Abstract
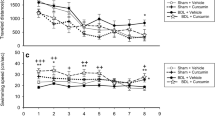
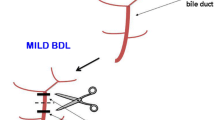
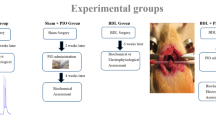
Background Defective learning/memory ability is a feature of MHE. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanisms leading to the impairment of learning/memory ability in MHE remain not clearly understood. Methods MHE rat modeling by intraperitoneal injection of TAA was successfully established using a Morris water maze, BAEP, and EEG tests. COMT inhibitor, a protein involved in the accumulation of dopamine (DA), was found to be up-regulated in cirrhotic livers in MHE by 2-DE/MS. Results The levels of DA in cirrhotic livers, serums and hippocampuses in the MHE group were more significantly increased than in the control group. In the hippocampuses of MHE rats, NMDA-induced formation of cGMP was reduced by 40 % as determined by in vivo brain microdialysis. Activation of sGC by NO was reduced by 38 %. The expression of NMDAR1, CaM, nNOS and sGC in the hippocampus in the MHE group were more significantly decreased than in controls. Chronic exposure of cultured hippocampus neurons to DA (50 μM) reduced by 53 % the NMDA-induced formation of cGMP. Activation of sGC by NO in these neurons was reduced by 44 %. Down-regulated NMDAR1, CaM, nNOS and sGC were also detected in neurons treated with dopamine, in contrast with the controls. Conclusions This study suggests that when the glutamate-NO-cGMP pathway in the hippocampus is inhibited by the elevation of DA from cirrhotic livers, this in turn may lead to the impairment of learning and memory ability of MHE.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhiman RK, Chawla YK. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2009;28(1):5–16
Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Chawla YK, Sharma A, Agarwal R. Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2007;45(3):549–559
Quero JC, Schalm SW. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Semin Liver Dis. 1996;16(3):321–328
Romero-Gómez M, Boza F, García-Valdecasas MS, García E, Aguilar-Reina J. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy predicts the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(9):2718–2723
Groeneweg M, Quero JC, De Bruijn I, Hartmann IJ, Essink-bot ML, Hop WC, Schalm SW. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy impairs daily functioning. Hepatology. 1998;28(1):45–49
Tan HH, Lee GH, Thia KT, Ng HS, Chow WC, Lui HF. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy runs a fluctuating course: results from a three-year prospective cohort follow-up study. Singapore Med J. 2009;50(3):255–260
Amodio P, Montagnese S, Gatta A, Morgan MY. Characteristics of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2004;19(3–4):253–267
Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Marchetti P, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, Caregaro L, Merkel C, Gerunda G, Gatta A. Clinical features and survival of cirrhotic patients with subclinical cognitive alterations detected by the number connection test and computerized psychometric tests. Hepatology. 1999;29(6):1662–1667
Hartmann IJ, Groeneweg M, Quero JC, Beijeman SJ, de Man RA, Hop WC, Schalm SW. The prognostic significance of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(8):2029–2034
Romero-Gómez M, Grande L, Camacho I. Prognostic value of altered oral glutamine challenge in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2004;39(4):939–943
Butterworth RF. Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: a new look at ammonia. Metab Brain Dis. 2002;17(4):221–227
Vaquero J, Chung C, Blei AT. Brain edema in acute liver failure. A window to the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Hepatol. 2003;2(1):12–22
Rama Rao KV, Reddy PV, Hazell AS, Norenberg MD. Manganese induces cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. Neurotoxicology. 2007;28(4):807–812
Das K, Singh P, Chawla Y, Duseja A, Dhiman RK, Suri S. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain in patients with cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(10):2793–2798
Shawcross DL, Wright G, Olde Damink SW, Jalan R. Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2007;22(1):125–138
Bernabeu R, Schmitz P, Faillace MP, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. Hippocampal cGMP and cAMP are differentially involved in memory processing of inhibitory avoidance learning. Neuroreport. 1996;7(2):585–588
Bernabeu R, Schroder N, Quevedo J, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. Further evidence for the involvement of a hippocampal cGMP/cGMP-dependent protein kinase cascade in memory consolidation. Neuroreport. 1997;8(9–10):2221–2224
Yamada K, Hiramatsu M, Noda Y, Mamiya T, Murai M, Kameyama T, Komori Y, Nikai T, Sugihara H, Nabeshima T. Role of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in the dizocilpine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behavior in mice. Neuroscience. 1996;74(2):365–374
