Abstract
Purpose
The 2 reported trials investigated the effectiveness of treatment with peginterferon alfa-2a in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Methods
Patients with HBeAg-positive (n = 708) or HBeAg-negative (n = 332) CHB were enrolled in 2 randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled studies. Patients received peginterferon alfa-2a 180 μg once weekly, peginterferon plus lamivudine 100 mg per day, or lamivudine alone for 48 weeks. Patients were followed up at 6 and 12 months posttreatment.
Results
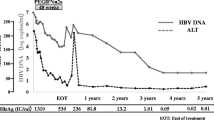
Peginterferon alfa-2a provided significantly higher rates of HBeAg seroconversion (31%) in HBeAg-positive patients than did lamivudine (19%, P = 0.005) 6 months posttreatment, irrespective of genotype. Of these, 83% achieving seroconversion during treatment or early posttreatment sustained their response at 12 months posttreatment. In patients who seroconverted, 69% maintained HBV DNA suppression at <10,000 copies/ml and alanine aminotrasferase (ALT) normalization. In HBeAg-negative patients, peginterferon produced a significantly higher combined response of HBV DNA at <20,000 copies/ml and ALT normalization (45%) than lamivudine (31%, P = 0.032), irrespective of genotype. Almost 80% of these patients sustained their response at 12 months posttreatment.
Conclusions
In conclusion, a finite course of peginterferon alfa-2a provides significant and sustained treatment benefit in Asian CHB patients, who have traditionally been regarded as difficult to treat.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merican I, Guan R, Amarapuka D, Alexander MJ, Chutaputti A, Chien RN, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Asian countries. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000;15:1356–61.
Yuen MF, Yuan HJ, Wong DK, Yuen JC, Wong WM, Chan AO, et al. Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications. Gut 2005;54:1610–4. Epub 2005 May 4.
Leung N. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: case selection and duration of therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002;17:409–14.
Craxì A, Di Bona D, Cammà C. Inteferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2003;39:S99–105.
Thomas HC, Lok AS, Carreno V, Farrell G, Tanno H, Perez V, et al., for The International Hepatitis Trial Group. Comparative study of three doses of interferon-alpha 2a in chronic active hepatitis B. J Viral Hepatol 1994;1:139–48.
Cooksley WG, Piratvisuth T, Lee SD, Mahachai V, Chao YC, Tanwandee T, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kDa): an advance in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepatol 2003;10:298–305.
Kao JH, Wu NH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Hepatitis B genotypes and the response to interferon therapy. J Hepatol 2000;33:998–1002.
Zhang X, Zoulim F, Habersetzer F, Xiong S, Trepo C. Analysis of hepatitis B virus genotypes and pre-core region variability during interferon treatment of HBe antigen negative chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol 1996;48:8–16.
Liaw YF, Leung N, Guan R, Lau GK, Merican I, McCaughan G, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2005 update. Liver Int 2005;25:472–89.
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update of recommendations. Hepatology 2004;39:857–61.
De Franchis R, Hadengue A, Lau G, Lavanchy D, Lok A, McIntyre N, et al. EASL International Consensus Conference on Hepatitis B. 13–14 September, 2002 Geneva, Switzerland. Consensus statement (long version). J Hepatol 2003;39:S3–25.
Niederau C, Heintges T, Lange S, Goldmann G, Niederau CM, Mohr L, et al. Long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with interferon alfa for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1422–7.
Fattovich G, Rugge M, Brollo L, Pontisso P, Noventa F, Guido M, et al. Clinical, virologic and histologic outcome following seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis type B. Hepatology 1986;6:167–72.
Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003;348:808–16.
Dienstag JL, Schiff ER, Wright TL, Perrillo RP, Hann HW, Goodman Z, et al. Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1256–63.
Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, et al., for the Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 1998;339:61–8.
Qi X, Snow A, Thibault V, et al. Long-term incidence of adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) resistance in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients after 144 weeks of therapy. J Hepatol 2004;40:A57.
Liaw YF. Results of lamivudine trials in Asia. J Hepatol 2003;39:S111–5.
Manesis EK, Hadziyannis SJ. Interferon alpha treatment and retreatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2001;121:101–9.
Oliveri F, Santantonio T, Bellati G, Colombatto P, Mels GC, Carriero L, et al. Long term response to therapy of chronic anti-HBe-positive hepatitis B is poor independent of type and schedule of interferon. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:1366–72.
Santantonio T, Mazzola M, Iacovazzi T, Miglietta A, Guastadisegni A, Pastore G. Long-term follow-up of patients with anti-HBe/HBV DNA-positive chronic hepatitis B treated for 12 months with lamivudine. J Hepatol 2000;32:300–6.
Tassopoulos NC, Volpes R, Pastore G, et al. Post lamivudine treatment follow up of patients with HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B [abstract]. J Hepatol 1999;30:117.
Reddy KR. Development and pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pegylated interferon alfa-2a (40 kD). Semin Liver Dis 2004;24:33–8.
Lin CC, Wu JC, Chang TT, Huang YH, Wang YJ, Tsay SH, et al. Long-term evaluation of recombinant interferon a2b in the treatment of patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative hepatitis B in Taiwan. J Viral Hepatol 2001;8:438–46.
Martin P, Han H-W, Westerberg S, Monoz SJ, Rubin R, Maddrey WC. Interferon -a2b therapy is efficacious in Asian-Americans with chronic hepatitis B infection. A prospective controlled trial. Dig Dis Sci 1998;43:875–9.
Janssen HL, Van Zonneveld M, Senturk H, Zeuzem S, Akarca US, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised trial. Lancet 2005;365:123–9.
