Abstract
Background and aims
Patients with cirrhosis have high prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED). The aim of this study was to study the efficacy and safety of tadalafil for ED in patients with cirrhosis.
Methods
140 cirrhotic males with ED were randomized into tadalafil 10 mg daily (n = 70) or placebo (n = 70) for 12 weeks. ED was diagnosed if erectile function (EF) domain score was < 25 in International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) questionnaire. The erectile function domain consists of six questions concerning erection frequency, erection firmness, frequency of partner penetration, frequency of maintaining erection after penetration, ability to maintain erection to completion of intercourse and confidence in achieving and maintaining erection. Primary outcome was proportion of patients having an increase in > 5 points in EF domain of the IIEF. Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7) questionnaire was used for screening and severity measuring of GAD. The presence of depression was screened using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and the assessment of health related quality of life was done using the Short Form (36) Health Survey.
Results
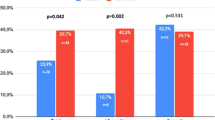
At the end of 12 weeks, more patients in tadalafil group achieved > 5 points increase in the EF domain of the IIEF when compared with the placebo group [44(62.9%) vs. 21(30%), p < 0.001]. At the end of 12 weeks, patients receiving tadalafil had significantly more change in scores on the erectile function domain, orgasmic function domain, intercourse satisfaction domain, overall satisfaction domain, erection vaginal penetration rates and successful intercourse; significantly more decline in the GAD-7 and PHQ-9 scores; significantly more improvement in scores of five of the eight domains of SF-36 (general health perception, vitality score, social functioning, role emotional and mental health) and the mental component summary rates when compared with placebo. The development of side effects and the changes in HVPG were not significantly different between the two groups.
Conclusions
Tadalafil therapy may enhance erectile function, improve anxiety, depression and quality of life; and is well tolerated by men with cirrhosis (CTP score < 10) and ED. However, further larger and long-term studies are needed to confirm these results and look for rarer side effects of using tadalafil in patients with cirrhosis.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier number NCT03566914; first posted date: June 25, 2018.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data transparency
All data, materials and software applications support the published claims and comply with field standards.
Abbreviations
- ASMI:
-
Appendicular skeletal muscle mass index
- DEXA:
-
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
- ED:
-
Erectile dysfunction
- GAD:
-
Generalized anxiety disorder
- IIEF:
-
International index of erectile function
- q ADAM:
-
Quantitative androgen deficiency in the aging male questionnaire
- PHQ:
-
Patient health questionnaire
- SEP:
-
Sexual encounter profile
References
Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 2013;381:153–165
Thakur J, Rathi S, Grover S, Chopra M, Agrawal S, Taneja S, et al. Tadalafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, improves erectile dysfunction in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2019;9(3):312–317
Maimone S, Saffioti F, Oliva G, Di Benedetto A, Alibrandi A, Filomia R, et al. Erectile dysfunction in compensated liver cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis 2019;51(6):843–849
Paternostro R, Heinisch BB, Reiberger T, Mandorfer M, Schwarzer R, Seeland B, et al. Erectile dysfunction in cirrhosis is impacted by liver dysfunction, portal hypertension, diabetes and arterial hypertension. Liver Int 2018;38(8):1427–1436
Cornely CM, Schade RR, Van Thiel DH, Gavaler JS. Chronic advanced liver disease and impotence: cause and effect? Hepatology 1984;4(6):1227–1230
Toda K, Miwa Y, Kuriyama S, Fukushima H, Shiraki M, Murakami N, et al. Erectile dysfunction in patients with chronic viral liver disease: its relevance to protein malnutrition. J Gastroenterol 2005;40(9):894–900
Jensen SB, Gluud C. Sexual dysfunction in men with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. A comparative study. Liver 1985;5(2):94–100
