Abstract
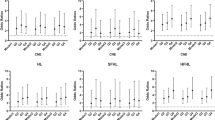
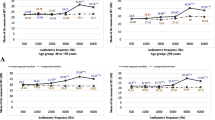
Noise and organic solvents are common in many industries and both of them affect hearing. In this study, we estimated the concurrent effect of them on hearing by evaluating the existence of notch in audiograms of workers. The number of 540 persons were enrolled in this study after eliminating workers who had the exclusion criteria. We divided them into 4 groups based on their exposure status; no exposure, exposure to noise, exposure to solvent, exposure to both of them. The presence of notch in left, right, or both ears were assessed through Coles model. The rates of notch presence in both ears in the groups of noise and organic solvents exposure, noise exposure only, solvents exposure only were 11.72, 4.49, 1.86 times higher than the control group and sole solvent exposure didn't affect hearing significantly. The same pattern was seen for notch presence in left or right ear and the solvent-noise exposure group had the highest rate of notch presence. This study aims to show the synergic effect of noise and organic solvents exposure on hearing loss. Hence, we recommend implementing a hearing protection program and a higher frequency of audiological assessments in the industries involved with concurrent exposure to noise and organic solvents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the relevant data and materials are presented in the paper.
References
Ashley K (2015) NIOSH manual of analytical methods 5(th) edition and harmonization of occupational exposure monitoring. Air Qual Control 2015(1–2):7–16
Barregård L, Axelsson A (1984) Is there an ototraumatic interaction between noise and solvents? Scand Audiol 13(3):151–155. https://doi.org/10.3109/01050398409043054
Campo P, Maguin K (2007) Solvent-induced hearing loss: mechanisms and prevention strategy. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 20(3):265–270. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10001-007-0031-3
Guerra MR, Lourenço PMC, Bustamante-Teixeira MT, Alves MJM (2005) Prevalence of noise-induced hearing loss in metallurgical company. Rev Saude Publica 39(2):238–244
Kurabi A, Keithley EM, Housley GD, Ryan AF, Wong ACY (2017) Cellular mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 349:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2016.11.013
Kurmis AP, Apps SA (2007) Occupationally-acquired noise-induced hearing loss: a senseless workplace hazard. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 20(2):127–136. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10001-007-0016-2
Le TN, Straatman LV, Lea J, Westerberg B (2017) Current insights in noise-induced hearing loss: a literature review of the underlying mechanism, pathophysiology, asymmetry, and management options. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 46(1):41–41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-017-0219-x
Loukzadeh Z, Shojaoddiny-Ardekani A, Mehrparvar AH, Yazdi Z, Mollasadeghi A (2014) Effect of exposure to a mixture of organic solvents on hearing thresholds in petrochemical industry workers. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 26(77):235–243
Metwally FM, Aziz HM, Mahdy-Abdallah H, ElGelil KS, El-Tahlawy EM (2012) Effect of combined occupational exposure to noise and organic solvents on hearing. Toxicol Ind Health 28(10):901–907. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233711427051
Mohammadi S, Labbafinejad Y, Attarchi M (2010) Combined effects of ototoxic solvents and noise on hearing in automobile plant workers in Iran. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 61(3):267–274. https://doi.org/10.2478/10004-1254-61-2010-2013
Morata TC, Dunn DE, Sieber WK (1994) Occupational exposure to noise and ototoxic organic solvents. Arch Environ Health Int J 49(5):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1994.9954988
Nakhooda F, Sartorius B, Govender SM (2019) The effects of combined exposure of solvents and noise on auditory function—a systematic review and meta-analysis. S Afr J Commun Disord 66(1):e1–e11. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajcd.v66i1.568
Pryor GT, Rebert CS, Howd RA (1987) Hearing loss in rats caused by inhalation of mixed xylenes and styrene. J Appl Toxicol 7(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2550070110
Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Zamyslowska-Szmytke E, Szymczak W, Kotylo P, Fiszer M, Wesolowski W, Pawlaczyk-Luszczynska M (2005) Exacerbation of noise-induced hearing loss by co-exposure to workplace chemicals. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19(3):547–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2004.12.018
Toppila E, Pyykkö I, Starck J (2001) Age and noise-induced hearing loss. Scand Audiol 30(4):236–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/01050390152704751
Wilson DH, Walsh PG, Sanchez L, Davis AC, Taylor AW, Tucker G, Meagher I (1999) The epidemiology of hearing impairment in an Australian adult population. Int J Epidemiol 28(2):247–252. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/28.2.247
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Clinical Research Development Unit (CRDU) of Baharloo Hospital and Occupational Sleep Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran for their support, cooperation and assistance throughout the period of study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and RO wrote the manuscript. SA analyzed the data. NI collected the data. OA and reviewed the results. SEM reviewed the whole manuscript and provided guidelines for presentation and interpretation. All of the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences and performed in accordance with the ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All of the participants were provided with informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saraei, M., Omidi, R., Aminian, O. et al. The Combined Effect of Noise and Solvent Exposure on Hearing Loss in the Tire Factory Workers. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 3), 3887–3892 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02697-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02697-4