Abstract
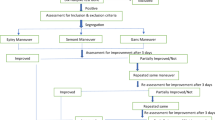
Patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) find it difficult to visit the hospital many times for a standard Epley’s maneuver performed only by a specialist. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of a home-based particle repositioning procedure (HBPRP) with the standard Epley’s maneuver in treating patients with posterior canal BPPV. A prospective non-blinded randomized controlled study was conducted. Patients were randomized into two groups, where one group received the standard treatment and other received a new HBPRP. The vertigo scale, duration of nystagmus during Dix-Hallpike test and frequency of vertigo, were documented on first, second and third visits, with complications noted during the second and third visits. These parameters were compared between both the groups following the treatment, during all visits. The patients were randomized into 2 arms with 15 each. Those belonging to group 1 received Epley’s maneuver and group 2 received HBPRP. There was no significant difference in the baseline characteristics of patients in both groups. Both groups of patients had significant improvement of symptoms at the end of the study. A comparison of both groups at 2nd and 3rd visits showed no differences in frequency of vertigo, reduction in vertigo scale and duration of nystagmus following Dix-Hallpike test between both groups. HBPRP is a safe and effective procedure and can be taught as a home-based treatment for patients diagnosed with posterior canal BPPV.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, Barrs D, Bronston LJ, Cass S et al (2008) Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139(5_supp):47–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.022
Froehling DA, Bowen JM, Mohr DN, Brey RH, Beatty CW, Wollan PC et al (2000) The canalith repositioning procedure for the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc 75(7):695–700. https://doi.org/10.4065/75.7.695
Parnes LS, Agrawal SK, Atlas J (2003) Diagnosis and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). CMAJ 169(7):681–693 (PMID: 14517129; PMCID: PMC202288)
von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F, Feldmann M, Ziese T, Lempert T et al (2006) Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(7):710–715. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.100420
Lynn S, Pool A, Rose D, Brey R, Suman V (1995) Randomized trial of the canalith repositioning procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113(6):712–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0194-5998(95)70010-2
Burton MJ, Eby TL, Rosenfeld RM (2012) Extracts from the cochrane library: modifications of the Epley (Canalith repositioning) maneuver for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147(3):407–411. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812457134
Gaur S, Awasthi SK, Bhadouriya SKS, Saxena R, Pathak VK, Bisht M (2015) Efficacy of Epley’s maneuver in treating BPPV patients: a prospective observational study. Int J Otolaryngol 2015:487160. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/487160
Moon SY, Kim JS, Kim B-K, Kim JI, Lee H, Son S-I et al (2006) Clinical characteristics of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Korea: a multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci 21(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.539
Nuti D, Mandalà M, Salerni L (2009) Lateral Canal Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Revisited. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1164(1):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03720.x
Yetiser D, Ince D (2015) Demographic analysis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo as a common public health problem. Ann Med Health Sci Res 5(1):50. https://doi.org/10.4103/2141-9248.149788
Hornibrook J (2011) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): history, pathophysiology, office treatment and future directions. Int J Otolaryngol 2011:835671. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/835671
Dix MR, Hallpike CS (1952) The pathology, symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Proc R Soc Med 45(6):341–354. https://doi.org/10.1177/003591575204500604
Davies RA, Luxon LM (1995) Dizziness following head injury: a neuro-otological study. J Neurol 242(4):222–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00919595
Balatsouras DG, Koukoutsis G, Aspris A, Fassolis A, Moukos A, Economou NC et al (2017) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to mild head trauma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 126(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489416674961
Balatsouras DG, Koukoutsis G, Ganelis P, Economou NC, Moukos A, Aspris A et al (2014) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(5):919–924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2484-2
Yetiser S (2020) Review of the pathology underlying benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Int Med Res 48(4):0300060519892370. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519892370
Martens C, Goplen FK, Aasen T, Gjestad R, Nordfalk KF, Nordahl SHG (2020) Treatment of horizontal canal BPPV—a randomized sham-controlled trial comparing two therapeutic maneuvers of different speeds. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 5(4):750–757. https://doi.org/10.1002/lio2.420
West N, Hansen S, Møller MN, Bloch SL, Klokker M (2016) Repositioning chairs in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: implications and clinical outcome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(3):573–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3583-z
Epley JM (1992) The canalith repositioning procedure: for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107(3):399–404. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989210700310
Semont A, Freyss G, Vitte E. Curing the BPPV with a Liberatory Maneuver. In: Barany Society, Pirodda E, editors. Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology [Internet]. S. Karger AG; 1988 [cited 2021 Aug 17]. p. 290–3. Available from: https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/416126. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000416126
Amor-Dorado JC, Barreira-Fernández MP, Aran-Gonzalez I, Casariego-Vales E, Llorca J, González-Gay MA (2012) Particle repositioning maneuver versus brandt-daroff exercise for treatment of unilateral idiopathic BPPV of the posterior semicircular canal: a randomized prospective clinical trial with short- and long-term outcome. Otol Neurotol 33(8):1401–1407. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e318268d50a
Prim-Espada MP, De Diego-Sastre JI, Pérez-Fernández E (2010) Meta-analysis on the efficacy of Epley’s manoeuvre in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurología (English Edition) 25(5):295–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2173-5808(10)70056-0
Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ, Zee DS, Proctor LR, Mattox DE (1993) Single treatment approaches to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119(4):450–454. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1993.01880160098015
Teixeira LJ, Machado JNP (2006) Maneuvers for the treatment of benign positional paroxysmal vertigo: a systematic review. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 72(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1808-8694(15)30046-x
Gans RE, Harrington-Gans PA (2002) Treatment efficacy of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) with canalith repositioning maneuver and semont liberatory maneuver in 376 patients. Semin Hear 23(2):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-33002
Helminski JO, Zee DS, Janssen I, Hain TC (2010) Effectiveness of particle repositioning maneuvers in the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review. Phys Ther 90(5):663–678. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20090071
Saberi A, Nemati S, Sabnan S, Mollahoseini F, Kazemnejad E (2017) A safe-repositioning maneuver for the management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Gans vs. Epley maneuver; a randomized comparative clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(8):2973–2979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4235-7
Foster CA, Ponnapan A, Zaccaro K, Strong D (2012) A comparison of two home exercises for benign positional vertigo: half somersault versus epley maneuver. Audiol Neurotol Extra 2(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1159/000337947
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the contributions from Dr. Tunny Sebastian in performing the statistical analysis for this study.
Funding
Limited funding was obtained from the institutional FLUID Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. AL conceptualised and designed the study. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Dr. RLR, Dr. AL, Dr. MDM and Mr. LV. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dr. RLR and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The Title Page manuscript has been read and approved by all authors, and the requirements for authorship have been met. Each author believes that the manuscript represents honest work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare, that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was conducted after obtaining approval from the institutional ethical committee and institutional review board (IRB No: 9642).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranju, R.L., Lepcha, A., Mammen, M.D. et al. An Effective Home-Based Particle Repositioning Procedure for Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74, 516–523 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-03021-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-03021-w