Abstract
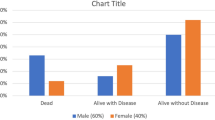
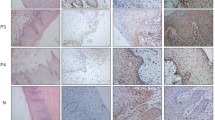
Cyclin D1 and p53 play an important role in tumorigenesis of human cancers. The present study aims to evaluate cyclin D1 and p53 expression in resectable OSCC, and to determine their prognostic significance at the end of 5 year follow-up: A total of 100 patients aged 31–74 years, stage 3/4 were recruited. Cyclin D1 and p53 expression in the tumour tissue was estimated by IHC and was statistically correlated with demographic and clinicopathological data and prognosis was evaluated at the end of 5 year outcome. The positive expression rate of cyclin D1 was 50% and p53 it was 40% and they neither showed any statistical significant correlation with each other nor with demographic or clinicopathological data. The OS was 32%.Negative and weak expression predicted better outcomes with regard to DFS and OS. DFS and OS were significantly worse in patients of overexpressed cyclin D1 (p < 0.001) and p53 (p = 0.008). Cyclin D1 is a better prognostic marker as compared to p53 for both DFS and OS. p53 expression (high versus low) for disease free non-survival and overall nonsurvival showed an OR of 3.576 (p = 0.003) and 8.803(p < 0.001) respectively for strong expression while in case of cyclin D1 it showed an OR of 13.067(p < 0.001) and 37.465(p < 0.001) for strong expression.So higher the level of expression of tumour markers higher is the odds ratio so poorer is the prognosis. Overexpression of cyclin D1 and p53 was significantly associated with poor prognosis in terms of DFS and OS




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kademani D (2007) Oral cancer. Mayo Clin Proc 82:878–887
Petersen PE (2003) The world oral health report: continuous improvement of oral health in the 21st century—the approach of WHO global oral programme. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 31:3–23
Neville BW, Day TA (2002) Oral cancer and precancerous lesions. CA Cancer J Clin 52:195–215
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Pestell RG, Albanese C, Reutens AT, Segall JE, Lee RJ, Arnold A (1999) The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr Rev 20:501–534
Hinds PW, Dowdy SF, Eaton EN, Arnold A, Weinberg RA (1994) Function of a human cyclin gene as an oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:709–713
Jiang W, Kahn SM, Zhou P, Zhang YJ, Cacace AM, Infante AS, Doi S, Santella RM, Weinstein IB (1993) Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene 8:3447–3457
Bova RJ, Quinn DI, Nankervis JS, Cole IE, Sheridan BF, Jensen MJ et al (1999) Cyclin D1 and p16INK4A expression predict reduced survival in carcinoma of the anterior tongue. Clin Cancer Res 5:2810–2819
Carlos de Vicente J, Herrero-Zapatero A, Fresno MF, Lopez-Arranz JS (2002) Expression of cyclin D1 and Ki-67 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: clinicopathological and prognostic significance. Oral Oncol 38:301–308
Feng Z, Guo W, Zhang C, Xu Q, Zhang P, Sun J et al (2011) CCND1 as a predictive biomarker of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 6:e26399
Kaminagakura E, Werneck da Cunha I, Soares FA, Nishimoto IN, Kowalski LP (2011) CCND1 amplification and protein overexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma of young patients. Head Neck 33:1413–1419
Huang SF, Cheng SD, Chuang WY, Chen IH, Liao CT, Wang HM et al (2012) Cyclin D1 overexpression and poor clinical outcomes in Taiwanese oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 10:40
Shah NG, Trivedi TI, Tankshali RA, Goswami JV, Jetly DH, Shukla SN et al (2009) Prognostic significance of molecular markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a multivariate analysis. Head Neck 31:1544–1556
Perisanidis C, Perisanidis B, Wrba F, Brandstetter A, El Gazzar S, Papadogeorgakis N et al (2012) Evaluation of immunohistochemical expression of p53, p21, p27, cyclin D1, and Ki67 in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 41:40–46
Khan H, Gupta S, Husain N et al (2014) Correlation between expressions of cyclin-D1, EGFR and p53 with chemo-radiation response in patients of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma. BBA Clin 3:11–17
Brandwein-Gensler M, Smith RV (2010) Prognostic indicators in head and neck oncology including the new 7th edition of the AJCC staging system. Head Neck Pathol 4:53–61
Sutton DN, Brown JS, Rogers SN, Vaughan JA, Woolgar JA (2003) The prognostic implications of the surgical margin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 32:30–34
Raju K, Punnayanapalya S, Mariyappa N (2015) Significance of p53, pRb and Ki-67 Markers in Cervical Intraepithelial Lesion and Malignancy. Biomed Res Ther 2(10):374–384
Hahn WC, Weinberg RA (2002) Rules for making human tumor cells. N Engl J Med 347(20):1593–1603
Schmitz S, Machiels JP (2010) Molecular biology of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: relevance and therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10(9):1471–1484
Monteiro LS, Diniz-Freitas M, Garcia-Caballero T, Warnakulasuriya S, Forteza J, Fraga M (2012) Combined cytoplasmic and membranous EGFR and p53 overexpression is a poor prognostic marker in early stage oral squamous cellcarcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 41(7):559–567
