Abstract
Purpose
To study and analyse the radiological and surgical findings of 25 cochlear implantees with SMS type—I cochleovestibular malformation and to compare their outcomes in terms of hearing and speech gains pre- and post-operatively.
Methods
Retrospective analysis of cochlear implanted candidates over a period of 8 year from 3 institutions was undertaken and 25 patients suffering from pre-lingual profound congenital sensori-neural hearing loss along with presence of SMS type I cochleovestibular malformation were studied. Pre-operative radiology, surgical difficulties and complication, and post-operative hearing and speech outcomes upto a period of 2 years, using IT-MAIS scores were noted. Statistical comparison pre- and post-implantation was done using Wilcoxon signed rank test and a p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
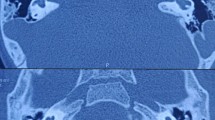
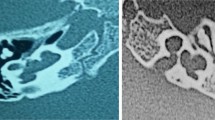
In 25 cases, we encountered 2 posterior SCC dysplasia, 15 enlarged vestibular aqueducts (LVA), 2 dilated vestibules, 4 superior SCC dysplasia, 2 cases with both posterior and superior SCC dysplasia and of those 1 had a dilated vestibule also. Intra-operatively, CSF leak was observed in 10 patients. Complete electrode insertion and good electrical response (NRT) was detected in all. No facial nerve anomaly was encountered. IT-MAIS scores increased from a pre-operative mean of 4.32 to 34.56 two years post-operatively and this difference was found to be statistically significant.
Conclusion
Our experience with SMS Type I malformations show promising and motivating results with less chances of complications, similar to implant candidates with normal anatomy. The outcomes in this group of patients are definitely not affected by any malformations in semicircular canals, vestibule or vestibular aqueduct.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen S (1969) Malformation of the inner ear in deaf children. Acta Radio 286:1–97
Dettman S, Sadeghi-Barzalighi A, Ambett R, Dowell R, Trotter M, Briggs R (2011) Cochlear implants in forty-eight children with cochlear and/or vestibular abnormality. Audio Neurotol 16(4):222–232
Jackler RK, Luxfor WM, House WF (1987) Congenital malformations of the inner ear: a classification based on embryogenesis. The Laryngoscope 97(S40):2–14
Sennaroglu L, Saatci I (2002) A new classification for cochleovestibular malformations. The Laryngoscope 112(12):2230–2241
Sennaroglu L (2010) Cochlear implantation in inner ear malformations–a review article. Cochlear implants Int 11:4–41
Sennaroğlu L, Bajin MD (2017 Sep) Classification and current management of inner ear malformations. Balkan Med J 34(5):397
Grover M, Sharma S, Preetam C, Gupta G, Samdani S, Agarwal S, Singh SN, Sharma MP (2019) New SMS classification of cochleovestibular malformation and its impact on decision-making. J Laryngol Otol 133(5):368–375
Zimmerman-Phillips S, Robbins AM, Osberger MJ (2000) Assessing cochlear implant benefit in very young children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 109(12):42–43
Robbins AM, Renshaw JJ, Berry SW (1991) Evaluating meaningful auditory integration in profoundly hearing-impaired children. Am J otol 12:144–150
Valvassori GE, Clemis JD (1978) The large vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Laryngo 88(5):723–728
Grover M, Kanodia A, Gupta G, Preetam C, Samdani S (2020) Application of the new SMS system of cochleovestibular anomalies: our experience with nine cases of type III anomaly. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 11:1–6
Lee KH, Lee J, Isaacson B, Kutz JW, Roland PS (2010) Cochlear implantation in children with enlarged vestibular aqueduct. Laryngo 120(8):1675–1681
Hongjian L, Guangke W, Song M, Xiaoli D, Daoxing Z (2012) The prediction of CSF gusher in cochlear implants with inner ear abnormality. Acta Otolaryngol 132(12):1271–1274
Harker LA, Vanderheiden S, Gentile N, Veazey D, McCleary E (1999) Multichannel cochlear implantation in children with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Annals Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108(4_suppl):39–43
Wootten CT, Backous DD, Haynes DS (2006) Management of cerebrospinal fluid leakage from cochleostomy during cochlear implant surgery. The Laryngoscope 116(11):2055–2059
Loundon N, Rouillon I, Munier N, Marlin S, Roger G, Garabedian EN (2005) Cochlear implantation in children with internal ear malformations. Otol Neurotol 26(4):668–673
Eisenman DJ, Ashbaugh C, Zwolan TA, Arts HA, Telian SA (2001) Implantation of the malformed cochlea. Otol Neurotol 22(6):834–841
Papsin BC (2005) Cochlear implantation in children with anomalous cochleovestibular anatomy. The Laryngoscope 115(S106):1–26
Phelps PD, King A, Michaels L (1994) Cochlear dysplasia and meningitis. Am J otology 15(4):551–557
Eftekharian A, Amizadeh M (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid gusher in cochlear implantation. Cochlear Implants Int 15(3):179–184
Sennaroglu L, Sarac S, Ergin T (2006 Aug 1) Surgical results of cochlear implantation in malformed cochlea. Otol Neurotol 27(5):615–623
Lin CY, Lin SL, Kao CC, Wu JL (2005) The remediation of hearing deterioration in children with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 32(2):99–105
Boston M, Halsted M, Meinzen-Derr J, Bean J, Vijayasekaran S, Arjmand E, Choo D, Benton C, Greinwald J (2007) The large vestibular aqueduct: a new definition based on audiologic and computed tomography correlation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136(6):972–7
Grover M, Sharma S, Bhargava S, Singh SN, Gupta G, Sharma MP (2017) Cochlear implantation in children with anomalous cochleovestibular anatomy: our experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69(4):504–508
Isaiah A, Lee D, Lenes-Voit F, Sweeney M, Kutz W, Isaacson B, Roland P, Lee KH (2017) Clinical outcomes following cochlear implantation in children with inner ear anomalies. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1(93):1–6
Ciorba A, Bovo R, Trevisi P, Rosignoli M, Aimoni C, Castiglione A, Martini A (2012) Postoperative complications in cochlear implants: a retrospective analysis of 438 consecutive cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(6):1599–1603
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All Authors declare that they have no conflict of Interest. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for profit sectors.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study..
Author Contributions Statement
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mohnish Grover and Shivam Sharma. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Shivam Sharma and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grover, M., Sharma, S., Samdani, S. et al. New SMS Classification of Cochleovestibular Anomalies: Our Experience with 25 Cases of Type I Anomaly. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 73, 333–339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02442-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02442-x