Abstract
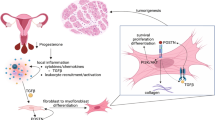
Uterine leiomyoma, commonly known as fibroids, is a benign neoplasm of smooth muscle in women. The incidence of clinically symptomatic fibroids in reproductive-age women is approximately 20 %, with nearly 80 % of black women suffering from this condition. Symptoms include severe pain and hemorrhage; fibroids are also a major cause of infertility or sub-fertility in women. Uterine leiomyoma consist of hyperplastic smooth muscle cells and an excess deposition of extracellular matrix, specifically collagen, fibronectin, and sulfated proteoglycans. Extracellular matrix components interact and signal through integrin-β1 on the surface of uterine leiomyoma smooth muscle cells, provide growth factor storage, and act as co-receptors for growth factor-receptor binding. ECM and growth factor signaling through integrin-β1 and growth factor receptors significantly increases cell proliferation and ECM deposition in uterine leiomyoma. Growth factors TGF-β, IGF, PDGF, FGF and EGF are all shown to promote uterine leiomyoma progression and signal through multiple pathways to increase the expression of genes encoding matrix or matrix-modifying proteins. Decreasing integrin expression, reducing growth factor action and inhibiting ECM action on uterine leiomyoma smooth muscle cells are important opportunities to treat uterine leiomyoma without use of the current surgical procedures. Both natural compounds and chemicals are shown to decrease fibrosis and uterine leiomyoma progression, but further analysis is needed to make inroads in treating this common women’s health issue.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKAP:
-
A-kinase anchor protein
- Bcl:
-
Burkitt cell lymphoma
- CDK:
-
cell division kinase
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- Erk:
-
extacellular signal-regulated kinase
- FGF:
-
fibroblast growth factor
- FGFR:
-
fibroblast growth factor receptor
- HSPG:
-
heparan sulfate proteoglycan
- IGF:
-
insulin-like growth factor
- IGFBP:
-
insulin-like growth factor binding protein
- MAPK:
-
mitosis-activating protein kinase
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloprotease
- PDGF:
-
platelet-derived growth factor
- SB:
-
Scutellaria barbata D. Don
- SMC:
-
smooth muscle cells
- TGF:
-
transforming growth factor
- UAE:
-
uterine artery embolization
- UL:
-
uterine leiomyoma
References
Anania CA (1997) Stewart., EA., Quade, BJ., Hill, JA., Nowak, RA. Expression of the fibroblast growth factor receptor in women with leiomyomas and abnormal uterine bleeding. Mol Hum Reprod 3(8):685–691
Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, Cousins D, Schectman JM (2003) High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: Ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstetrical Gynecology 188:100–107
Baird DD, Hill MC, Schectman JM, Hollis BW (2013) Vitamin D and the risk of uterine fibroids. Epidemiology 24(3):447–453
Barnard J, Lyons R, Moses H (1990) The cell biology of transforming growth factor β. Biochim Biophy 1032:79–87
Block E, Matela A, SundarRaj N, Iszkula E, Klarlund J (2004) Wounding Induces Motility in Sheets of Corneal Epithelial Cells through Loss of Spatial Constraints. J Biol Chem 279:24307–24312
Bogusiewicz M, Stryjecka-Zimmer M, Postawski K, Jakimiuk AJ, Rechberger T (2007) Activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and contents of their tissue inhibitors in uterine leiomyoma and corresponding myometrium. Utery 23(9):541–546
Britten J, Malik M, Levy G, Mendoza M, Catherino W (2012) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist leuprolide acetate and GnRH antagonist cetrorelix acetate directly inhibit leiomyoma extracellular matrix production. Fertil Steril 98(5):1299–1307
Burroughs KD, Howe SR, Okubo Y, Fuchs-Young R, LeRoith D, Walker CL (2002) Dysregulation of IGF-1 signaling in uterine leiomyoma. J Endocrinol 172:83–93
