Abstract
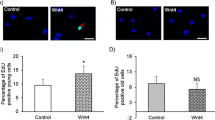
The role of CCN proteins in vivo is only just becoming understood. A prototypical member of the CCN family, CCN3 suppresses proliferation. In a study in press, Shimoyama and colleagues show that mice lacking CCN3 have a hyperproliferative response to vascular injury. These data, along with other recent observations, suggest that CCN3 may represent a novel therapy for hyperproliferative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleau AM, Planque N, Perbal B (2005) CCN proteins and cancer: two to tango. Front Biosci 10:998–1009
Heath E, Tahri D, Andermarcher E, Schofield P, Fleming S, Boulter CA (2008) Abnormal skeletal and cardiac development, cardiomyopathy, muscle atrophy and cataracts in mice with a targeted disruption of the Nov (Ccn3) gene. BMC Dev Biol 8:18
Ivkovic S, Yoon BS, Popoff SN, Safadi FF, Libuda DE, Stephenson RC, Daluiski A, Lyons KM (2003) Connective tissue growth factor coordinates chondrogenesis and angiogenesis during skeletal development. Development 130:2779–2791
Kawaki H, Kubota S, Suzuki A, Lazar N, Yamada T, Matsumura T, Ohgawara T, Maeda T, Perbal B, Lyons KM, Takigawa M (2008) Cooperative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by CCN2 and CCN3 shown by a comprehensive analysis of the CCN family proteins in cartilage. J Bone Miner Res 23:1751–1764
Leask A (2007) CCN3: a novel function in vivo. J Cell Commun Signal 1:227–228
Leask A (2009) Yin and Yang: CCN3 inhibits the pro-fibrotic effects of CCN2. J Cell Commun Signal 3:161–162
Leask A, Abraham DJ (2006) All in the CCN family. J Cell Science 119:4803–4810
Mo FE, Muntean AG, Chen CC, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Lau LF (2002) CYR61 (CCN1) is essential for placental development and vascular integrity. Mol Cell Biol 22:8709–8720
Perbal B (2007) CCN3-mutant mice are distinct from CCN3-null mice. J Cell Commun Signal 1:229–230
Perbal B (2008) CCN3: doctor Jekyll and mister Hyde. J Cell Commun Signal 2:3–7
Riser BL, Najmabadi F, Perbal B, Peterson DR, Rambow JA, Riser ML, Sukowski E, Yeger H, Riser SC (2009) CCN3 (NOV) is a negative regulator of CCN2 (CTGF) and a novel endogenous inhibitor of the fibrotic pathway in an in vitro model of renal disease. Am J Pathol 174:1725–1734
Shimoyama S, Hiraoka S, Takemoto M, Koshizaka M, Tokuyama H, Tokuyama T, Watanabe A, Fujimoto M, Kawamura H, Sato S, Tsurutani Y, Saito Y, Perbal B, Koseki H, Yokote K (2010) CCN3 inhibits neointimal hyperplasia through modulation of smooth muscle cell growth and migration, in press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leask, A. It’s a knockout: CCN3 suppresses neointimal thickening. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 4, 109–110 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0086-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0086-y