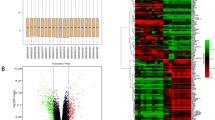
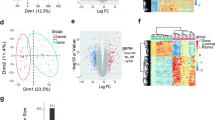
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most diagnosed cancer in the world. A better understanding of the molecular mechanism of CRC is essential for making novel strategies for the CRC management and its prevention. The present study aims to explore the molecular mechanism through integrated bioinformatics analysis by analyzing genes and their co-expression pattern in normal and CRC states. GSE110223, GSE110224 and GSE113513 gene expression profiles were analyzed in this study. The co-expression networks for normal and tumor samples were constructed separately and analyzed to identify the modules, sub-networks and key genes. Gene regulatory network analysis was done to understand the regulatory mechanism of selected genes. Survival analysis was performed for the identified sub-networks and key genes to understand their role in CRC progression. A total of seven modules were detected and the KEGG pathway analysis revealed these modules were mainly enriched with cell cycle, metabolism and signaling-related pathways. E2F6 and ETV4 transcription factors regulating the activity of multiple genes of identified modules were found to be up-regulated in CRC. Six Sub-networks and seven key genes, BORA, CCT7, DTL, RUVBL1, RUVBL2, THEM6 and TMEM97 associated with the CRC progression were identified. Disease-gene association analysis identified a novel association of the BORA gene with CRC that activates and regulates the AURORA-PLK1 cascades in the cell cycle. Survival analysis indicates that the overexpressed BORA is associated with unfavourable overall survival in CRC. The mechanistic role of BORA in the regulation of cell cycle progression suggests that BORA might act as a potential therapeutic target for CRC.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Gamboa R, Gomez-Rueda H, Martínez-Ledesma E, Martínez-Torteya A, Chacolla-Huaringa R, Rodriguez-Barrientos A, Tamez-Pena JG, Trevino V (2013) Survexpress: an online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene expression data using survival analysis. PloS one 8(9):e74250
Arshad Z, McDonald JF (2021) Changes in gene-gene interactions associated with cancer onset and progression are largely independent of changes in gene expression. Iscience 24(12):103522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103522
Asteriti IA, De Mattia F, Guarguaglini G (2015) Cross-talk between aurka and plk1 in mitotic entry and spindle assembly. Front Oncol 5:283. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2015.00283
Bader GD, Hogue CW (2003) An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform 4(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Benatti P, Chiaramonte ML, Lorenzo M, Hartley JA, Hochhauser D, Gnesutta N, Mantovani R, Imbriano C, Dolfini D (2016) Nf-y activates genes of metabolic pathways altered in cancer cells. Oncotarget 7(2):1633. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6453
Blomme A, Peter C, Mui E, Rodriguez Blanco G, An N, Mason LM, Jamieson LE, McGregor GH, Lilla S, Ntala C et al (2022) Them6-mediated reprogramming of lipid metabolism supports treatment resistance in prostate cancer. EMBO Molecular Med 14(3):e14764. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.202114764
Chen H, Liu H, Qing G (2018) Targeting oncogenic myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal Trans Targeted therapy 3(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-018-0008-7
Cheng S, Peng T, Zhu X, Zhou F, Wang G, Ju L, Xiao Y, Liu X, Wang X (2020) Bora regulates cell proliferation and migration in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell Int 20(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01392-8
Chin C-H, Chen S-H, Wu H-H, Ho C-W, Ko M-T, Lin C-Y (2014) cytohubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8(4):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Cui H, Wang Q, Lei Z, Feng M, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Wei G (2019) Dtl promotes cancer progression by pdcd4 ubiquitin-dependent degradation. J Exper Clinical Cancer Res 38(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1358-x
de Martin X, Sodaei R, Santpere G (2021) Mechanisms of binding specificity among bhlh transcription factors. Int J Molecular Sci 22(17):9150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179150
Dennis G, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA (2003) David: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol 4(9):1–11