Butcher DT, Alliston T, Weaver VM (2009) A tense situation: forcing tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 9(2):108–122
Cardozo ER, Clark AD, Banks NK, Henne MB, Stegmann BJ, Segars JH (2012) The estimated annual cost of uterine leiomyomata in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol 206(3):211
Carrino DA, Mesiano S, Barker NM, Hurd WW, Caplan A (2012) Proteoglycans of uterine fibroids and keloid scars: similarity in their proteoglycan composition. Biochem J 443(2):361–368
Casimiro, MC., Valasco-Velazquez, M., Aguierre-Alvarado, C., Pestell, RG. Overview of cyclins D function in cancer and the CDK inhibitor landscape: past and present. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2014; Epub. Access: Jan 26, 2014. http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.1517/13543784.2014.867017
Cavin S, Maric D, Diviani D (2014) A-kinase anchoring protein-Lbc promotes pro-fibrotic signaling in cardiac fibroblasts. Biogeosciences 1843(2):335–345
Chaturvedi LS, Marsh HM, Basson MD (2007) Src and focal adhesion kinase mediate mechanical strain-induced proliferation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in human H441 pulmonary epithelial cells. Am J Cell Physiol 292(5):C1701–C1713
Chen HM, Lin YH, Cheng YM, Wing LY, Tsai SJ (2013) Overexpression of integrin-B1 in leiomyoma promotes cell spreading and proliferation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(5):E837–E846
Chwalisz K, Larsen L, Mattia-Goldberg C, Edmonds A, Elger W, Winkel CA (2007) A randomized, controlled trial of asoprisnil, a novel selective progesterone receptor modulator, in women with uterine leiomyomata. Fertil Sterl 87(6):1399–1412
Cirilo PD, Marchi FA, Barros Filho Mde C, Rocha RM, Domingues MA, Jurisica I, Pontes A, Rogatto SR. An integrative genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals potential targets associated with cell proliferation in uterine leiomyoma. PLoS One 2013; 8 (3): Epub. Accessed on Feb 8, 2014. http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0057901
Clemmons DR (1991) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: roles in regulating IGF physiology. J Dev Physiol 15(2):105–110
Csatlós E, Rigó J Jr, Laky M, Joó JG (2013) Gene expression patterns of insulin-like growth factor 2 in human uterine fibroid tissues: a genetic study with clinical correlations. Gynecol Obstet Invest 75(3):185–190
DeMali KA, Wennerberg K, Burridge K (2003) Integrin signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15(5):572–582
Di Tommaso S, Massari S, Malvasi A, Bozzeti MP, Tinelli A (2013) Gene expression analysis reveals an angiogenic profile in uterine leiomyoma pseudocapsule. Mol Hum Reprod 19(6):380–387
Ding L, Xu J, Luo X, Chegini N (2004) Gonadotropin releasing hormone and transforming growth factor beta activate mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellularly regulated kinase and differentially regulate fibronectin, type I collagen, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in leiomyoma and myometrial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(11):5549–5557
Dzamba BJ, Wu H, Jaenisch R, Peters DM (1993) Fibronectin binding site in type I collagen regulates fibronectin fibril formation. J Cell Biol 121(5):1165–1172
Edmondson SR, Thumiger SP, Werther GA, Wraight CJ (2003) Epidermal homeostasis: the role of the growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor systems. Endocr Rev 24(6):737–764
Esko JD, Linhardt RJ (2009) Proteins that Bind Sulfated glycosaminoglycans. In: Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD (eds) Essentials of Glycobiology, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Fayed YM, Tsibris JC, Langenberg PW, Robertson AL Jr (1989) Human uterine leiomyoma cells: binding and growth responses to epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and insulin. Lab Invest 60(1):30–37