Wang YJ, Wu JC, Lee SD, Tsai YT, Lo KJ. Gonadal dysfunction and changes in sex hormones in postnecrotic cirrhotic men: a matched study with alcoholic cirrhotic men. Hepatogastroenterology 1991;38(6):531–534
Simsek I, Aslan G, Akarsu M, Koseoglu H, Esen A. Assessment of sexual functions in patients with chronic liver disease. Int J Impot Res 2005;17(4):343–345
Huyghe E, Kamar N, Wagner F, Capietto AH, El-Kahwaji L, Muscari F, et al. Erectile dysfunction in end-stage liver disease men. J Sex Med 2009;6(5):1395–1401
Danoff A, Khan O, Wan DW, et al. Sexual dysfunction is highly prevalent among men with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and negatively impacts health-related quality of life. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:1235–1243
Grimm RH Jr, Grandits GA, Prineas RJ, McDonald RH, Lewis CE, Flack JM, et al. Long-term effects on sexual function of five antihypertensive drugs and nutritional hygienic treatment in hypertensive men and women. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study (TOMHS). Hypertension 1997;29(1 Pt 1):8–14
Litwin MS, Nied RJ, Dhanani N. Health-related quality of life in men with erectile dysfunction. J Gen Intern Med 1998;13:159–166
Liu Q, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. Erectile dysfunction and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med 2018;15:1073–1082
Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Amodio P, Salerno F, Merli M, Panella C, et al. Factors associated with poor health-related quality of life of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2001;120:170–178
Daugan A, Grondin P, Ruault C, et al. The discovery of tadalafil: a novel and highly selective PDE5 inhibitor. 1: 5,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo( 1’,5’: 1,6)pyrido(3,4-b)indole-1,3(2H)-dione analogues. J Med Chem 2003;46(21):4525–4532
Gupta M, Kovar A, Meibohm B. The clinical pharmacokinetics of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. J Clin Pharmacol 2005;45:987–1003
CIALIS (tadalafil) tablets Label–FDA. 2021. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs. Accessed 2 Jan 2018
Tzathas C, Christidou A, Ladas SD. Sildenafil (viagra) is a risk factor for acute variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:1856
Finley DS, Lugo B, Ridgway J, Teng W, Imagawa DK. Fatal variceal rupture after sildenafil use: report of a case. Curr Surg 2005;62:55–56
Tandon P, Inayat I, Tal M, Spector M, Shea M, Groszmann RJ, et al. Sildenafil has no effect on portal pressure but lowers arterial pressure in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;8(6):546–549
Clemmesen JO, Giraldi A, Ott P, Dalhoff K, Hansen BA, Larsen FS. Sildenafil does not influence hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients with cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14(40):6208–6212
Lee KC, Yang YY, Wang YW, Hou MC, Lee FY, Lin HC, et al. Acute administration of sildenafil enhances hepatic cyclic guanosine monophosphate production and reduces hepatic sinusoid resistance in cirrhotic patients. Hepatol Res 2008;38(12):1186–1193
Deibert P, Schumacher YO, Ruecker G, Opitz OG, Blum HE, Rössle M, et al. Effect of vardenafil, an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-5, on portal haemodynamics in normal and cirrhotic liver – results of a pilot study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;23(1):121–128
Kreisel W, Deibert P, Kupcinskas L, Sumskiene J, Appenrodt B, Roth S, et al. The phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor udenafil lowers portal pressure in compensated preascitic liver cirrhosis. A dose-finding phase-II-study. Dig Liver Dis 2015;47(2):144–150
Deibert P, Lazaro A, Stankovic Z, Schaffner D, Rössle M, Kreisel W. Beneficial long term effect of a phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor in cirrhotic portal hypertension: a case report with 8 years follow-up. World J Gastroenterol 2018;24(3):438–444
Andersson KE. PDE5 inhibitors - pharmacology and clinical applications 20 years after sildenafil discovery. Br J Pharmacol 2018;175(13):2554–2565
Cappelleri JC, Rosen RC, Smith MD, Mishra A, Osterloh IH. Diagnostic evaluation of the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function. Urology 1999;54:346
Karnofsky DA, Abelmann WH, Craver LF, Burchenal JH. The use of the nitrogen mustards in the palliative treatment of carcinoma–with particular reference to bronchogenic carcinoma. Cancer 1948;1(4):634–656