Dong M, Xie Y, Xu Y (2019) mir-7-5p regulates the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by negatively regulating the expression of krüppel-like factor 4. Oncol Lett 17(3):3241–3246. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10001
Ducker C, Shaw PE (2021) Ubiquitin-mediated control of ets transcription factors: roles in cancer and development. Int J Molecular Sci 22(10):5119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105119
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cbioportal. Sci Signaling, 6 (269): pl1–pl1
Ghafouri-Fard S, Khoshbakht T, Hussen BM, Kadkhoda S, Taheri M, Tafrishinejad A (2021) A review on the role of mir-149-5p in the carcinogenesis. Int J Molecular Sci 23(1):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010415
Goïta AA, Guenot D (1810) Colorectal cancer: The contribution of cxcl12 and its receptors cxcr4 and cxcr7. Cancers 14(7):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071810
Heberle H, Meirelles GV, da Silva FR, Telles GP, Minghim R (2015) Interactivenn: a web-based tool for the analysis of sets through venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform 16(1):1–7
Huang C-R, Lee C-T, Chang K-Y, Chang W-C, Liu Y-W, Lee J-C, Chen B-K (2015) Down-regulation of arnt promotes cancer metastasis by activating the fibronectin/integrin \(\beta \)1/fak axis. Oncotarget 6(13):11530. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3448
Huang X, Wang H, Xu F, Lv L, Wang R, Jiang B, Liu T, Hu H, Jiang Y (2022) Overexpression of chaperonin containing tcp1 subunit 7 has diagnostic and prognostic value for hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 14(2):747. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203809
Ideker T, Ozier O, Schwikowski B, Siegel AF (2002) Discovering regulatory and signalling circuits in molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics 18(suppl-1):S233–S240
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, Speed TP (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 4(2):249–264. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/4.2.249
Izadi F (2019) Differential connectivity in colorectal cancer gene expression network. Iranian Biomed J 23(1):34. https://doi.org/10.29252/.23.1.34
Jung IH, Jung DE, Chung Y-Y, Kim K-S, Park SW (2019) Iroquois homeobox 1 acts as a true tumor suppressor in multiple organs by regulating cell cycle progression. Neoplasia 21(10):1003–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2019.08.001
Kalluru VG (2012) Identify Condition Specific Gene Co-expression Networks. PhD thesis, The Ohio State University
Kanehisa M et al (2002) The Kegg database. In: Novartis foundation symposium, pp 91–100. Wiley Online Library,
Karaayvaz M, Pal T, Song B, Zhang C, Georgakopoulos P, Mehmood S, Burke S, Shroyer K, Ju J (2011) Prognostic significance of mir-215 in colon cancer. Clinical Colorectal Cancer 10(4):340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2011.06.002
Kume H, Muraoka S, Kuga T, Adachi J, Narumi R, Watanabe S, Kuwano M, Kodera Y, Matsushita K, Fukuoka J et al (2014) Discovery of colorectal cancer biomarker candidates by membrane proteomic analysis and subsequent verification using selected reaction monitoring (srm) and tissue microarray (tma) analysis. Molecular Cellular Proteom 13(6):1471–1484. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.037093
La Vecchia S, Sebastián C (2020) Metabolic pathways regulating colorectal cancer initiation and progression. In: Seminars in cell & developmental biology, vol 98, pp 63–70. Elsevier, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.018
Landeghem SV, Parys TV, Dubois M, Inzé D, de Peer YV (2016) Diffany: an ontology-driven framework to infer, visualise and analyse differential molecular networks. BMC Bioinform 17(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0863-y
Liebl MC, Hofmann TG (2021) The role of p53 signaling in colorectal cancer. Cancers 13(9):2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092125
Li M, Liu Z, Song J, Wang T, Wang H, Wang Y, Guo J (2022) Identification of down-regulated adh1c is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Front Molecular Biosci, 9, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.791249
Lin M, Zhang Z, Gao M, Yu H, Sheng H, Huang J (2019) Microrna-193a-3p suppresses the colorectal cancer cell proliferation and progression through downregulating the plau expression. Cancer Manag Res 11:5353. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S208233
Liu X, Lin C-Y, Lei M, Yan S, Zhou T, Erikson RL (2005) Cct chaperonin complex is required for the biogenesis of functional plk1. Molecular Cellular Biol 25(12):4993–5010. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.12.4993-5010.2005
