Abstract
Background and objective
Cytokines have been reported to be involved in the cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Many aspects on the correlation between minimal HE (MHE) and cytokine levels were still unclear.
Methods
Two hundred eighty-nine HBV-infected cirrhotic patients were grouped: non MHE (n = 156), MHE (n = 98) and clinical HE (CHE, n = 213). Another 88 healthy volunteers were included as controls. Clinical and laboratory findings and levels of ten serum cytokines were analyzed.
Results
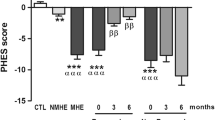
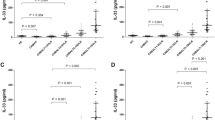
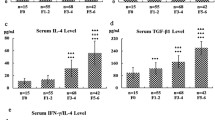
All tested cytokines were significantly elevated in cirrhotic patients and patients with CHE compared with controls. Statistical analysis showed only IL-6, IFNγ and IL-17a were correlated MHE (all three p < 0.001). Multivariate regression analysis indicated that serum IL-6 and IL-17a levels were independent risk factors for MHE. Moreover, all patients with MHE had IL-17a levels higher than 49 pg/mL, whereas those without MHE had IL-17a levels lower than 49 pg/mL.
Conclusions
IL-6, IFNγ, and IL-17a were correlated with MHE in HBV-infected patients. Two independent risk factors (IL-6, IL-17a) for MHE were identified. Our findings pointed out the crucial roles of cytokines in MHE in HBV-infected patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- MHE:
-
Minimal hepatic encephalopathy
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- CHE:
-
Clinical hepatic encephalopathy
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSF:
-
Cerebral spinal fluid
- PHES:
-
Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score
- GLU:
-
Blood glucose
- LYM:
-
Percentage of lymphocytes
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- CL:
-
Blood chlorine
- WBC:
-
White blood cell counts
- CK:
-
Creatine kinase
- CK-MB:
-
Creatine kinase-MB
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
References
Bustamante J, Rimola A, Ventura PJ, Navasa M, Cirera I, Reggiardo V, et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 1999;30(5):890–895
Hui AY, Chan HL, Leung NW, Hung LC, Chan FK, Sung JJ. Survival and prognostic indicators in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis after onset of hepatic decompensation. J Clin Gastroenterol 2002;34(5):569–572
Romero-Gomez M, Boza F, Garcia-Valdecasas MS, Garcia E, Aguilar-Reina J. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy predicts the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96(9):2718–2723
Das A, Dhiman RK, Saraswat VA, Verma M, Naik SR. Prevalence and natural history of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001;16(5):531–535
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002;35(3):716–721
Amodio P, Montagnese S, Gatta A, Morgan MY. Characteristics of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2004;19(3–4):253–267
Li SW, Wang K, Yu YQ, Wang HB, Li YH, Xu JM. Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score for diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in China. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19(46):8745–8751
Ban E, Milon G, Prudhomme N, Fillion G, Haour F. Receptors for interleukin-1 (alpha and beta) in mouse brain: mapping and neuronal localization in hippocampus. Neuroscience 1991;43(1):21–30
Rezaie P, Trillo-Pazos G, Everall IP, Male DK. Expression of beta-chemokines and chemokine receptors in human fetal astrocyte and microglial co-cultures: potential role of chemokines in the developing CNS. Glia 2002;37(1):64–75
Lee YB, Nagai A, Kim SU. Cytokines, chemokines, and cytokine receptors in human microglia. J Neurosci Res 2002;69(1):94–103
Montoliu C, Piedrafita B, Serra MA, del Olmo JA, Urios A, Rodrigo JM, et al. IL-6 and IL-18 in blood may discriminate cirrhotic patients with and without minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43(3):272–279
Bemeur C, Qu H, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF. IL-1 or TNF receptor gene deletion delays onset of encephalopathy and attenuates brain edema in experimental acute liver failure. Neurochem Int 2010;56(2):213–215
Onal IK, Akdogan M, Oztas E, Balci M, Kurt M, Kacar S, et al. Does interleukin-18 play a role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy? Hepatogastroenterology 2011;58(106):497–502
