Abstract
Background
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) class I and IIa are highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and associated with decreased survival. However, clinically used pan and class I inhibitors have serious adverse events. In this study, we assessed the antitumor effects and tolerability of class IIa HDAC inhibitor (HDACI) with lenvatinib, which is a standard therapy for HCC.
Methods and result
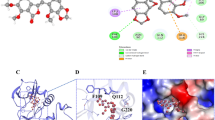
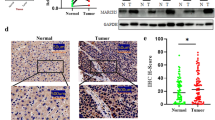
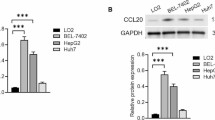
Combination therapy with class IIa HDACI and lenvatinib exerted synergistic antitumor effect in human HCC cell lines. In mouse models, this therapy showed significant antitumor effects, and few adverse events occurred. In immunoblotting, the expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) and fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) was high in cell lines that showed a high antitumor effect. In addition, class IIa HDACI administration decreased the expression of FGFR4. In the small interfering RNA (siRNA) analysis, knockdown of HDAC9, which is an isoform of HDAC class IIa, reduced the expression of FGFR4 and induced apoptosis. Immunohistochemistry of human clinical specimens showed a positivity rate of 32% for FGFR4 and 84% for HDAC9 in HCC, and all FGFR4-positive patients were HDAC9 positive.
Conclusion
Class IIa HDACI and lenvatinib combination therapy induces apoptosis by downregulating FGFR4 and blocking the FGFR signaling in FGFR4-positive HCC cell lines and has demonstrated synergistic antitumor effects and safety. This combination therapy overcomes the problems of conventional therapies and will be beneficial for FGFR4-positive HCC patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- ORR:
-
Objective response rate
- MKI:
-
Multi-kinase inhibitor
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HDACI:
-
HDAC inhibitor
- IVIS:
-
In vivo bioluminescence imaging system
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- FGFR:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
References
Yeo W, Mok TS, Zee B, Leung TW, Lai PB, Lau WY, et al. A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(20):1532–1538
Song R, Song H, Liang Y, Yin D, Zhang H, Zheng T, et al. Reciprocal activation between ATPase inhibitory factor 1 and NF-kappaB drives hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis and metastasis. Hepatology. 2014;60(5):1659–1673
Galle PR, Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Zhu AX, Kim TY, et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (IMbrave150): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(7):991–1001
Wada T, Kikuchi J, Nishimura N, Shimizu R, Kitamura T, Furukawa Y. Expression levels of histone deacetylases determine the cell fate of hematopoietic progenitors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(44):30673–30683
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5(9):769–784
Freese K, Seitz T, Dietrich P, Lee SML, Thasler WE, Bosserhoff A, et al. Histone deacetylase expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma and functional effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on liver cancer cells in vitro. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10):1587
Richon VM, Sandhoff TW, Rifkind RA, Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitor selectively induces p21WAF1 expression and gene-associated histone acetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(18):10014–10019
Maruyama D, Tobinai K, Ogura M, Uchida T, Hatake K, Taniwaki M, et al. Romidepsin in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a phase I/II and pharmacokinetics study. Int J Hematol. 2017;106(5):655–665
Lahm A, Paolini C, Pallaoro M, Nardi MC, Jones P, Neddermann P, et al. Unraveling the hidden catalytic activity of vertebrate class IIa histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(44):17335–17340
Kaletsch A, Pinkerneil M, Hoffmann MJ, Jaguva Vasudevan AA, Wang C, Hansen FK, et al. Effects of novel HDAC inhibitors on urothelial carcinoma cells. Clin Epigenetics. 2018;10(1):100
Kikuchi S, Suzuki R, Ohguchi H, Yoshida Y, Lu D, Cottini F, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell death in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2015;29(9):1918–1927
Ozaki K, Kosugi M, Baba N, Fujio K, Sakamoto T, Kimura S, et al. Blockade of the ERK or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway enhances the cytotoxicity of histone deacetylase inhibitors in tumor cells resistant to gefitinib or imatinib. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391(4):1610–1615
Tsujioka T, Sasaki D, Takeda A, Harashima H, Yamada Y. Resveratrol-encapsulated mitochondria-targeting liposome enhances mitochondrial respiratory capacity in myocardial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):112
Ogasawara S, Mihara Y, Kondo R, Kusano H, Akiba J, Yano H. Antiproliferative effect of lenvatinib on human liver cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2019;39(11):5973–5982
Guerriero JL, Sotayo A, Ponichtera HE, Castrillon JA, Pourzia AL, Schad S, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition reduces breast tumours and metastases through anti-tumour macrophages. Nature. 2017;543(7645):428–432
Iijima K, Nakamura H, Takada K, Hayasaka N, Kubo T, Umeyama Y, et al. Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 accelerates cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc in liver cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2021;22(1):546
Yamauchi M, Ono A, Ishikawa A, Kodama K, Uchikawa S, Hatooka H, et al. Tumor fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 level predicts the efficacy of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020;11(5): e00179
Gregoire S, Yang XJ. Association with class IIa histone deacetylases upregulates the sumoylation of MEF2 transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(6):2273–2287
Tao Z, Cui Y, Xu X, Han T. FGFR redundancy limits the efficacy of FGFR4-selective inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119(40): e2208844119
Stott AJ, Maillard MC, Beaumont V, Allcock D, Aziz O, Borchers AH, et al. Evaluation of 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole-based class IIa HDAC inhibitors for huntington’s disease. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021;12(3):380–388
Lobera M, Madauss KP, Pohlhaus DT, Wright QG, Trocha M, Schmidt DR, et al. Selective class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition via a nonchelating zinc-binding group. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(5):319–325
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(10):981–989
Hagel M, Miduturu C, Sheets M, Rubin N, Weng W, Stransky N, et al. First selective small molecule inhibitor of FGFR4 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas with an activated FGFR4 signaling pathway. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(4):424–437
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank for Michitoshi Kimura and Mami Yamaguchi (Biomedical Research Center Division of Morphological Research, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan) their technical assistance in immunohistochemical determination.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K07914.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM, TK, KH, and TO: conceptualization, design, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, visualization, writing—original draft. ST, HO, KM, KT, MN, YK, TM, IT, and JK: investigation, resources, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
All mouse experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine (number of ethics approvals 20–100) and followed national guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, R., Miyanishi, K., Kubo, T. et al. Synergistic antitumor effect of histone deacetylase class IIa inhibitor with lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 17, 735–744 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-023-10484-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-023-10484-2