Liu X, Zhang X, Chen J, Ye B, Ren S, Lin Y, Sun X-F, Zhang H, Shen B (2020) Crc-ebd: epigenetic biomarker database for colorectal cancer. Front Genet 11:907
Mao Y-Q, Houry WA (2017) The role of pontin and reptin in cellular physiology and cancer etiology. Front Molecular Biosci 4:58. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2017.00058
Martin M, Sun M, Motolani A, Lu T (2021) The pivotal player: Components of nf-\(\kappa \)b pathway as promising biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Int J Molecular Sci 22(14):7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147429
Mattiuzzi C, Sanchis-Gomar F, Lippi G (2019) Concise update on colorectal cancer epidemiology. Ann Transl Med, 7 (21),. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.07.91
Miyamoto K, Seki N, Matsushita R, Yonemori M, Yoshino H, Nakagawa M, Enokida H (2016) Tumour-suppressive mirna-26a-5p and mir-26b-5p inhibit cell aggressiveness by regulating plod2 in bladder cancer. British J Cancer 115(3):354–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.179
Mohammed M, Mwambi H, Omolo B (2021) Colorectal cancer classification and survival analysis based on an integrated rna and dna molecular signature. Current Bioinform 16(4):583–600. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574893615999200711170445
Neubig G, Dyer C, Goldberg Y, Matthews A, Ammar W, Anastasopoulos A, Ballesteros M, Chiang D, Clothiaux D, Cohn T, et al (2017) Dynet: The dynamic neural network toolkit. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.03980
Ng WTW, Shin J-S, Roberts TL, Wang B, Lee CS (2016) Molecular interactions of polo-like kinase 1 in human cancers. J Clinical Pathol 69(7):557–562. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2016-203656
Onodera Y, Takagi K, Neoi Y, Sato A, Yamaguchi M, Miki Y, Ebata A, Miyashita M, Sasano H, Suzuki T (2021) Forkhead box i1 in breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Acta histochemica et cytochemica, pages 21–00034, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1267/ahc.21-00034
Otto T, Sicinski P (2017) Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nature Rev Cancer 17(2):93–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.138
Peng Y, Croce CM (2016) The role of micrornas in human cancer. Signal Trans Targeted Therapy 1(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2015.4
Piñero J, Bravo À, Queralt-Rosinach N, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Deu-Pons J, Centeno E, García-García J, Sanz F, Furlong LI (2016) Disgenet: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res, page gkw943
Rani A, Greenlaw R, Smith RA, Galustian C (2016) Hes1 in immunity and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 30:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.03.010
Raudvere U, Kolberg L, Kuzmin I, Arak T, Adler P, Peterson H, Vilo J (2019) g: Profiler: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W191–W198
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for rna-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Schmit K, Michiels C (2018) Tmem proteins in cancer: a review. Front Pharmacol 9:1345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01345
Seki A, Coppinger JA, Jang C-Y, Yates JR III, Fang G (2008) Bora and aurora a cooperatively activate plk1 and control the entry into mitosis. Science (New York, NY) 320(5883):1655. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1157425
Serra M, Columbano A, Ammarah U, Mazzone M, Menga A (2020) Understanding metal dynamics between cancer cells and macrophages: competition or synergism? Front Oncol 10:646. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00646
Shen A, Liu L, Huang Y, Shen Z, Wu M, Chen X, Wu X, Lin X, Chen Y, Li L et al (2021) Down-regulating haus6 suppresses cell proliferation by activating the p53/p21 pathway in colorectal cancer. Front Cell Develop Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.772077
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang P-L, Ideker T (2011) Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27(3):431–432
Subramanian C, Cohen MS (2019) Over expression of DNA damage and cell cycle dependent proteins are associated with poor survival in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma. Surgery 165(1):202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.04.080
Suehiro Y, Takemoto Y, Nishimoto A, Ueno K, Shirasawa B, Tanaka T, Kugimiya N, Suga A, Harada E, Hamano K (2018) Dclk1 inhibition cancels 5-fu-induced cell-cycle arrest and decreases cell survival in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 38(11):6225–6230. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12977