Forsten-Williams K, Chua C, Nugent M (2005) The kinetics of FGF-2 binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans and MAP kinase signaling. J of Theo Biol 233:483–499
Gaarenstroom, T., Hill, CS. TGF-β signaling to chromatin: How Smads regulate transcription during self-renewal and differentiation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; Epub. Accessed on Feb 10, 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S108495211400010X
Gao Z, Matsuo H, Wang Y, Nakago S, Maruo T (2001) Up-regulation by IGF-1 of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Bcl-2 protein expression in human uterine leiomyoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(11):5593–5599
Gilden M, Malik M, Britten J, Delgado T, Levy G, Catherino W (2012) Leiomyoma fibrosis inhibited by liarozole, a retinoic acid metabolic blocking agent. Fertil Steril 98(6):1557–1562
Giudice LC, Irwin JC, Dsupin BA, Pannier EM, Jin IH, Vu TH, Hoffman AR (1993) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF), IGF binding protein (IGFBP), and IGF receptor gene expression and IGFBP synthesis in human uterine leiomyomata. Hum Reprod 8(11):1796–1806
Goustin AS, Leof EB, Shipley GD (1986) Growth factors and Cancer. Cancer Res 46:1015–1029
Halder SK, Goodwin JS, Al-Hendy A (2011) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces TGF-B3-induced fibrosis-related gene expression in human uterine leiomyoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(4):E754–E762
Halder SK, Sharan C, Al-Hendy A (2012) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment shrinks uterine leiomyoma tumors in the Eker rat model. Biol Reprod 86(4):116
Han J, Zhang L, Chen X, Yang B, Guo N, Fan Y. Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on signal pathway of cyclooxygenase-2 and Smad3 in transforming growth factor-β-stimulated glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Biol Med 2014; Epub. Accessed on Feb 10, 2014. http://ebm.sagepub.com/content/early/2014/02/04/1535370213519216.long.
Hannink M, Donoghue DJ (1989) Structure and function of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and relatd proteins. Biochim Biophys 989(1):1–10
Hoekstra AV, Sefton EC, Berry E, Lu Z, Hardt J, Marsh E, Yin P, Clardy J, Chakravarti D, Bulun S, Kim JJ (2009) Progestins activate the AKT pathway in leiomyoma cells and promote survival. J Clin Endocrinol Metabl 94(5):1768–1774
Imai Y1, Busby WH Jr, Smith CE, Clarke JB, Garmong AJ, Horwitz GD, Rees C, Clemmons DR. Protease-resistant form of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 is an inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-I actions on porcine smooth muscle cells in culture. J Clin Invest 1997; 100 (10): 2596-605.
Ingber D, Folkman J (1989) Mechanochemical switching between growth and differentiation during fibroblast growth factor-stimulated angiogenesis in vitro: role of extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 109:317–330
Iwahashi M, Muragaki Y, Ikoma M, Mabuchi Y, Kobayashi A, Tanizaki Y, Ino K (2011) Immunohistochemical analysis of collagen expression in uterine leiomyomata during the menstrual cycle. Exp Ther Med 2(2):287–290
Iwahashi M, Muragaki Y, Ino K. Human prolyl hydroxylase expression in uterine leiomyoma during the menstrual cycle. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2012; 10 (111).
Jones JI, Gockerman A, Busby WH, Camacho-Hubner C, Clemmons DR (1993) Extracellular matrix contains insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5: potentiation of the effects of IGF-1. J Cell Biol 121(3):679–687
Joseph DS1, Malik M, Nurudeen S, Catherino WH. Myometrial cells undergo fibrotic transformation under the influence of transforming growth factor beta-3. Fertil Steril 2010; 93 (5): 1500-8.
