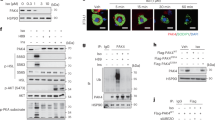
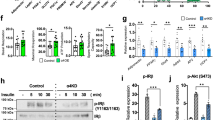
Abstract
Lipin-1 is a protein that plays a critical role in many cellular functions. At molecular level, it acts as a phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase and a transcriptional coactivator. The functions of lipin-1 are largely dependent upon its subcellular localization, post-translational modifications like phosphorylation and acetylation, and also on its interaction with other proteins such as 14-3-3. However, the kinases and phosphatases that are responsible for these post translational modifications are not entirely known. Using bioinformatics and other biochemical approaches, we demonstrate lipin-1 as a novel target for AKT1 and LKB1. While AKT1 stabilizes lipin-1, LKB1 causes its degradation. Interestingly, our findings further show that lipin-1 enhances AKT1 activity as can be seen by increased phosphorylation of the substrates of AKT1. Taken together, our results suggest that lipin-1 plays an important role in the regulation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, which is dysregulated in majority of cancers. Therefore, understating the role of lipin-1 may provide new and important insights into the regulation and functions of the PI3K-mTOR pathway, which is one of the major targets for anti-cancer drug development strategies.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahmanyar S, Biggs R, Schuh AL, Desai A, Müller-Reichert T, Audhya A, Dixon JE, Oegema K (2014) Spatial control of phospholipid flux restricts endoplasmic reticulum sheet formation to allow nuclear envelope breakdown. Genes Dev 28(2):121–126. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.230599.113
Brohée L, Demine S, Willems J, Arnould T, Alain C, Deroanne CF (2015) Lipin-1 regulates cancer cell phenotype and is a potential target to potentiate rapamycin treatment. Oncotarget 6(13):11264
Chen D, Frezza M, Schmitt S, Kanwar J, Dou QP (2011) Bortezomib as the first proteasome inhibitor anticancer drug: current status and future perspectives. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11(3):239–253. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800911794519752
Coleman RA, Mashek DG (2011) Mammalian triacylglycerol metabolism: synthesis, lipolysis, and signaling. Chem Rev 111(10):6359–6386. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100404w
Csaki LS, Dwyer JR, Fong LG, Tontonoz P, Young SG, Reue K (2013) Lipins, lipinopathies, and the modulation of cellular lipid storage and signaling. Prog Lipid Res 52(3):305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2013.04.001
Finck BN, Gropler MC, Chen Z, Leone TC, Croce MA, Harris TE Jr, Lawrence JC, Kelly DP (2006) Lipin 1 is an inducible amplifier of the hepatic PGC-1 a/PPAR a regulatory pathway. Cell Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2006.08.005
Gillani SQ, Reshi I, Nabi N, Un Nisa M, Sarwar Z, Bhat S, Roberts TM, Higgins JMG, Andrabi S (2022) PCTAIRE1 promotes mitotic progression and resistance against antimitotic and apoptotic signals. J Cell Sci. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.258831
Grimsey N, Han GS, O'Hara L, Rochford JJ, Carman GM, Siniossoglou S (2008) Temporal and spatial regulation of the phosphatidate phosphatases lipin 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 283(43):29166–29174. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804278200
Grimsrud PA, Carson JJ, Hebert AS, Hubler SL, Niemi NM, Bailey DJ, Jochem A, Stapleton DS, Keller MP, Westphall MS, Yandell BS, Attie AD, Coon JJ, Pagliarini DJ (2012) A quantitative map of the liver mitochondrial phosphoproteome reveals posttranslational control of ketogenesis. Cell Metab 16(5):672–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.10.004
Han GS, Carman GM (2010) Characterization of the human LPIN1-encoded phosphatidate phosphatase isoforms. J Biol Chem 285(19):14628–14638. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.117747
Han GS, Wu WI, Carman GM (2006) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae lipin homolog is a Mg2+-dependent phosphatidate phosphatase enzyme. J Biol Chem 281(14):9210–9218. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600425200
Han S, Bahmanyar S, Zhang P, Grishin N, Oegema K, Crooke R, Graham M, Reue K, Dixon JE, Goodman JM (2012) Nuclear envelope phosphatase 1-regulatory subunit 1 (Formerly TMEM188) is the metazoan Spo7p ortholog and functions in the lipin activation pathway. J Biol Chem 287(5):3123–3137. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.324350
Harris TE, Huffman TA, Chi A, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Kumar A (2007) Insulin controls subcellular localization and multisite phosphorylation of the phosphatidic acid phosphatase, lipin 1. J Biol Chem 282(1):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M609537200
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL, Mustard KJ, Udd L, Mäkelä TP, Alessi DR, Hardie DG (2003) Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol 2(4):28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-4924-2-28
Hennessy M, Granade ME, Hassaninasab A, Wang D, Kwiatek JM, Han GS, Harris TE, Carman GM (2019) Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of lipin 1β phosphatidate phosphatase at Ser-285 and Ser-287 regulates its interaction with 14-3-3β protein. J Biol Chem 294(7):2365–2374. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.007246
Huffman TA, Mothe-satney I, Lawrence JC (2002) Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of lipin mediated by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(2):1047–1052
Humphrey SJ, Yang G, Yang P, Fazakerley DJ, Stöckli J, Yang JY, James DE (2013) Dynamic adipocyte phosphoproteome reveals that Akt directly regulates mTORC2. Cell Metab 17(6):1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.010
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan K-L (2003) TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 115(5):577–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00929-2
Inoki K, Li Y, Zhu T, Wu J, Guan K-L (2002) TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4(9):648–657. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb839