Yang YY. Can serum cytokines predict hepatic cytokine expression in liver cirrhosis? J Chin Med Assoc 2011;74(11):485–486
Cheng KS, Tang HL, Chou FT, Chou JW, Hsu CH, Yu CJ, et al. Cytokine evaluation in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2009;56(93):1105–1110
Li W, Henderson LJ, Major EO, Al-Harthi L. IFN-gamma mediates enhancement of HIV replication in astrocytes by inducing an antagonist of the beta-catenin pathway (DKK1) in a STAT 3-dependent manner. J Immunol 2011;186(12):6771–6778
Luo M, Li L, Yang EN, Dai CY, Liang SR, Cao WK. Correlation between interleukin-6 and ammonia in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy due to cirrhosis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2013;37(4):384–390
Luo M, Li L, Yang EN, Cao WK. Relationship between interleukin-6 and ammonia in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy due to liver cirrhosis. Hepatol Res 2012;42(12):1202–1210
Wang W, Li W, Yang X, Zhang T, Wang Y, Zhong R, et al. Interleukin-8 is elevated in severe hand, foot, and mouth disease. J Infect Dev Ctries 2014;8(1):94–100
Wang W, Zhu Y, Wu H, Jiao Y, Van Halm-Lutterodt N, Li W. IL-6 and IFNgamma are elevated in severe mumps cases: a study of 960 mumps patients in China. J Infect Dev Ctries 2014;8(2):208–214
Spangelo BL, Gorospe WC. Role of the cytokines in the neuroendocrine-immune system axis. Front Neuroendocrinol 1995;16(1):1–22
Bauer S, Cepok S, Todorova-Rudolph A, Nowak M, Koller M, Lorenz R, et al. Etiology and site of temporal lobe epilepsy influence postictal cytokine release. Epilepsy Res 2009;86(1):82–88
Woodroofe MN, Sarna GS, Wadhwa M, Hayes GM, Loughlin AJ, Tinker A, et al. Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol 1991;33(3):227–236
Frei K, Leist TP, Meager A, Gallo P, Leppert D, Zinkernagel RM, et al. Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med 1988;168(1):449–453
Montes M, Zhang X, Berthelot L, Laplaud DA, Brouard S, Jin J, et al. Oligoclonal myelin-reactive T-cell infiltrates derived from multiple sclerosis lesions are enriched in Th17 cells. Clin Immunol 2009;130(2):133–144
Mao LY, Ding J, Peng WF, Ma Y, Zhang YH, Fan W, et al. Interictal interleukin-17A levels are elevated and correlate with seizure severity of epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 2013;54(9):e142–e145
Tarantino G, Costantini S, Finelli C, Capone F, Guerriero E, La Sala N, et al. Is serum interleukin-17 associated with early atherosclerosis in obese patients? J Transl Med 2014;12:214
Simon T, Taleb S, Danchin N, Laurans L, Rousseau B, Cattan S, et al. Circulating levels of interleukin-17 and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2013;34(8):570–577
Danzaki K, Matsui Y, Ikesue M, Ohta D, Ito K, Kanayama M, et al. Interleukin-17A deficiency accelerates unstable atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012;32(2):273–280
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the China’s 12th Five-Year Major Project on the prevention and treatment of AIDS, viral hepatitis and other infectious diseases (2014ZX10001002-001-002), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7132077) and the National Natural Science Foundation (81371332). We also thank the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding Support (ZY201401) and the Beijing Key Laboratory of HIV/AIDS research (BZ0089) for financial support to this work. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. None of the information in this manuscript has been presented in any meeting or conference. The authors have declared no commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethical requirements and Conflict of interest
Wei Li, Ning Li, Rui Wang, Qunhui Li and Hao Wu declare that they have no conflict of interest. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. The Beijing Youan Hospital Ethics Committee approved the study, and all involved patients gave written informed consent for their clinical data and samples (blood, serum) to be used in this study. Human experimentation guidelines of P.R.China were followed in the conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Li, N., Wang, R. et al. Interferon gamma, interleukin-6, and -17a levels were correlated with minimal hepatic encephalopathy in HBV patients. Hepatol Int 9, 218–223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9610-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9610-8