Kang Y, Choi Y, Yun C, Park J, Suk K, Kim H et al (2014) Down-regulation of collagen synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase expression in myofibroblasts from dupuytren nodule using adenovirus-mediated relaxin gene therapy. J Orthopaedic Res 32(4):515–523
Karagiannis ED, Pope AS (2006) Distinct modes of collagen type I proteolysis by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and membrane type I MMP during the migration of a tip endothelial cell: Insights from a computational model. J Theo Biol 238:124–145
Karsenty G, Park R (1995) Regulation of type I collagen genes expression. Int Rev Immuno 12(2–4):177–185
Khan A, Shehmar M, Gupta J (2014) Uterine fibroids: current perspectives. Int J Womens Health 6:95–114
Kim D, Lee T, Lim I, Kim H, Lee Y, Kim C (2005) Regulation of IGF-I production and proliferation of human leiomyomal smooth muscle cells by Scutellaria barbata D Don in vitro: isolation of flavonoids of apigenin and luteolin as acting compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharm 205(3):213–224
Kobayashi Y, Nikaido T, Zhai YL, Iinuma M, Shiozawa T, Shirota M, Fuji S (1996) In-vitro model of uterine leiomyoma: formation of ball-like aggregates. Hum Reprod 11(8):1724–1730
Koohestani, F., Braundmeier, A., Mhadian, A., Seo J., Bi, J., Nowak R. Extracellular Matrix Collagen Alters Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression of Human Uterine Leiomyoma Smooth Muscle Cells. PLoS One 2013; 8 (9): published online Sept 11, 2013. Accessed Dec 20, 2013 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3770620/?report=classic
Lamminen S, Rantala I, Helin H, Rorarius M, Tuimala R (1992) Proliferative activity of human uterine leiomyoma cells as measured by automatic image analysis. Gynecol Obstet Invest 34(2):111–114
Laron Z (2001) Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): a growth hormone. Mol Pathol 54(5):311–316
Lee, BS., Nowak, RA. Human Leiomyoma Smooth Muscle Cells Show Increased Expression of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 (TGFβ3) and Altered Responses to the Antiproliferative Effects of TGFβ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86 (2): Epub. Accessed on Jan 26, 2014. http://press.endocrine.org.ezproxy.library.tufts.edu/doi/full/10.1210/jcem.86.2.7237.
Leppert PC, Baginski T, Prupas C, Catherino WH, Pletcher S, Segars JH (2004) comparative ultrastructure of collagen fibrils in uterine leiomyoma and normal myometrium. Fertil Steril 82:1182–1187
Levens E, Luo X, Ding L, Williams RS, Chegini N (2005) Fibromodulin is expressed in leiomyoma and myometrium and regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue therapy and TGF-beta through Smad and MAPK-mediated signaling. Mol Hum Reprod 11(7):489–494
Levy G, Hill MJ, Zarek SM, Segars JH, Catherino WH (2012) Leiomyoma: genetics, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and therapeutic advances. J of Assist Reprod Genet 29(8):703–712
Liang M1, Wang H, Zhang Y, Lu S, Wang Z. Expression and functional analysis of platelet-derived growth factor in uterine leiomyomata. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006; 5 (1): 28-33.
Lin F, Ren XD, Pan Z, Macri L, Zong WX, Tonnesen MG et al (2011) Fibronectin growth factor-binding domains are required for fibroblast survival. J Invest Dermatol 131(1):84–98
Lobel M, Somasundaram P, Morton C (2006) The genetic heterogeneity of uterine leiomyomata. Obstet Gynecol Clin N Am 33:13–39
MacLennan A (1991) The role of the hormone relaxin in human reproduction and pelvic girdle relaxation. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 88:7–15
Malik M1, Mendoza M, Payson M, Catherino WH. Curcumin, a nutritional supplement with antineoplastic activity, enhances leiomyoma cell apoptosis and decreases fibronectin expression. Fertil Steril 2009; 91 (5): 2177-84.
Malik M, Segars J, Catherino WH (2012) Integrin B1 regulates leiomyoma cytoskeletal integrity and growth. Matrix Biol 1(7–8):389–397
Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Willett WC et al (1997) Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol 90:967–973
Martino MM, Tortelli F, Mochizuki M, Traub S, Ben-David D, Kuhn GA (2011) Engineering the growth factor microenvironment with fibronectin domains to promote wound and bone tissue healing. Sci Transl Med 3(100):100
Martino MM, Briquez PS, Ranga A, Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA (2013) Heparin-binding domain of fibrin (ogen) binds growth factors and promotes tissue repair when incorporated within a synthetic matrix. PNAS 110(12):4563–4568
Mitropoulou, TN., Theocharis, AD., Stagiannis, KD., Karamanos, NK. Identification, quantification and fine structural characterization of glycosaminoglycans from uterine leiomyoma and normal myometrium. Biochimie 2001; 83 (6): 529-36. G
Moore AB, Castro L, Yu L, Zheng X, Di X, Sifre MI et al (2007) Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of genistein on human uterine leiomyoma cell proliferation are influenced by the concentration. Hum Reprod 22(10):2623–2631
Moore, AB., Yu, L., Swartz, CD., Zheng, X., Wang, L., Castro, L., Kissling, GE., et al. Human uterine leiomyoma-derived fibroblasts stimulate uterine leiomyoma cell proliferation and collagen type I production, and activate RTKs and TGF beta receptor signaling in coculture. J Cell Commun Signal 2010; 8 (10)
Moran NE, Erdman JW Jr, Clinton SK. Complex interactions between dietary and genetic factors impact lycopene metabolism and distribution. Arch Biochem Biophys 2013; 539) 2_: 171-80.
