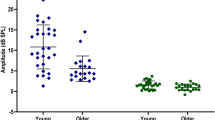
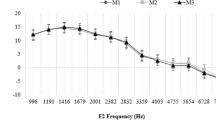
Abstract
This study aimed to assess the stability of Medial Olivocochlear Reflex (MOCR) function in typical hearing adults with the use of Contralateral Suppression (CS) of Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs). This study included fifty-three (90 ears) participants between the ages of 18–30. Participants were divided into 3 groups (Group A-daily stability, Group B-short-term stability, and Group C- long-term stability). For each group, 4 measurements (30 × 4 = 120sessions) were taken. Group A measurements were taken daily, Group B measurements were taken weekly and Group C measurements were taken monthly. DPOAEs and Contralateral Suppression of DPOAEs were measured for each group. Analyses indicated that Medial Olivocochlear Reflex (MOCR) measured through contralateral suppression of DPOAE was unstable. This result indicates a DPOAE-based measure of the MOCR was not repeated across time. A great deal has been learned using CS of DPOAEs to study medial efferent activation, but several unresolved methodological issues that could impact the data to produce poor stability across time. Those methodological issues need to be explored and researched in the future.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data not available due to [ethical/legal/commercial] restrictions. Due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly, so supporting data is not available.
References
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) (1992) Definitions of communication disorders and variation. ASHA 56(2):949–958
Bassim MK, Miller RL, Buss E, Smith DW (2003) Rapid adaptation of the 2f1–f2 DPOAE in humans: binaural and contralateral stimulation effects. Hear Res 182(1–2):140–152
Bhatt I (2017) Increased medial olivocochlear reflex strength in normal-hearing, noise-exposed humans. PLoS ONE 12(9):e0184036
de Boer J, Thornton ARD, Krumbholz K (2012) What is the role of the medial olivocochlear system in speech-in-noise processing? J Neurophysiol 107(5):1301–1312
Deeter R, Abel R, Calandruccio L, Dhar S (2009) Contralateral acoustic stimulation alters the magnitude and phase of distortion product otoacoustic emissions. J Acoust Soc Amer 126(5):2413–2424
Dreisbach LE, Long KM, Croze SC, Lees SE (2006) Repeatability of high-frequency distortion-product otoacoustic emissions in normal-hearing adults. Ear Hear 27(4):466–479
Jennings SG (2021) The role of the medial olivocochlear reflex in psychophysical masking and intensity resolution in humans: a review. J Neurophysiol 125(6):2279–2308
Kalaiah MK, Lasrado A, Pinto N, Shastri U (2018) Short term test-retest reliability of contralateral inhibition of distortion product otoacoustic emissions. J Audiol Otol 22(4):189
Kumar UA, Methi R, Avinash MC (2013) Test/retest re-peatability of effect contralateral acoustic stimulation on the magnitudes of distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Laryngoscope 123(2):463–471
Marrufo-Pérez MI, Johannesen PT, Lopez-Poveda EA (2021) Correlation and reliability of behavioral and otoacoustic-emission estimates of contralateral medial olivocochlear reflex strength in humans. Front Neurosci 15:640127
Mishra SK, Abdala C (2008) Considering distortion product otoacoustic emission fine structure in measurements of the medial olivocochlear reflex. J Acoust Soc Am 17(3):1584–1594
Mishra SK, Lutman ME (2013) Repeatability of click-evoked otoacoustic emission-based medial olivocochlear efferent assay. Ear Hear 97(4):789–798
Mishra SK, Abdala C (2015) Stability of the medial olivocochlear reflex as measured by distortion product otoacoustic emissions. J Speech Lang Hear Res 58(2):122–134
Otsuka S, Tsuzaki M, Sonoda J, Tanaka S, Furukawa S (2016) A role of medial olivocochlear reflex as a protection mechanism from noise-induced hearing loss revealed in short-practicing violinists. PLoS ONE 11(1):e0146751
Sun XM (2008) Distortion product otoacoustic emission fine structure is responsible for variability of distortion product otoacoustic emission contralateral suppression. J Acoust Soc Am 211(3):4310–4320
Wagner W, Heppelmann G, Vonthein R, Zenner HP (2008) Test-retest repeatability of distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Ear Hear 29(3):378–391
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruba, S., Panda, M.R. Short-Term and Long-Term Stability of Medial Olivocochlear Reflex in Adults with Typical Hearing. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75 (Suppl 1), 297–300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03448-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03448-9