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile function. Urology 1997;49:822–830
Dogra PN, Saini AK, Seth A. Erectile dysfunction after anterior urethroplasty: a prospective analysis of incidence and probability of recovery–single-center experience. Urology 2011;78(1):78–81
Mohamed O, Freundlich RE, Dakik HK, Grober ED, Najari B, Lipshultz LI, et al. The quantitative ADAM questionnaire: a new tool in quantifying the severity of hypogonadism. Int J Impot Res 2010;22(1):20–24
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med 2006;166(10):1092–1097
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 2001;16(9):606–613
Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 1992;30:473–483
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 2019;70(1):172–193
Giusto M, Lattanzi B, Albanese C, Galtieri A, Farcomeni A, Giannelli V, et al. Sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis: the role of computed tomography scan for the assessment of muscle mass compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;27(3):328–334
Jaeschke R, Singer J, Guyatt GH. Measurement of health status. Ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference. Control Clin Trials 1989;10:407–415
Rosen RC, Allen KR, Ni X, Araujo AB. Minimal clinically important differences in the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function scale. Eur Urol 2011;60:1010–1016
de Sáenz TI, Anglin G, Knight JR, Emmick JT. Effects of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25(12):2159–2164
Kim KS, Jeong TY, Moon HS. Effect of daily tadalafil on reported outcomes in patients with erectile dysfunction and depressive symptoms: STROBE, a case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99(23): e20546
Choi JB, Cho KJ, Kim JC, Pae CU, Koh JS. An open-label, single-arm pilot study to evaluate the efficacy of daily low dose tadalafil on depression in patients with erectile dysfunction. Transl Androl Urol 2019;8(5):501–506
Kishi T, Yoshimura R, Ikuta T, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and major depressive disorder: evidence from meta-analyses. Front Psychiatry 2018;8:308
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 2007;81:294–330
Wang C, Zhang J, Lu Y, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor etazolate and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil via cyclic AMP or cyclic GMP signaling in mice. Metab Brain Dis 2014;29:673–682
Shim YS, Pae CU, Cho KJ, et al. Effects of daily low-dose treatment with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor on cognition, depression, somatization and erectile function in patients with erectile dysfunction: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Impot Res 2014;26:76–80
Lee JG, Kim BD, Han CH, Lee KK, Yum KS. Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of a daily dose of 5 mg of tadalafil, over an 8-week period, for improving quality of life among Korean men with andropause symptoms, including erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97(51): e13827
Rubio-Aurioles E, Kim ED, Rosen RC, et al. Impact on erectile function and sexual quality of life of couples: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of tadalafil taken once daily. J Sex Med 2009;6:1314–1323
Giuliano F, Peña BM, Mishra A, Smith MD. Efficacy results and quality-of-life measures in men receiving sildenafil citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Qual Life Res 2001;10(4):359–369
Sampson LJ, Hinton JM, Garland CJ. Evidence for expression and function of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-V) in rat resistance arteries. Br J Pharmacol 2001;132:13–17
Colle I, De Vriese AS, Van Vlierberghe H, Lameire NH, DeVos M. Systemic and splanchnic haemodynamic effects of sildenafil in an in vivo animal model of cirrhosis support for a risk in cirrhotic patients. Liver Int 2004;24:63–68
Wallis RM, Corbin JD, Francis SH, Ellis P. Tissue distribution of phosphodiesterase families and the effects of sildenafil on tissue cyclic nucleotides, platelet function, and the contractile responses of trabeculae carneae and aortic rings in vitro. Am J Cardiol 1999;83:3C-12C
Reichenberger F, Voswinckel R, Steveling E, Enke B, Kreckel A, Olschewski H, et al. Sildenafil treatment for portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2006;28:563–567