Morikawa A, Ohara N, Xu Q, Nakabayashi K, DeManno D, Chwalisz K et al (2008) Selective progesterone receptor modulator asoprisnil down-regulates collagen synthesis in cultured human uterine leiomyoma cells through up-regulating extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer. Hum Reprod 23(4):944–951
Moschos SJ, Mantzoros CS (2002) The role of IGF system in cancer: from basic to clinical studies and clinical applications. Oncol 63:317–332
Mueller MM, Fusenig N (2004) Friends or foes—bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev 4:839–849
Norian JM, Owen CM, Taboas J, Korecki C, Tuan R, Malik M (2012) Characterization of tissue biomechanics and mechanical signaling in uterine leiomyoma. Matrix Biol 31(1):57–65
Othman E (2008) Molecular genetics and racial disparities of uterine leiomyomas. Best Pract Res Cl Ob 22(4):589–601
Paffoni A, Somigliana E, Vigano’ P, Benaglia L, Cardellicchio L, Pagliardini L (2013) Vitamin D status in women with uterine leiomyomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(8):1374–8
Pankov R, Yamada K (2002) Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci 115:3861–3863
Park B, Nguyen NT, Dutt P, Merdek KD, Bashar M, Sterpetti P (2002) Association of LBC Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor with a-catenin-related protein, a-catulin/CTNNAL1, supports serum response factor activation. J Biol Chem 277:45361–45370
Peng, L, Wen, Y., Han, Y., Wei, A., Shi, G., Mizuguchi, M. et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF signaling molecular complexity in uterine leiomyomas. Fertil and Steril 2009; 91) 6: 2664-75.
Rauk PN, Surti U, Roberts JM, Michalpoulos G (1994) Mitogenic effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and estradiol on cultured human myometrial and leiomyoma cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173(2):571–577
Ravindran, J., Prasad, S., Aggarwal, B. Curcumin and Cancer Cells: How Many Ways Can Curry Kill Tumor Cells Selectively? AAPS J 2009; 11 (3) L 495-510.
Rogers, R., Norian, J., Malik, M., Christman, G., Abu-Asab, M., Chen, F., et al. Mechanical homeostasis is altered in uterine leiomyoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008; 198 (4) : 474 e.1-474 e.11.
Salama SA, Nasr AB, Dubey RK, Al-Hendy A (2006) Estrogen metabolite 2-methoxyestradiol induces apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation and collagen production in rat and human leiomyoma cells: a potential medicinal treatment for uterine fibroids. J Soc Gynecol Investig 13(8):542–550
Salama SA, Diaz-Arrastia CR, Kilic GS, Kamel MW (2012) 2-Methoxyestradiol causes functional repression of transforming growth factor β3 signaling by ameliorating Smad and non-Smad signaling pathways in immortalized uterine fibroid cells. Fertil Sterl 98(1):178–184
Sato T, Sakai T, Noguchi Y, Takita M, Hirakawa S, Ito A (2004) Tumor-stromal cell contact promotes invasion of human uterine cervical carcinoma cells by augmenting the expression and activation of stromal matrix metalloproteinases. Gynecol Oncol 92(1):47–56
Scheurig-Muenkler C1, Koesters C, Powerski MJ, Grieser C, Froeling V, Kroencke TJ. Clinical long-term outcome after uterine artery embolization: sustained symptom control and improvement of quality of life. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2013; 24 (6): 765-71.