Chan Hl, Leung NW, Hui AY, Wong VW, Liew CT, Chim AM, et al. A randomised, controlled trial of combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B: comparing pegylated interferon-alpha2b and lamivudine with lamivudine alone. Ann Intern Med 2005;142:240–50.
Bailon P, Palleroni A, Schaffer CA, Spence CL, Fung WJ, Porter JE, et al. Rational design of a potent, long-lasting form of interferon: a 40 kDa branched polyethylene glycol-conjugated interferon alpha-2a for the treatment of hepatitis C. Bioconjug Chem 2001;12:195–202.
Perry CM, Jarvis B. Peginterferon-alpha-2a (40 kD): a review of its use in the management of chronic hepatitis C. Drugs 2001;61:2263–88.
Marcellin P, Lau GK, Bonino F, Farci P, Hadziyannis S, Jin R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1206–17.
Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX, Marcellin P, Thongsawat S, Cooksley G, et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a, lamivudine, and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2005;352:2682–95.
Kessler HH, Pierer K, Dragon E, Lackner H, Santner B, Stunzner D, et al. Evaluation of a new assay for HBV DNA quantitation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Diagn Virol 1998;9:37–43.
Mahoney FJ. Update on diagnosis, management, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 1999;12:351–66.
Aggarwal R, Ranjan P. Preventing and treating hepatitis B infection. BMJ 2004;329:1080–86.
Chien RN, Yeh CT, Tsai SL, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Determinants for sustained HBeAg response to lamivudine therapy. Hepatology 2003;38:1267–73.
Lee KM, Cho SW, Kim SW, Kim HJ, Hahm KB, Kim JH. Effect of virological response on posttreatment durability of lamivudine-induced HBeAg seroconversion. J Viral Hepatol 2002;9:208–12.
Song BC, Suh DJ, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS. Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion after lamivudine therapy is not durable in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea. Hepatology 2000;32:803–6.
Zhao H, Si C-W, Wei L, Wan M-B, Ying Y-K, Hou J-L, et al. A multicenter, randomized, open-label study of peginterferon alpha-2b vs interferon alpha-2b for the treatment of Chinese patients with HBeAg+ve chronic Hepatitis B [abstract]. J Hepatol 2006;44 Suppl 2:S20.
Lai CL, Yuen MF. Profound suppression of hepatitis B virus replication with lamivudine. J Med Virol 2000;61:367–73.
Papatheodoridis GV, Hadziyannis SJ. Review article: current management of chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;19:25–37.
Lok AS, Heathcote EJ, Hoofnagle JH. Management of hepatitis B: 2000—summary of a workshop. Gastroenterology 2001;120:1828–53.
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2001;34:1225–41.
Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med 2004;350:1118–29.
Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV, Vassilopoulos D. Treatment of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Semin Liver Dis 2003;23:81–8.
Conjeevaram HS, Lok AS. Management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2003;38:S90–103.
Komori M, Yuki N, Nagaoka T, Yamashiro M, Mochizuki K, Kaneko A, et al. Long-term clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 2001;35:798–804.
Kuhns M, McNamara A, Mason A, Campbell C, Perrillo R. Serum and liver hepatitis B virus DNA in chronic hepatitis B after sustained loss of surface antigen. Gastroenterology 1992;103:1649–56.
Korenman J, Baker B, Waggoner J, Everhart JE, Di Bisceglie AM, Hoofnagle JH. Long-term remission of chronic hepatitis B after alpha-interferon therapy. Ann Intern Med 1991;114:629–34.
Papatheodoridis GV, Manesis E, Hadziyannis SJ. The long-term outcome of interferon-alpha treated and untreated patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2001;34:306–13.
Tassopoulos NC, Volpes R, Pastore G, Heathcote J, Buti M, Goldin RD, et al. for the Lamivudine Precore Mutant Study Group. Efficacy of lamivudine in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative/hepatitis B virus DNA-positive (precore mutant) chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 1999;29:889–96.
Donada C, Piva S, Faelli A, Mazzero C, Zantette G, Donadon V. Interferon alfa and lamivudine in patients with chronic anti-HBe positive hepatitis B. J Hepatol 1999;30:246.
Brunetto MR, Oliveri F, Coco B, Leandro G, Colombatto P, Gorin JM, Bonino F. Outcome of anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B in alpha-interferon treated and untreated patients: a long term cohort study. J Hepatol 2002;36:263–70.
Lin CC, Wu JC, Chang TT, Huang YH, Wang YJ, Tsay SH, et al. Long-term evaluation of recombinant interferon alpha2b in the treatment of patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Taiwan. J Viral Hepatol 2001;8:438–46.
Lampertico P, Del Ninno E, Manzin A, Donato MF, Rumi MG, Lunghi G, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of a 24-month course of interferon alfa 2b in patients with chronic hepatitis B who had hepatitis B virus DNA without hepatitis B e antigen in serum. Hepatology 1997;26:1621–5.
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, Kuo E, You SL, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus DNA level predicts the incidence of liver cirrhosis in persons chronically infected with HBV. J Hepatol 2005;42 Suppl 2:180.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006;295:65–73.
Acknowledgments
Editorial support for this manuscript has been gratefully provided by Peter Levantis of Wells Healthcare Communications, UK. This study was supported by a research grant from Roche, Basel, Switzerland.
Disclaimer: Prof. Piratvisuth has received reimbursement from Roche for speaking at symposia and undertaking clinical research, but he has no stock ownership, equity interest, or patent-licensing arrangement with Roche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piratvisuth, T., Lau, G., Chao, YC. et al. Sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a (40 kD) with or without lamivudine in Asian patients with HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Int 2, 102–110 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-007-9022-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-007-9022-5