Abstract
Introduction
Fat cell differentiation (FCD) potentiates adipose cell characteristics including lipid storage and insulin sensitivity. In vitro, we have demonstrated that CCN2, also known as connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), inhibits FCD in NIH3T3-L1 cells and in adipocytes isolated from mouse epididymal fat pads. The aim of this study was to determine if the CCN2 effect on FCD is dependent on TGF-β and TGF-β downstream pathway signalling.
Methods
NIH3T3-L1 cells were differentiated using standard methods with IBMX/Dex/Insulin. FCD at day 10 was confirmed by induced gene markers resistin and adiponectin and by lipid accumulation. Cells were treated at d0 with single dose active rhTGF-β1 (2 ng/mL), rhCCN2 (500 ng/mL) and/or TGF-β type 1 receptor blocker (SB431542, 5 μM). Early induction of FCD transcription factors: CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ), were also determined.
Results
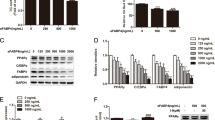
In an early time course from 2 h, single doses of rhTGF-β1 or rhCCN2 significantly inhibited by ~70 % the induction of C/EBP-β and -δ mRNA, and also nuclear protein levels otherwise seen during FCD, whereas only delayed effects on PPAR-γ, at 48 h, occurred. Furthermore, the CCN2 inhibition of FCD markers adiponectin and resistin and lipid accumulation by Oil red O stain were each prevented by TGF-β receptor blockade. Similar prevention was found using pan-specific anti-TGF-β neutralising antibody. CCN2 and TGF-β treatment each rapidly phosphorylated SMAD-3 signalling in early stages of FCD.
Conclusion
This work shows novel findings that CCN2 effects on FCD are both TGF-β and TGF-β pathway dependent and are related to early effects on C/EBPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu JG, Ketpura NI, Reversade B, De Robertis EM (2002) Connective-tissue growth factor (CTGF) modulates cell signalling by BMP and TGF-beta. Nat Cell Biol 4(8):599–604
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith SC Jr, International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention, Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, American Heart Association, World Heart Federation, International Atherosclerosis Society, International Association for the Study of Obesity (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120(16):1640–1645
Arnott JA, Zhang X, Sanjay A, Owen TA, Smock SL, Rehman S, DeLong WG, Safadi FF, Popoff SN (2008) Molecular requirements for induction of CTGF expression by TGF-beta1 in primary osteoblasts. Bone 42(5):871–885
Baxter RC, Twigg SM (2009) Actions of IGF binding proteins and related proteins in adipose tissue. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(10):499–505
Bhat N, Feinstein DL, Shen Q, Bhat AN (2002) p38 MAPK-mediated Transcriptional Activation of Inducible Nitric-oxide Synthase in Glial Cells, J Biol Chem.277, 33:29584–29592
Brigstock DR (2003) The CCN family: a new stimulus package. J Endocrinol 178(2):169–175
Chan SS, Schedlich LJ, Twigg SM, Baxter RC (2009) Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation by insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296(4):E654–E663
Choy L, Derynck R (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits adipocyte differentiation by Smad3 interacting with CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and repressing C/EBP transactivation function. J Biol Chem 278(11):9609–9619
Choy L, Skillington J, Derynck R (2000) Roles of autocrine TGF-beta receptor and Smad signaling in adipocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol 149(3):667–682
de Silva HC, Firth SM, Twigg SM, Baxter RC (2012) Interaction between IGF binding protein-3 and TGFβ in the regulation of adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 153(10):4799–4807
Dixon TM, Daniel KW, Farmer SR, Collins S (2001) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is required for transcription of the beta 3-adrenergic receptor gene during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 276(1):722–728
Fernyhough ME, Bucci LR, Hausman GJ, Antonio J, Vierck JL, Dodson MV (2005) Gaining a solid grip on adipogenesis. Tissue Cell 37(4):335–338
