Abstract
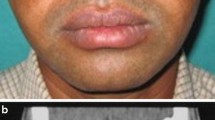
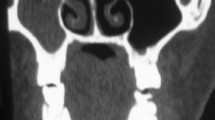
Maxillofacial trauma, a common injury in urban population following road traffic accident or act of interpersonal violence of which orbital floor fractures is common. It impairs the integrity of the extraocular muscles and may be accompanied by enophthalmos, orbital deformity and diplopia. Orbital reconstruction is essential to improve anatomical and visual deformity. Repair of orbital floor is done by autologous bone graft or synthetic implants. Compare outcome of orbital floor reconstruction in blow out orbital fracture using autogenous bone graft from iliac crest, outer table of mandible, alloplastic implant- silastic block and titanium mesh. 30 patients having orbital fractures were considered in study population. All the patients were treated by ORIF and repair of floor by subcilliary incision. Out of 30 patients, repair of orbital floor was done by autologous bone graft from iliac crest in 7 patients (Group A), bone graft from outer table of mandible in 5 patients (Group B), implant using silastic block in 8 patients (Group C) and titanium mesh in 10 patients (Group D). Factors analyzed were age, sex, cause of fracture and treatment outcome in terms of correction of pre operative diplopia and enophthalmos, rate of development of post operative infection, wound dehiscence and implant exposure. All patents were reviewed at 4 weeks and 12 weeks following operation. 71.42% of patients in Group A had early correction of diplopia and enophthalmos. This was 100% in rest of the groups. All patients had complete correction when assessed at 12 weeks post operatively. Post operative complication rate was 20% and 12.5% in Group B and C respectively. There were no complications in the rest of the groups within the follow up period. No statistically significant difference as to the chance of occurrence of complication could be found amongst the groups. Autologous bone graft has no immunological reaction but donor site morbidity. Silastic block may case immunological reaction, infection, poor drainage of orbital floor. But titanium mesh for orbital floor repair has excellent outcome and superior to other modality of treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forrest S, John C, Jonathan S, Charles NS (2010) Pearls of orbital trauma management. Semin Plasr Surg. 24(4):398–410
Ahmad F, Kirkpatrick NA, Lyne J, Urdang M, Waterhouse N (2006) Buckling and hydraulic mechanisms in orbital blowout fractures: fact or fiction? J Craniofac Surg 17(3):438–441
Anitha GL, Uma Maheswari G, Sethurajan B (2012) Mandibular symphysis graft versus iliac cortical graft in reconstructing floor in orbital blow out fracture: a comparative study. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2(1):24–29
Birur NP, Patrick S, Gurushanth K, Raghavan AS, Gurudath S (2017) Comparison of gray values of cone-beam computed tomography with hounsfield units of multislice computed tomography: an in vitro study. Indian J Dent Res 28(1):66
Roncevic R, Malinger B (1981) Experience with various procedures in the treatment of orbital floor fractures. J Maxillofac Surg 9:81–84
Kim JY, Choi G, Kwon JH (2015) Transantral orbital floor fracture repair using silastic tube. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 8(3):250–255
Patrick K, David A, Ralph E, David C, Paul N (1993) Bone-graft reconstruction of the monkey orbital floor with iliac grafts and titanium mesh plates: a histometric study. Plast Reconstr Surg 91(5):769–777
Edward E, Yinghui T (2003) Assessment of internal orbital reconstructions for pure blow out fractures: cranial bone grafts versus titanium mesh. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(4):442–453
Gear AJ, Lokesh A et al (2002) Safety of titanium mesh for orbital reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 48(1):1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author of this article declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
Animals were not involved in the study.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human population were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Approval from the Institutional Ethical Committee, Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, was obtained for the study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all the individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, A.K., Samaddar, S., Kumar, A. et al. A Comparative Study of Orbital Blow Out Fracture Repair, Using Autogenous Bone Graft and Alloplastic Materials. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71, 542–549 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01724-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01724-9