel extracellular protease from the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillus karajensis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:21–27
Shafiei M, Ziaee AA, Amoozegar MA (2012) Purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-tolerant halophilic alpha amylase from the moderately halophilic Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:275–281
Siroosi M, Amoozegar MA, Khajeh K, Fazeli M, Rezaei MH (2014) Purification and characterization of a novel extracellular halophilic and organic solvent-tolerant amylopullulanase from the haloarchaeon, Halorubrum sp. strain Ha25. Extremophiles 18:25–33
Sanchez-Porro C, Martin S, Mellado E, Ventosa A (2002) Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J Appl Microbiol 94:295–300
Makhdoumi KA, Amoozegar MA, Mahmodi KE (2011) Diversity of hydrolytic enzymes in haloarchaeal strains isolated from salt lake. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8:705–714
Martin S, Marquez M, Sanchez-Porro C, Mellado E, Arahal DR, Ventosa A (2003) Marinobacter lipolytic sp. nov. a novel moderate halophile with lipolytic activity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1383–1387
Amoozegar MA, Salehghamari E, Khajeh K, Kabiri M, Naddaf S (2008) Production of an extracellular thermohalophilic lipase from a moderately halophilic bacterium, Salinivibrio sp. strain SA-2. J Basic Microbiol 48:160–167
Kamble KD, Kadu SS (2012) Enhancement of DNase production from a moderate halophilic bacterium and studies on its phylogeny. Int J Environ Sci 3:1031–1037
Jayani RS, Shukla SK, Gupta R (2010) Screening of bacterial strains for polygalacturonase activity: its production by Bacillus sphaericus (MTCC 7542). Enzym Res 3:1–5
Li AX, Guo LZ, Fu Q, Lu WD (2011) A simple and rapid plate assay for screening of inulin-degrading microorganisms using Lugol’s iodine solution. Afr J Biotechnol 10:9518–9521
Zhou XH, Li Z (2004) CMCase activity assay as a method for cellulose adsorption analysis. Enzym Microb Technol 35:455–459
Khandeparker R, Verma P, Deobagkar D (2011) A novel halotolerant xylanase from marine isolate Bacillus subtilis cho40: gene cloning and sequencing. N Biotechnol 28:814–821
Sanchez-Porro C, Amoozegar MA, Fernandez AB, Babavalian H, Ramezani M, Ventosa A (2010) Lentibacillus persicus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic species isolated from a saline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1407–1412
Ventosa A, Quesada E, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1982) Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic gram-negative rods. J Gen Microbiol 128:1959–1968
Hanelt I, Muller V (2013) Molecular mechanisms of adaptation of the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillis halophilus to its environment. Life 3:234–243
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Sundarakrishnan B, Pushpanathan M, Jayashree S, Rajendhran J, Sakthivel N, Jayachandran S, Gunasekaran P (2012) Assessment of microbial richness in pelagic sediment of Andaman Sea by bacterial tag encoded FLX titanium amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). Indian J Microbiol 52:544–550
Chen J, Yin X (2013) Stratified communities of methanogens in the Jiulong River estuarine sediments, southern China. Indian J Microbiol 53:432–437
Silva AE, Villanueva WJ, Knidel H, Bonato VC, Reis SF, Von Zuben FJ (2005) A multi-neighbor-joining approach for phylogenetic tree reconstruction and visualization. Genet Mol Res 4:525–534
Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2003) Applying the bootstrap in phylogeny reconstruction. Stat Sci 18:256–267
Kumar S, Karan R, Kapoor S, Singh SP, Khare SK (2012) Screening and Isolation of Halophilic bacteria producing industrially important enzymes. Braz J Microbiol 43:1595–1603
Acknowledgments
This study was supported and conducted by University of Tehran. We would like to thanks from our colleagues in the Extremophiles Lab Group for their kind assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babavalian, H., Amoozegar, M.A., Zahraei, S. et al. Comparison of Bacterial Biodiversity and Enzyme Production in Three Hypersaline Lakes; Urmia, Howz-Soltan and Aran-Bidgol. Indian J Microbiol 54, 444–449 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-014-0481-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-014-0481-9