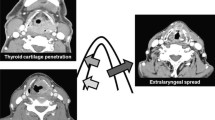
Abstract
In locally advanced cases of carcinoma larynx, which are being treated with total laryngectomy, routine excision of the thyroid gland (either total or hemi section) is carried out. This study was carried out to evaluate the requirement of routine thyroidectomise with total laryngectomy. An analysis of the final histology of 83 patients, who underwent the traditional treatment, together with the preoperative contrast enhanced CT scan was carried out. Among 58 cases of T3 carcinoma larynx 2 revealed thyroid involvement by metastasis (3.45%), 1 of them was suspected in preoperative CT and confirmed by FNAC. Among 25 cases of T4a carcinoma larynx 6 revealed thyroid involvement by direct extension (24%) with evidence of same in preoperative CT. Risk of thyroid involvement is low in T3 cases (3.45%) and is by metastasis. Risk of thyroid involvement is higher in T4a cases (24%) and is by direct extension. Preoperative CECT is a good tool to predict thyroid gland involvement either by metastasis or by direct spread. This study thus raises doubts about the requirement of routine thyroidectomise in association with total laryngectomies in advanced carcinoma larynx. We thus believe that further investigations, on a larger scale and multi-institutional, is warranted.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sparano A, Chernock R, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G (2005) Predictors of thyroid gland invasion in glottic squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope 115(7):1247–1250
Gaillardin L, Beutter P, Cottier J-P, Arbion F, Morinière S (2011) Thyroid gland invasion in laryngopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: prevalence, endoscopic and CT predictors. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 129:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2011.04.002
Biel MA, Maisel RH (1985) Indications of performing hemithyroidectomy for tumours requiring total laryngectomy. Am J Surg 150(4):435–439
Iype EM, Jagad V, Nochikattil SK, Varghese BT, Sebastian P (2016) Thyroid gland involvement in carcinoma larynx and hypopharynx-predictive factors and prognostic significance. J Clin Diagn Res 10(2):XC05–XC07
Funding
The treatment of patients was carried out in a hospital funded by the Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mozumder, S., Chatterjee, K., Dubey, S. et al. Contrast CT Scan Evaluation of Incidence and Pattern of Thyroid Gland Involvement in Locally Advanced Ca Larynx Modifying the Need of Routine Thyroidectomy with Total Laryngectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 72, 14–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01711-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01711-0