Weissenborn K, Heidenreich S, Giewekemeyer K, Rückert N, Hecker H. Memory function in early hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2003;39(3):320–325
Monfort P, Corbalán R, Martinez L, López-Talavera J, Córdoba J, Felipo V. Altered content and modulation of soluble guanylate cyclase in the cerebellum of rats with portacaval anastomosis. Neuroscience. 2001;104(4):1119–1125
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernández-Viadel M, Rodrigo R, Montoliu C, Felipo V. Oral administration of sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology. 2005;41(2):299–306
Simpson GV, Knight RT, Brailowsky S, Prospero-Garcia O, Scabini D. Altered peripheral and brainstem auditory function in aged rats. Brain Res. 1985;348(1):28–35
Li C, Xiao Z, Chen Z, Zhang X, Li J, Wu X, Li X, Yi H, Li M, Zhu G, Liang S. Proteome analysis of human lung squamous carcinoma. Proteomics. 2006;6(2):547–558
Li C, Wang W, Wang H, Zhong Y, Di J, Lin Y. Proteomic analysis of proteins differentially expressed in uterine lymphocytes obtained from wild-type and NOD mice. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(2):447–457
Colado MI, Ormazabal MJ, Alfaro MJ, Martin MI. Effect of Bay K 8644 on the synthesis and metabolism of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in various brain areas of the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993;45(3):220–222
Yi Z, Petralia RS, Fu Z, Swanwick CC, Wang YX, Prybylowski K, Sans N, Vicini S, Wenthold RJ. The role of the PDZ protein GIPC in regulating NMDA receptor trafficking. J Neurosci. 2007;27(43):11663–11675
Marini AM, Paul SM. N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells requires new RNA and protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89(14):6555–6559
Morris RG, Garrud P, Rawlins JN, O’Keefe J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature. 1982;297(5868):681–683
Morris RG, Hagan JJ, Rawlins JN. Allocentric spatial learning by hippocampectomised rats: a further test of the “spatial mapping” and “working memory” theories of hippocampal function. Q J Exp Psychol B. 1986;38(4):365–395
Packard MG, Teather LA. Posttraining injections of MK-801 produce a time-dependent impairment of memory in two water maze tasks. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1997;68(1):42–50
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP. Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001;36(1):60–90
Mehndiratta MM, Sood GK, Sarin SK, Gupta M. Comparative evaluation of visual, somatosensory, and auditory evoked potentials in the detection of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in patients with nonalcoholic cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990;85(7):799–803
Boulton CL, Southam E, Garthwaite J. Nitric oxide-dependent long-term potentiation is blocked by a specific inhibitor of soluble guanylyl cyclase. Neuroscience. 1995;69(3):699–703
Hawkins RD, Son H, Arancio O. Nitric oxide as a retrograde messenger during long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Prog Brain Res. 1998;118:155–172
Chen J, Zhang S, Zuo P, Tang L. Memory-related changes of nitric oxide synthase activity and nitrite level in rat brain. Neuroreport. 1997;8(7):1771–1774
Danysz W, Zajaczkowski W, Parsons CG. Modulation of learning processes by ionotropic glutamate receptor ligands. Behav Pharmacol. 1995;6(5 And 6):455–474
Ingram DK, Spangler EL, Kametani H, Meyer RC, London ED. Intracerebroventricular injection of N-omega-nitro-l-arginine in rats impairs learning in a 14-unit T-maze. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;341(1):11–16
Meyer RC, Knox J, Purwin DA, Spangler EL, Ingram DK. Combined stimulation of the glycine and polyamine sites of the NMDA receptor attenuates NMDA blockade-induced learning deficits of rats in a 14-unit T-maze. Psychopharmacology. 1998;135(3):290–295
Prickaerts J, Steinbusch HW, Smits JF, de Vente J. Possible role of nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway in object recognition memory: effects of 7-nitroindazole and zaprinast. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997;337(2–3):125–136
Zou LB, Yamada K, Nabeshima T. Sigma receptor ligands (+)-SKF10,047 and SA4503 improve dizocilpine-induced spatial memory deficits in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;355(1):1–10
Córdoba J, Cabrera J, Lataif L, Penev P, Zee P, Blei AT. High prevalence of sleep disturbance in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27(2):339–345
Garfinkel D, Zisapel N. Liver cirrhosis and circadian rhythm. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125(2):154
O’Carroll RE, Hayes PC, Ebmeier KP, Dougall N, Murray C, Best JJ, Bouchier IA, Goodwin GM. Regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive function in patients with chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1991;337(8752):1250–1253