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clinicians 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y, Wu F-X (2015) Cytonca: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks. Biosystems 127:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.11.005
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T, Zhang Z (2019) Gepia2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W556–W560
Vishnoi K, Viswakarma N, Rana A, Rana B (2020) Transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. Cancers 12(8):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082296
Vlachavas E-I, Pilalis E, Papadodima O, Koczan D, Willis S, Klippel S, Cheng C, Pan L, Sachpekidis C, Pintzas A et al (2019) Radiogenomic analysis of f-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and gene expression data elucidates the epidemiological complexity of colorectal cancer landscape. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2019.01.007
Wen B, Wei Y-T, Zhao K (2021) The role of high mobility group protein b3 (hmgb3) in tumor proliferation and drug resistance. Molecular Cellular Biochem 476(4):1729–1739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-04015-y
Werner S, Stamm H, Pandjaitan M, Kemming D, Brors B, Pantel K, Wikman H (2015) Iroquois homeobox 2 suppresses cellular motility and chemokine expression in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 15(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1907-4
Xi Y, Xu P (2021) Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Trans Oncol 14(10):101174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101174
Xie B, Ding Q, Han H, Wu D (2013) mircancer: a microrna-cancer association database constructed by text mining on literature. Bioinformatics 29(5):638–644
Xu P, Du G, Guan H, Xiao W, Sun L, Yang H (2021) A role of tti1 in the colorectal cancer by promoting proliferation. Trans Cancer Res 10(3):1378. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-3322
Xu W-X, Song W, Jiang M-P, Yang S-J, Zhang J, Wang D-D, Tang J-H (2021) Systematic characterization of expression profiles and prognostic values of the eight subunits of the chaperonin tric in breast cancer. Front Genet 12:637887. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.637887
Xu Z, Qu H, Ren Y, Gong Z, Ri HJ, Chen X (2021) An update on the potential roles of e2f family members in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res 13:5509. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S320193
Yan M, Wang C, He B, Yang M, Tong M, Long Z, Liu B, Peng F, Xu L, Zhang Y et al (2016) Aurora-a kinase: a potent oncogene and target for cancer therapy. Medicinal Res Rev 36(6):1036–1079. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21399
Yang L, Yang S, Ren C, Liu S, Zhang X, Sui A (2022) Deciphering the roles of mir-16-5p in malignant solid tumorsmalignant solid tumors. Biomed Pharm 148:112703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112703
Yu CY, Mitrofanova A (2021) Mechanism-centric approaches for biomarker detection and precision therapeutics in cancer. Front Genet, p 1315, https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.687813
Zhang Q-X, Gao R, Xiang J, Yuan Z-Y, Qian Y-M, Yan M, Wang Z-F, Liu Q, Zhao H-D, Liu C-H (2017) Cell cycle protein bora serves as a novel poor prognostic factor in multiple adenocarcinomas. Oncotarget 8(27):43838. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16631
Zhang D, Huo D, Xie H, Wu L, Zhang J, Liu L, Jin Q, Chen X (2020) Chg: a systematically integrated database of cancer hallmark genes. Front Genet 11:29
Zhang X, Sun X-F, Cao Y, Ye B, Peng Q, Liu X, Shen B, Zhang H (2018) Cbd: a biomarker database for colorectal cancer. Database, 2018
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments. The Authors also thanks Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, K.K. Birla Goa Campus for supporting this work.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM and SM conceived and designed the experiments. MM, AS and SM analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments. MM performed the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahajan, M., Sarkar, A. & Mondal, S. Cell cycle protein BORA is associated with colorectal cancer progression by AURORA-PLK1 cascades: a bioinformatics analysis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 773–791 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00719-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00719-6