Fu M, Zhang J, Lin Y, Zhu X, Zhao L, Ahmad M, Ehrengruber MU, Chen YE (2003) Early stimulation and late inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) gene expression by transforming growth factor beta in human aortic smooth muscle cells: role of early growth-response factor-1 (Egr-1), activator protein 1 (AP1) and Smads. Biochem J 370(Pt 3):1019–1025
Gregoire FM, Smas CM, Sul HS (1998) Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev 78(3):783–809
Ignotz RA, Massague J (1985) Type beta transforming growth factor controls the adipogenic differentiation of 3 T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82(24):8530–8534
Kumar A, Ruan M, Clifton K, Syed F, Khosla S, Oursler MJ (2012) TGF-β mediates suppression of adipogenesis by estradiol through connective tissue growth factor induction. Endocrinology 153(1):254–263
Li HX, Luo X, Liu RX, Yang YJ, Yang GS (2008) Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 291(1–2):116–124
McLennan SV, Wang XY, Moreno V, Yue DK, Twigg SM (2004) Connective tissue growth factor mediates high glucose effects on matrix degradation through tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase type 1: implications for diabetic nephropathy. Endocrinology 145(12):5646–5655
Perbal B (2004) CCN proteins: multifunctional signalling regulators. Lancet 363(9402):62–64
Perbal B (2013) CCN proteins: a centralized communication network. J Cell Commun Signal 7(3):169–177
Riser BL, Najmabadi F, Perbal B, Peterson DR, Rambow JA, Riser ML, Sukowski E, Yeger H, Riser SC (2009) CCN3 (NOV) is a negative regulator of CCN2 (CTGF) and a novel endogenous inhibitor of the fibrotic pathway in an in vitro model of renal disease. Am J Pathol 174:1725–1734
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2000) Molecular regulation of adipogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:145–171
Secker GA, Shortt AJ, Sampson E, Schwarz QP, Schultz GS, Daniels JT (2008) TGFbeta stimulated re-epithelialisation is regulated by CTGF and Ras/MEK/ERK signalling. Exp Cell Res 314(1):131–142
Song K, Wang H, Krebs TL, Danielpour D (2006) Novel roles of Akt and mTOR in suppressing TGF-beta/ALK5-mediated Smad3 activation. EMBO J 25(1):58–69
Sul HS (2009) Minireview: Pref-1: role in adipogenesis and mesenchymal cell fate. Mol Endocrinol 23(11):717–725
Tan JT, McLennan SV, Song WW, Lo LW, Bonner JG, Williams PF, Twigg SM (2008) Connective tissue growth factor inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295(3):C740–C751
Tchkonia T, Giorgadze N, Pirtskhalava T, Tchoukalova Y, Karagiannides I, Forse RA, DePonte M, Stevenson M, Guo W, Han J, Waloga G, Lash TL, Jensen MD, Kirkland JL (2002) Fat depot origin affects adipogenesis in primary cultured and cloned human preadipocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282(5):R1286–R1296
Thompson K, Murphy-Marshman H, Leask A (2014) ALK5 inhibition blocks TGFβ-induced CCN1 expression in human foreskin fibroblasts. J Cell Commun Signal 8(1):59–63
Tontonoz P, Spiegelman BM (2008) Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem 77:289–312
Tsai YS, Tsai PJ, Jiang MJ, Chou TY, Pendse A, Kim HS, Maeda N (2009) Decreased PPAR gamma expression compromises perigonadal-specific fat deposition and insulin sensitivity. Mol Endocrinol 23(11):1787–1798
Wahab NA, Weston BS, Mason RM (2005) Modulation of the TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway in mesangial cells by CTGF/CCN2. Exp Cell Res 307(2):305–314
Wrighton KH, Feng XH (2008) To (TGF) beta or not to (TGF) beta: fine-tuning of Smad signaling via post-translational modifications. Cell Signal 20(9):1579–1591
Zhang Y, Feng XH, Derynck R (1998) Smad3 and Smad4 cooperate with c-Jun/c-Fos to mediate TGF-beta-induced transcription. Nature 394(6696):909–913
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council (NH&MRC) of Australia Project Grant #457373, to SMT, RCB and SVM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W.W., McLennan, S.V., Tam, C. et al. CCN2 requires TGF-β signalling to regulate CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins and inhibit fat cell differentiation. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 9, 27–36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0252-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0252-8