Abstract
Background
This study mainly focus on hearing loss pattern in CSOM patients undergoing tympanoplasty surgery or tympanomastoidectomy pre-operatively and analysis of the outcome of the surgery in terms of improvement in hearing (air-bone gap) after 3 months of the surgery.
Methodology
All patients of age 15–65 years reporting to ENT OPD with ear discharge and decreased hearing were screened with detailed history, clinical examination and microscopic examination.110 cases of tympanic membrane perforation who were fit for surgery were advised tympanoplasty or tympanoplasty with mastoidectomy.
Results
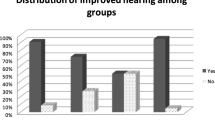
Our study shows that postoperative air-bone gap closure is maximum for cortical mastoidectomy type I tympanoplasty (14.03 dB), followed with cortical mastoidectomy with type II (12.2 dB), Type I tympanoplasty (11 dB), cortical mastoidectomy with type III (7.72 dB). Procedures combined with modified radical mastoidectomy showed a very poor mean improvement in our study.
Conclusion
It is very difficult to predict the results preoperatively because outcome will depend on extent of involvement of middle ear cleft by the disease process which can only be assessed intraoperatively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuin J (2004) World Health Organization: chronic suppurative otitis media: burden of illness and management options. World Health Organization, Geneva
George GB, Merchant SN, Kelly G, Swan IR, Canter R, Mckerrow WS (2008) Chronic otitis media. In: Gleeson M (ed) Scott-Brown’s otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery, 7th edn. Edward Arnold Publishers, London, pp 3397–3438
Sismanis A (2003) Tympanoplasty. In: Glascock ME (ed) Glsscock-Shambaugh surgery of the Ear, 5th edn. Decker BC, WB Saunders Company, Hamilton, pp 463–484
Merchant SN, Ravicz ME, Puria S, Voss SE, Whittemore KR Jr, Peake WT et al (1997) Analysis of middle ear mechanics and application to diseased and reconstructed ears. Am J Otol 18(2):139–154
Muqtadir F et al (2018) A study of hearing improvement gained after tympanoplasty using various methods in cases of CSOM. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 4(1):107–111
Balasubramaniam GK, ThirunavukkarasuR KRB, Palaniappan H, Shanmugam PR (2015) Hearing benefits in various types of tympanoplasties: a prospective study. Indian J Otol 21:129–133
Indorewala S, Adedeji TO, Indorewala A, Nemade G (2015) Tympanoplasty outcomes: a review of 789 cases. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 27(79):101
Acknowledgement
All the authors are thankful to Dr. V.K.Mahadik (Medical Director, R.D Gardi Medical College, Ujjain) for giving us the permission for conducting the study in the institute and encouragement.
Funding
No funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakti, A., Vaidya, S., Agrawal, A. et al. Comparative Study of Hearing Results in Various Types of Tympanoplasties. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 1), 74–78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01832-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01832-x