Hemnes AR, Robbins IM. Sildenafil monotherapy in portopulmonary hypertension can facilitate liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2009;15:15–19
Gough MS, White RJ. Sildenafil therapy is associated with improved hemodynamics in liver transplantation candidates with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Liver Transpl 2009;15:30–36
Fisher JH, Johnson SR, Chau C, Kron AT, Granton JT. Effectiveness of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor therapy for portopulmonary hypertension. Can Respir J 2015;22:42–46
Deibert P, Bremer H, Roessle M, Kurz-Schmieg AK, Kreisel W. PDE-5 inhibitors lower portal and pulmonary pressure in portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2007;29:220–221
Jevnikar M, Ebstein N, Jais X, Boucly A, Montani D, Humbert M, et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil in portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2018;52:050
Kalambokis GN, Kosta P, Pappas K, Tsianos EV. Haemodynamic and renal effects of tadalafil in patients with cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16(39):5009–5010
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernández-Viadel M, Rodrigo R, Montoliu C, Felipo V. Oral administration of sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 2005;41(2):299–306
Hellstrom WJ, Gittelman M, Jarow J, Steidle C, McMurray J, Talley D, et al. An evaluation of semen characteristics in men 45 years of age or older after daily dosing with tadalafil 20mg: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 9-month study. Eur Urol 2008;53(5):1058–1065
Neong SF, Billington EO, Congly SE. Sexual dysfunction and sex hormone abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis: review of pathogenesis and management. Hepatology 2019;69(6):2683–2695
Washington SL 3rd, Shindel AW. A once-daily dose of tadalafil for erectile dysfunction: compliance and efficacy. Drug Des Dev Ther 2010;7(4):159–171
Park H, Jang IY, Han M, Lee H, Jung HW, Lee E, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with severe erectile dysfunction in older adults: a population-based cohort study. Korean J Intern Med 2020;35(5):1245–1253
Ucak S, Sivritepe R, Kara O, et al. Association between sarcopenia and erectile dysfunction in males with type II diabetes mellitus. Aging Male 2019;22:20–27
Gluud C, Wantzin P, Eriksen J. No effect of oral testosterone treatment on sexual dysfunction in alcoholic cirrhotic men. Gastroenterology 1988;95:1582–1587
Sinclair M, Grossmann M, Hoermann R, Angus PW, Gow PJ. Testosterone therapy increases muscle mass in men with cirrhosis and low testosterone: a randomised controlled trial. J Hepatol 2016;65:906–913
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Mr. Sandip Kumar from the information technology department of the Institute of Liver and Biliary sciences, for generating the allocation sequence on computer.
Funding
No funding was taken from any pharmaceutical company and funding was done by the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences research fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RKJ, MK and SKS developed the protocol. RKJ, MK and AB enrolled participants in the study. SMS, AK, JB, RM, AJ, AC, VR and VA reviewed and provided inputs to the protocol and manuscript. Guresh Kumar helped with statistical analysis and protocol development.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Rakesh Kumar Jagdish, Ahmed Kamaal, Saggere Muralikrishna Shasthry, Jaya Benjamin, Rakhi Maiwall, Ankur Jindal, Ashok Choudhary, Vijayaraghavan Rajan, Vinod Arora, Ankit Bhardwaj, Guresh Kumar, Manoj Kumar, Shiv K. Sarin have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval and registration
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences, New Delhi, India, where the study was conducted (Institutional ethical committee number: IEC/2018/60/MA04and the trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov with identifier number: NCT03566914.
Informed consent to participate and publish
Informed consent was taken from the participants and the work was done in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagdish, R.K., Kamaal, A., Shasthry, S.M. et al. Tadalafil improves erectile dysfunction and quality of life in men with cirrhosis: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. Hepatol Int 17, 434–451 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10264-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10264-w