Abstract
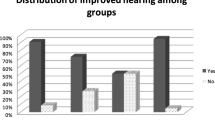
Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is one of the important health problems in our country. The present study was conducted to compare Cartilage and Temporalis Fascia as graft material for Type 1 Tympanoplasty for CSOM. The study was conducted to assess hearing outcome as average AB Gap closure respect to age of the patient and size of perforation, to evaluate Graft uptake with both grafting material and with respect to size of perforation and to find the complication rate. Prospective Comparative study was conducted on 60 patients of CSOM divided in two groups and randomly selected for cartilage Typanoplasty and Temporalis Fascia Tympanoplasty. Hearing result are compared pre and post operative. Group 1(cartilage): Average AB Gap closure was 55% for Small CP, 50% for Moderate CP, 40% for Large CP, 38% for Subtotal CP. In Group 2(Temoralis Fascia): Average AB Gap closure was 81% for Small CP, 72% for Moderate CP, 64% for Large CP, 52% for Subtotal CP. In Group 1, 46% and in Group 2, 69% Average closure of AB gap observed at 12 weeks post operatively. The p value for our study was found to be < 0.05, which statistically indicates better hearing outcome with TF graft. Cartilage is an excellent grafting material because of its accessibility, resistance to negative pressure and high graft uptake rate. Temporalis Fascia is easily available with similar thickness to TM. It showed inferior morphological uptake rate compared to cartilage though functional gain was better.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhinav. D. Wankar, Sanjiv Golha (2014) To determine prevalence of chronic suppurative otitis media with reference to unsafe otitis media in primary school going children of rural setup of Wardha District , Global) Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 1 Version1.0 Year2014
Chronic suppurative otitis media Burden of Illness and Management Options, Child and Adolescent Health and Development Prevention of Blindness and Deafness World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland 2004. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42941
Patil K, Baisakhiya N, Deshmukh PT (2014) Evaluation of different graft material in type 1 tympanoplasty. Indian J Otol 20:106–114. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-7749.136844
Sridhara Narayanan D, Vijay Kumar B, Hari PM (2016) Comparative study of graft materials used in myringoplasty. J Pharm Sci Res 8(12):1339–1342. https://www.jpsr.pharmainfo.in/Documents/Volumes/vol8Issue12/jpsr08112602.pdf
Tayyar Kalcioglu M, YezdanFirat (2009) Erol selimoglu cartilage tympanoplasty with Island technique: a comparison with the temporalis muscle fascia technique. Int Adv Otol 5(1):45–50. https://www.advancedotology.org/en/cartilage-tympanoplasty-with-island-technique-a-comparison-with-the-temporalis-muscle-fascia-technique-16717
Chopra H, Grover G (2009) The results of tympanoplasty in paediatric age group. Ind J Otol 5:210–212
Gupta N, Mishra RK (2002) Tympanoplasty in children. Ind J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 54:271–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02993741
Singh GB, Arora R, Garg S, Kumar S, Kumar D (2016) Paediatric tympanoplasty: comparative study between patients aged 5–8 years and those aged over 14 years. J Laryngol Otol 130(7):635–639. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002221511600815X
Murat Şahan, Serhan Derin, Mehmet Deveer, Ömer Sağlam, Neşat Çullu, Leyla Şahan (2014) Factors affecting success and results of cartilage-perichondrium island graft in revision tympanoplasty· Int Adv Otol 10(1):64–67. https://doi.org/10.5152/iao.2014.014
Vivek V Harkare, Rakesh K Mishra, Nitin V Deosthale, Sonali P Khadakkar, Priti R Dhoke, Kanchan Dhote, Nudrat Kamal, Sudheer T. Reddy (2013) A comparative study of different tissues used for tympanic membrane grafting. J Evol Med Dental Sci 2(41):4834–4840. https://jemds.com/data_pdf/vivek%2520harkare.pdf
Rakesh Kumar, Rajesh Kumar Suman, Yogesh A. Garje, Suman P. Rao (2014) Comparative study of underlay tympanoplasty with temporalis fascia and tragal perichondrium. IOSR J Dental Med Sci. e-ISSN: 2279–0853, ISSN: 2279–0861.Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III, pp 89–98. https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jdms/papers/Vol13-issue5/Version-3/U013538998.pdf
Shyamakant Prasad, Vineet Gupta, Ashok Kumar, Sulabha M. Naik, Shaheed Hasan Khan (2015) Cartilage tympanoplasty: is it more effective than temporalis fascia grafting for tympanoplasty? Otolaryngology. ISSN: 2250–0359 Volume 5 Issue 4 2015 https://www.alliedacademies.org/articles/cartilage-tympanoplasty-is-it-more-effective-than-temporalis-fascia-grafting-for-tympanoplasty.pdf
Quraishi MS, Jones NS (1995) Day case myringoplasty using tragal perichondrium. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 20(1):12–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1995.tb00004.x
Sapçi T, Almaç S, Usta C, Karavuş A, Mercangöz E, Evcimik MF (2006) Kartilaj perikondriyal kompozit greft ve temporal fasya greft timpanoplastilerinde işitme ve iyileşme sonuçlarinin karşilaştirilmasi [Comparison between tympanoplasties with cartilage-perichondrium composite graft and temporal fascia graft in terms of hearing levels and healing]. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 16(6):255–260. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17220657/
Jiang Z, Lou Z (2017) Effects of perforation size on the success rate of tympanoplasty using a cartilage graft. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 83:494–495. https://www.scielo.br/pdf/bjorl/v83n4/1808–8694-bjorl-83–04–0494.pdf
Das A, Sen B, Ghosh D, Sengupta A (2015) Myringoplasty: impact of size and site of perforation on the success rate. Ind J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67(2):185–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0810-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, R., Gangani, H.M., Aiyer, R.G. et al. Is Cartilage a Better Option than Temporalis Fascia for Grafting in Type 1 Tympanoplasty?: An Institutional Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 1), 246–251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02037-y