Ishimoto K, Hayase A, Kumagai F, Kawai M, Okuno H, Hino N, Okada Y, Kawamura T, Tanaka T, Hamakubo T, Sakai J, Kodama T, Tachibana K, Doi T (2017) Degradation of human Lipin-1 by BTRC E3 ubiquitin ligase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 488(1):159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.159
Kim Y, Gentry MS, Harris TE, Wiley SE, Lawrence JC Jr, Dixon JE. A conserved phosphatase cascade that regulates nuclear membrane biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(16):6596–6601. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702099104
Koh Y, Lee M, Kim J, Kim M, Moon J, Lee Y, Ahn Y, Kim K (2008) Lipin1 is a key factor for the maturation and maintenance of adipocytes in the regulatory network with CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ2. J Biol Chem 283(50):34896–34906. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804007200
Langner CA, Birkenmeier EH, Ben-Zeev O, Schotz MC, Sweet HO, Davisson MT, Gordon JI (1989) The fatty liver dystrophy (fld) mutation. A new mutant mouse with a developmental abnormality in triglyceride metabolism and associated tissue-specific defects in lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase activities. J Biol Chem 264(14):7994–8003
Li TY, Song L, Sun Y, Li J, Yi C, Lam SM, Xu D, Zhou L, Li X, Yang Y, Zhang C-S, Xie C, Huang X, Shui G, Lin S-Y, Reue K, Lin S-C (2018) Tip60-mediated lipin 1 acetylation and ER translocation determine triacylglycerol synthesis rate. Nat Commun 9(1):1916. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04363-w
Liu G, Gerace L (2009) Sumoylation regulates nuclear localization of lipin-1 a in neuronal cells. PLoS ONE 4(9):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007031
Manning BD, Toker A (2017) Review AKT/PKB signaling: navigating the network. Cell 169(3):381–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.001
Okuno H, Okuzono H, Hayase A, Kumagai F, Tanii S, Hino N, Okada Y, Tachibana K, Doi T, Ishimoto K (2019) Lipin-1 is a novel substrate of protein phosphatase PGAM5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 509(4):886–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.01.031
Péterfy M, Phan J, Xu P, Reue K (2001) Lipodystrophy in the fld mouse results from mutation of a new gene encoding a nuclear protein, lipin. Nat Genet 27(1):121–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/83685
Peterson TR, Sengupta SS, Harris TE, Carmack AE, Kang SA, Balderas E, Guertin DA, Madden KL, Carpenter AE, Finck BN, Sabatini DM (2011) mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1 localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell 146(3):408–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.034
Phan J, Reue K (2005) Alternatively spliced lipin isoforms exhibit distinct expression pattern, subcellular localization, and role in adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 280(38):32883–32889. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M503885200
Rena G, Guo S, Cichy SC, Unterman TG, Cohen P (1999) Phosphorylation of the transcription factor forkhead family member FKHR by protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 274(24):17179–17183. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.24.17179
Reue K, Brindley DN (2008) Multiple roles for lipins/phosphatidate phosphatase enzymes in lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res 49(12):2493–2503. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R800019-JLR200
Sarwar Z, Nabi N, Bhat SA, Gillani SQ, Reshi I, Nisa MU, Adelmant G, Marto JA, Andrabi S (2022) Interaction of DBC1 with polyoma small T antigen promotes its degradation and negatively regulates tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 298(2):101496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101496
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L, Kosmatka M, DePinho RA, Cantley LC (2004) The LKB1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell 6(1):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.007
Shimizu K, Fukushima H, Ogura K, Lien EC, Nihira NT, Zhang J, North BJ, Guo A, Nagashima K, Nakagawa T, Hoshikawa S, Watahiki A, Okabe K, Yamada A, Toker A, Asara JM, Fukumoto S, Nakayama KI, Nakayama K, Inuzuka H, Wei W. The SCFβ-TRCP E3 ubiquitin ligase complex targets Lipin1 for ubiquitination and degradation to promote hepatic lipogenesis. Sci Signal 10(460):eaah4117. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aah4117
Tiainen M, Ylikorkala A, Mäkelä TP (1999) Growth suppression by Lkb1 is mediated by a G1 cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(16):9248–9251. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.16.9248
Wang H, Airola MV, Reue K (2017) How lipid droplets “TAG” along: Glycerolipid synthetic enzymes and lipid storage. Biochim Biophysica Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1862(10):1131–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.06.010
Yang G, Murashige DS, Humphrey J, James DE (2015) Report report a positive feedback loop between Akt. Cell Rep 12(6):937–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.016
Zanivan S, Gnad F, Wickström SA, Geiger T, Macek B, Cox J, Fässler R, Mann M (2008) Solid tumor proteome and phosphoproteome analysis by high resolution mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 7(12):5314–5326. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr800599n
Zhao JJ, Liu Z, Wang L, Shin E, Loda MF, Roberts TM (2005) The oncogenic properties of mutant p110α and p110β phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in human mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(51):18443–18448. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508988102
Acknowledgements
The research work in this study was supported by grants to Shaida Andrabi through the Ramalingaswami Fellowship, Department of Biotechnology, and through the FIST grant to the Department of Science and Technology, India. Misbah Un Nisa, Nusrat Nabi and Irfana Reshi were provided fellowships by the CSIR. Syed Qaaifah Gillani, Zarka Sarwar and Sameer A Bhat were provided INSPIRE fellowships by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Un Nisa, M., Gillani, S.Q., Nabi, N. et al. Lipin-1 stability and its adipogenesis functions are regulated in contrasting ways by AKT1 and LKB1. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 689–704 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00708-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00708-9