Sejersen T, Betsholtz C, Sjolund M, Heldin CH, Westermark B, Thyberg J (1986) Rat skeletal myoblasts and arterial smooth muscle cells express the gene for the A chain but not the gene for the B chain (c-sis) of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and produce a PDGF-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83(18):6844–6848
Shalitin N, Schlesinger H, Levy MJ, Kessler E, Kessler-Icekson G (2003) Expression of procollagen C-proteinase enhancer in cultured rat heart fibroblasts: Evidence for co-regulation with type I collagen. J Cell Biochem 90(2):397–407
Shapiro SS1, Seiberg M, Cole CA. Vitamin A and its derivatives in experimental photocarcinogenesis: preventive effects and relevance to humans. J Drugs Dermatol 2013; 12 (4): 458-63.
Sharan C, Halder SK, Thota C, Jaleel T, Nair S, Al-Hendy A (2011) Vitamin D inhibits proliferation of human uterine leiomyoma cells via catechol-O-methyltransferase. Fertil Steril 95(1):247–253
Shen, Y., Xu, Q., Ren, M., Feng, X., Cai, Y., Gao, Y. Measurement of phenolic environmental estrogens in women with uterine leiomyoma. PLoS One 2013; 8 (11).
Shibolet O, Giallourakis C, Rosenberg I, Mueller T, Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK (2007) AKAP13, a RhoA GTPase-specific guanine exchange factor, is a novel regulator of TLR2 signaling. J Biol Chem 282:35308–35317
Steffensen B, Wallon UM, Overall CM (1995) Extracellular matrix binding properties of recombinant fibronectin type II-like modules of human 72-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase High affinity binding to native type I collagen but not native type IV collagen. J Biol Chem 270(19):11555–11566
Suo G, Jiang Y, Cowan B, Wang J (2009) Platelet-Derived Growth Factor C Is Upregulated in Human Uterine Fibroids and Regulates Uterine Smooth Muscle Cell Growth. Biol Reprod 81(4):749–758
Svensson L, Heinegard D, Oldberg A (1995) Decorin-binding sites for Collagen Type I are mainly Located in Leucine Rich Repeats 4-5*. J of Biol Chem 270(35):20712–20716
Taipale J, Keski-Oja J (1997) Growth factors in the extracellular matrix. The FASEB J 11(1):51–59
Takeuchi H, Kobori H, Kikuchi I, Sato Y, Mitsuhashi N (2000) A prospective randomized study comparing endocrinological and clinical effects of two types of GnRH agonists in cases of uterine leiomyoma or endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 26(5):325–331
Taylor CV, Letarte M, Lye SJ (1996) The expression of integrins and cadherins in normal human uterus and uterine leiomyoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175(2):411–419
Tinelli A1, Hurst BS, Hudelist G, Tsin DA, Stark M, Mettler L, Guido M, Malvasi A. Laparoscopic myomectomy focusing on the myoma pseudocapsule: technical and outcome reports. Hum Reprod 2012; 27 (2): 427-35.
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chapponier C, Brown RA (2002) Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:349–363
Torre A1, Paillusson B, Fain V, Labauge P, Pelage JP, Fauconnier A. Uterine artery embolization for severe symptomatic fibroids: effects on fertility and symptoms. Hum Reprod 2014; 29 (3): 490-501.
Tsai FC1, Liu WM, Pai MH, Hsieh MS, Lin JY, Chou CM. Downregulation of the integrin α (v) signaling pathway in uterine leiomyomas. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2011; 71 (2): 129-35.