Pantiga C, Rodrigo LR, Cuesta M, Lopez L, Arias JL. Cognitive deficits in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and in liver transplant recipients. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;15(1):84–89
Hermenegildo C, Montoliu C, Llansola M, Muñoz MD, Gaztelu JM, Miñana MD, Felipo V. Chronic hyperammonemia impairs the glutamate-nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway in cerebellar neurons in culture and in the rat in vivo. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10(10):3201–3209
Corbalán R, Chatauret N, Behrends S, Butterworth RF, Felipo V. Region selective alterations of soluble guanylate cyclase content and modulation in brain of cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 2002;36(5):1155–1162
Moustafa AA, Herzallah MM, Gluck MA. Dissociating the cognitive effects of levodopa versus dopamine agonists in a neurocomputational model of learning in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2012;31:102–111
Castro NG, de Mello MC, de Mello FG, Aracava Y. Direct inhibition of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor channel by dopamine and (+)-SKF38393. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;126(8):1847–1855
Zheng P, Zhang XX, Bunney BS, Shi WX. Opposite modulation of cortical N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated responses by low and high concentrations of dopamine. Neuroscience. 1999;91(2):527–535
Seamans JK, Yang CR. The principal features and mechanisms of dopamine modulation in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neurobiol. 2004;74(1):1–58
Cui C, Xu M, Atzor M. Voltage-dependent block of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors by dopamine D1 receptor ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70(5):61–1770
Altar CA, Boyar WC, Kim HS. Discriminatory roles for D1 and D2 dopamine receptor subtypes in the in vivo control of neostriatal cyclic GMP. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;181(1–2):17–21
Di Stefano A, Sozio P, Cacciatore I, Cocco A, Giorgioni G, Costa B, Montali M, Lucacchini A, Martini C, Spoto G, Di Pietrantonio F, Di Matteo E, Pinnen F. Preparation and pharmacological characterization of trans-2-amino-5(6)-fluoro-6(5)-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indenes as D2-like dopamine receptor agonists. J Med Chem. 2005;48(7):2646–2654
Hoque KE, Indorkar RP, Sammut S, West AR. Impact of dopamine-glutamate interactions on striatal neuronal nitric oxide synthase activity. Psychopharmacology. 2010;207(4):571–581
Park DJ, West AR. Regulation of striatal nitric oxide synthesis by local dopamine and glutamate interactions. J Neurochem. 2009;111(6):1457–1465
Sammut S, Dec A, Mitchell D, Linardakis J, Ortiguela M, West AR. Phasic dopaminergic transmission increases NO efflux in the rat dorsal striatum via a neuronal NOS and a dopamine D(1/5) receptor-dependent mechanism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(3):493–505
Siuciak JA, McCarthy SA, Chapin DS, Fujiwara RA, James LC, Williams RD, Stock JL, McNeish JD, Strick CA, Menniti FS, Schmidt CJ. Genetic deletion of the striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase PDE10A: evidence for altered striatal function. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51(2):374–385
Calabresi P, Centonze D, Gubellini P, Marfia GA, Pisani A, Sancesario G, Bernardi G. Synaptic transmission in the striatum: from plasticity to neurodegeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;61(3):231–265
Centonze D, Gubellini P, Pisani A, Bernardi G, Calabresi P. Dopamine, acetylcholine and nitric oxide systems interact to induce corticostriatal synaptic plasticity. Rev Neurosci. 2003;14(3):207–216
Kawaguchi Y. Neostriatal cell subtypes and their functional roles. Neurosci Res. 1997;27(1):1–8
West AR, Grace AA. Opposite influences of endogenous dopamine D1 and D2 receptor activation on activity states and electrophysiological properties of striatal neurons: studies combining in vivo intracellular recordings and reverse microdialysis. J Neurosci. 2002;22(1):294–304
Galati S, D’angelo V, Scarnati E, Stanzione P, Martorana A, Procopio T, Sancesario G, Stefani A. In vivo electrophysiology of dopamine-denervated striatum: focus on the nitric oxide/cGMP signaling pathway. Synapse. 2008;62(6):409–420
Funding
This study was funded by science and technology plan projects of Wenzhou city (Y20110155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, S., Liu, L., Jing, H. et al. Dopamine from cirrhotic liver contributes to the impaired learning and memory ability of hippocampus in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatol Int 7, 923–936 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9431-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9431-6