Mishra R (2013) Cell cycle-regulatory cyclins and their deregulation in oral cancer. Oral Oncol 9(6):475–481
Pillay M, Vasudevan DM, Rao CP, Vidya M (2003) p53 expression in oral cancer: observations of a South Indian study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 22(3):447–451
Saawarn S, Astekar M, Saawarn N, Dhakar N (2012) Cyclin D1expression and its correlation with histopathological differentiation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci World J 65:1–5
Zhong L-P (2013) Elevated cyclin D1 expression is predictive for a benefit from TPF induction chemotherapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with advanced nodal disease. Mol Cancer Ther 12(6):1112–1120
Khan H et al (2014) Correlation between expressions of Cyclin-D1, EGFR and p53with chemoradiation response in patients of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma. BBA Clinical 3:11–17
Marx J (1994) How cells cycle toward cancer. Science 263:319–321
Callender T, el Naggar AK, Lee MS, Frankenthaler R, Luna MA, Batsakis JG (1994) PRAD-1 (CCND1)/cyclin D1 oncogene amplification in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 74:152–158
Dong Y, Sui L, Sugimoto K, Tai Y, Tokuda M (2001) Cyclin D1-CDK4 complex, a possible critical factor for cell proliferation and prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 95:209–215
Pignataro L, Pruneri G, Carboni N et al (1998) Clinical relevance of cyclin D1 protein overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 16:3069–3077
Namazie A, Alavi S, Olopade OI et al (2002) Cyclin D1 amplification and p16(MTS1/CDK4I) deletion correlate with poor prognosis in head and neck tumors. Laryngoscope 112:472–481
Strano S, Dell’Orso S, Mongiovi AM et al (2007) Mutant p53 proteins: between loss and gain of function. Head Neck 29(5):488–496
Abrahao AC, Bonelli BV, Nunes FD, Dias EP, Cabral MG (2011) Immunohistochemical expression of p53, p16 and hTERT in oral squamous cell carcinoma and potentiallymalignant disorders. Brazilian Oral Res 25(1):34–41
Grabenbauer GG, Muhlfriedel CH, Rodel F, Niedobitek G (2000) Squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx: Ki-67 and p53 can identify patients at high risk for local recurrence after surgery and postoperative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:1041–1050
Field JK, Zomupourlis V, Spandidos DA, Jones AS (1994) P53 expression and mutation in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: expression correlates with the patients’ use of tobacco and alcohol. Cancer Detect Prev 18(3):197–208
Sisk EA, Soltys SG, Zhu S, Fisher SG, Carey TE, Bradford CR (2002) Human papillomavirus and p53 mutational status as prognostic factors in head and neck carcinoma. Head Neck 24:841–849
Bosch FX, Ritter D, Enders C, Flechtenmacher C, Abel U, Dietz A, Hergenhahn M, Weidauer H (2004) Head and neck tumor sites differ in prevalence and spectrum of p53 alterations but these have limited prognostic value. Int J Cancer 111:530–538
Vlachtsis K, Nikolaou A, Markou K, Fountzilas G, Daniilidis I (2005) Clinical and molecular prognostic factors in operable laryngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262:890–898
Waitzberg AF, Nonogaki S, Nishimoto IN, Kowalski LP, Miguel RE, Brentani RR, Brentani MM (2004) Clinical significance of c-Myc and p53 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Detect Prev 28(3):178–186
Poeta ML, Manola J, Goldwasser MA, Forastiere A, Benoit N, Califano JA, Ridge JA, Goodwin J, Kenady D, Saunders J, Westra W, Sidransky D, Koch WM (2007) TP53 mutations and survival in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 357:2552–2561
Shin DM, Lee JS, Lippman SM, Lee JJ, Tu ZN, Choi G, Heyne K, Shin HJ, Ro JY, Goepfert H, Hong WK, Hittelman WN (1996) p53 expression: predicting recurrence and secondary primary tumors in head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma. J Nat Cancer Inst 88:519–529
Smith EM, Wang D, Rubenstein LM (2008) WA Morris, Turek LP, Haugen TH: Association between p53 and human papillomavirus in head and neck cancer curvival. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17:421–427
Hirvikoski P, Kumpulainen E, Virtaniemi J, Johansson R, Haapasala R, Marin S, Halonen P, Helin H, Raitiola H, Pukander J, Kosma VM, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P (1997) p53expression and cell proliferation as prognostic factors in laryngeal squamous-cell carcinoma. J clin Oncol 15:3111–3120
Blons H, Laurent-Puig P (2003) TP53 and head and neck neoplasms. Hum Mutat 21:252–257
Almangush A, Heikkinen I, Mäkitie AA, Coletta RD, Läärä E, Leivo I, Salo T (2017) Prognostic biomarkers for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 117(6):856–866
Freier K, Bosch FX, Flechtenmacher C et al (2003) Distinct site-specific oncoprotein overexpression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a tissue microarray analysis. Anticancer Res 23:3971–3977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakkar, V., Sarin, V., Chatterjee, A. et al. Expression of Cyclin-D1 and p53 as Prognostic Markers in Treatment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 3), 6136–6145 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02716-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02716-4