Turner N, Grose R (2010) Fibroblast growth factor signaling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10:116–129
Varga J, Rosenbloom J, Jimenez SA (1987) Transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem J 247(3):597–604
Wang J, Ohara N, Takekida S, Xu Q, Maruo T (2005) Comparative effects of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor on the growth of cultured human uterine leiomyoma cells and myometrial cells. Hum Reprod 20(6):1456–1465
Wang J, Ohara N, Wang Z, Chen W, Morikawa A, Sasaki H, DeManno DA, Chwalisz K, Maruo T (2006) A novel selective progesterone receptor modulator asoprisnil (J867) down-regulates the expression of EGF, IGF-I, TGFbeta3 and their receptors in cultured uterine leiomyoma cells. Hum Reprod 21(7):1869–1877
Wang Y, Yao M, Zhou J, Zheng W, Zhou C, Dong D et al (2011) The promotion of neural progenitor cells proliferation by aligned and randomly oriented collagen nanofibers through β1 integrin/MAPK signaling pathway. Biomaterials 32(28):6737–6744
Watanabe Y, Nakamura G, Matsuguchi H, Nozaki M, Sano M, Nakano H (1992) Efficacy of a low-dose leuprolide acetate depot in the treatment of uterine leiomyomata in Japanese women. Fertil Steril 58(1):66–71
Weaver VM, Petersen OW, Wang F, Larabell CA, Briand P, Damsky C et al (1997) Reversion of the malignant phenotype of human breast cells in three-dimensional culture and in vivo by integrin blocking antibodies. J Cell Biol 137(7):231–245
Wolanska M, Bankowski E (2006) Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) in human myometrium and uterine leiomyoma in various stages of tumour growth. Biochimie 88(2):141–146
Wolanska M, Sobolewski K, Drozdzewicz M, Bankowski E (1998) Extracellular matrix components in uterine leiomyoma and their alteration during the tumour growth. Mol Cell Biochem 189(1–2):145–152
Wolanska M, Sobolewski K, Bankowski E, Jaworski S (2004) Matrix Metalloproteinases of Human Leiomyoma in Various Stages of Tumor Growth. Gynecol Obstet Invest 58:14–18
Xu Q, Lili Q, Zhu L, Luo L, Xu C (2010) Levonorgestrel inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in uterine leiomyoma cells. Contraception 82(3):301–308
Yamaguchi Y, Mann DM, Ruoslahti E (1990) Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-B by the proteoglycan decorin. Nat Rev 346(19):281–284
Yamamoto, H., Arakaki, K., Morimatsu, K., Zaitsu, Y., Fujita, A., Kohashi, K., et al. Insulin-like growth factor II messenger RNA-binding protein 3 expression in gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors. Human pathol 2013; Epub. Accessed Feb 8, 2014: http://www.humanpathol.com/article/S0046-8177(13)00425-5.
You D, Nam M (2013) Effects of human epidermal growth factor gene-transfected mesenchymal stem cells on fibroblast migration and proliferation. Cell Proliferat 46(4):408–415
Yu C, Wang F, Jin C, Huang X, Miller D, Basillco C et al (2003) Role of fibroblast growth factor type 1 and 2 in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury and fibrogenesis. Am J of Pathol 163(4):1653–1662
Yu L, Saile K, Swartz C, He H, Zheng X, Kissling G et al (2008) Differential expression of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and IGF-1 pathway activation in human uterine leiomyoma. Mol Med 14(5–6):264–275
Yu, L., Moore, AB., Castro, L., Gao, X., Huynh, HC., Klippel, M., et al. Estrogen regulates MAPK-related genes through genomic and nongenomic interactions between IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase and estrogen receptor-alpha signaling pathways in human uterine leiomyoma cells. J Signal Transduct; 2012; PMC 20426. Access date: Dec 13, 2013. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3474284/.
Zeng, F., Harris, R. Epidermal growth factor, from gene organization to bedside. In press available online February 7, 2014. Accessed on Feb 10, 2014: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084952114000135
Zhang, D., Al-Hendy, M., Richard-Davis, G., Montgomery-Rice, V., Sharan, C., Rajaratnam, V., Khurana, A., Al-Hendy, A. Green tea extract inhibits proliferation of uterine leiomyoma cells in vitro and in nude mice. Am J of Obstet Gynecol 2010; 202 (3): 289.e1-289.e9.
Zimmerman A, Bernuit D, Gerlinger C, Schaefers M, Geppert K (2012) Prevalence, symptoms and management of uterine fibroids: an international internet-based survey of 21,746 women. BMC Women’s Health 12:6
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Russell Fujisawa for his generous assistance in editing this manuscript. We also thank Dr. Margery Beinfeld for reading the manuscript and providing helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujisawa, C., Castellot, J.J. Matrix production and remodeling as therapeutic targets for uterine leiomyoma. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 8, 179–194 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0234-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0234-x