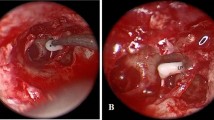
Abstract
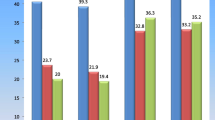
Chronic otitis media (COM) is a common disease that can cause damage to the middle ear ossicles and thus lead to conductive hearing loss. The purpose of this study was to compare two methods of incus partial ossicular reconstruction prosthesis (PORP) and reconstruction with titanium angular clip prosthesis in patients with incudostapedial joint erosion. In this interventional randomized clinical trial carried out in a tertiary referral hospital, patients with chronic otitis media and incudostapedial joint erosion who were candidates for surgery, were randomly allocated into two groups of incus PORP surgery and reconstruction with a titanium angular clip prosthesis. Audiometry was performed for the patients prior to and six months after surgery. Pre- and post-operative air–bone gap (ABG) and bone conduction (BC) thresholds were calculated and means were compared by analysis of variances (ANOVA). A P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. The study consisted of 24 and 14 subjects in the incus PORP and angular clip groups, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference between the mean pre- and post-operative ABG, BC thresholds and ABG reduction in the compared groups. Considering issues such as high cost and inaccessibility of titanium angular clips in all centers, incus PORP may be a more acceptable method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisch U, May JS, Linder T (2010) Tympanoplasty, mastoidectomy, and stapes surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 92(1):81–81. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588410X12518836440441d
Fong JC, Michael P, Raut V (2010) Titanium versus autograft ossiculoplasty. Acta Otolaryngol. 130(5):554–8. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016480903338131
Celenk F, Baglam T, Baysal E et al (2013) Management of incus long process defects: incus interposition versus incudostapedial rebridging with bone cement. J Laryngol Otol 127(9):842–847
Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium Guidelines for the Evaluation of Results of Treatment of Conductive Hearing Loss (1995) Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 113(3):186–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0194-5998(95)70103-6
Woods O, Fata FE, Saliba I (2009) Ossicular reconstruction: incus versus universal titanium prosthesis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 36(4):387–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2008.10.001
Naragund A, Mudhol R, Harugop A, Patil P (2011) Ossiculoplasty with autologous incus versus titanium prosthesis: a comparison of anatomical and functional results. Indian J Otol. 17(2):75–79. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-7749.91042
Ceccato SB, Maunsell R, Morata GC, Portmann D (2005) Comparative results of type II ossiculoplasty: incus transposition versus titanium PORP (Kurz). Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 126(3):175–179
Zakzouk A, Bonmardion N, Bouchetemble P, Lerosey Y, Marie JP (2015) Titanium prosthesis or autologous incus for total ossicular reconstruction in the absence of the stapes suprastructure and presence of mobile footplate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(10):2653–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3212-2
Thamizharasan P, Ravi K (2017) Comparative study of autologous ossicular graft versus titanium prosthesis (TORP & PORP) in ossiculoplasty. Bengal J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 25(1):1–7
Funding
This study was funded by Otorhinolaryngology Research Center of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (IR.TUMS.IKHC.REC.1395.1673).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emami, H., Shojasefat, F., Moghtadaie, A. et al. Incus Autograft Partial Ossicular Reconstruction Prosthesis vs. Titanium Angular Clip Prosthesis in Patients with Incudostapedial Joint Erosion Caused by Chronic Otitis Media; A Randomized Clinical Trial. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74, 85–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02605-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02605-w