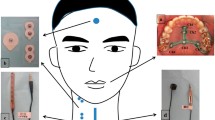
Abstract
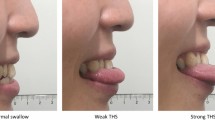
In healthy normal individuals, the act of swallowing can be performed volitionally or can occur spontaneously. Several attempts have been made to look into the possible differences that might exist between automatic swallow (AS) and volitional swallow (VS). The present study is an attempt to physiologically differentiate AS from that of VS, using combined modules of tongue array and cervical auscultation of Digital Swallowing Workstation. 15 males and 15 female participants in the age range of 18–25 participated in the present study. They performed an AS task and a VS task. These were analyzed for parameters of maximum amplitude, duration and pressure. The result of the study revealed higher values for all the parameters of VS, but a statistically significant difference only for the duration parameter of cervical auscultation. This finding leads to the impression that the duration of vocal fold closure plays a major role in airway protection. Similar interesting findings on effect of gender and nature and organization of AS and VS have been discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA (1984) Aspiration in head and neck surgical patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 94(4 Pt 1):373–376
Cassiani RA, Santos CM, Parreira LC, Dantas RO (2011) The relationship between the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Clinics 66(8):1385–1388
Miller AJ (1982) Deglutition. Physiol Rev 62(1):129–184
Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Logemann JA, Shanahan TK (1994) Oropharyngeal swallow efficiency as a representative measure of swallowing function. J Speech Lang Hear Res 37(2):314–325
Ertekin C, Kiylioglu N, Tarlaci S, Turman AB, Secil Y, Aydogdu I (2001) Voluntary and reflex influences on the initiation of swallowing reflex in man. Dysphagia 16(1):40–47
Nomura K, Utsumake A, Tomita K, Watanabe M, Ooka T, Hironaka S, Mukai Y (2011) Influence of command on tongue elevation during swallowing: examination of tongue pressure and ultrasound imaging. J Disabil Oral Health 12(4):149–158
Thexton AJ, Crompton AW, German RZ (2007) Electromyographic activity during the reflex pharyngeal swallow in the pig: Doty and Bosma (1956) revisited. J Appl Physiol 102(2):587–600
Thexton AJ, Crompton AW, Owerkowicz T, German RZ (2009) Impact of rhythmic oral activity on the timing of muscle activation in the swallow of the decerebrate pig. J Neurophysiol 101(3):1386–1393
Ertekin C (2011) Voluntary versus spontaneous swallowing in man. Dysphagia 26(2):183–192
Martin RE, Goodyear BG, Gati JS, Menon RS (2001) Cerebral cortical representation of automatic and volitional swallowing in humans. J Neurophysiol 85(2):938–950
Dziewas R, Sörös P, Ishii R, Chau W, Henningsen H, Ringelstein EB, Knecht S, Pantev C (2003) Neuroimaging evidence for cortical involvement in the preparation and in the act of swallowing. Neuroimage 20(1):135–144
Lowell SY, Reynolds RC, Chen G, Horwitz B, Ludlow CL (2012) Functional connectivity and laterality of the motor and sensory components in the volitional swallowing network. Exp Brain Res 219(1):85–96
Nonaka T, Yoshida M, Yamaguchi T, Uchida A, Ohba H, Oka S (2009) Contingent negative variations associated with command swallowing in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 120(10):1845–1851
Humbert IA, German RZ (2013) New directions for understanding neural control in swallowing: the potential and promise of motor learning. Dysphagia 28(1):1–10
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, Nitschke T, Massey B, Daniels S et al (2002) Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening. Gastroenterology 122(5):1314–1321
Nagy A, Leigh C, Hori SF, Molfenter SM, Shariff T, Steele CM (2013) Timing differences between cued and noncued swallows in healthy young adults. Dysphagia 28(3):428–434
Al-Toubi AK, Doeltgen SH, Daniels SK, Corey DM, Huckabee ML (2015) Pharyngeal pressure differences between four types of swallowing in healthy participants. Physiol Behav 140:132–138
Nishino T, Takiwaze K, Yokokawa N, Hiraga K (1987) Depression of the swallowing reflex during sedation and/or relative analgesia produced by inhalation of 50% nitrous oxide in oxygen. Anesthesiology 67:995–998
Singhi P, Kumar M, Malhi P, Kumar R (2007) Utility of the WHO ten questions screen for disability detection in a rural community—the North Indian experience. J Trop Pediatr 53(6):383–387
Mackowiak RC, Brenman HS, Friedman MH (1967) Acoustic profile of deglutition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 125:149–152
Hamlet S, Nelson R, Patterson R (1990) Interpreting the sounds of swallowing: fluid flow through the cricopharyngeous. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 99:749–752
Hiss SG, Treole K, Stuart A (2001) Effects of age, gender, bolus volume, and trial on swallowing apnea duration and swallow/respiratory phase relationships of normal adults. Dysphagia 16(2):128–135
Kim Y, McCullough GH, Asp CW (2005) Temporal measurements of pharyngeal swallowing in normal populations. Dysphagia 20(4):290–296
Martin-Harris B, Brodsky MB, Michel Y, Ford CL, Walters B, Heffner J (2005) Breathing and swallowing dynamics across the adult lifespan. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131(9):762–770
Balasubramanium RK, Bhat JS (2012) Respiratory swallow coordination in healthy individuals. Int J Adv Speech Hear Res 1(1):1–9
Nikhil J, Naidu RK, Krishnan G, Manjula R (2014) Oral and pharyngeal transit time as a factor of age, gender, and consistency of liquid bolus. J Laryngol Voice 4(2):45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of the present study declare that, we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
An informed consent was obtained from all the participants of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Modified Screening Checklist Based on WHO Ten Point Disability Checklist
S. no. | Particulars | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Does the individual have any orosensory problems? | ||
2 | Does the individual have any swallowing problems? | ||
3 | Does the individual express through intelligible speech? | ||
4 | Can the individual understand spoken speech? | ||
5 | Does the individual have any vision problem? | ||
6 | Does the individual have any hearing problem? | ||
7 | Does the individual have any behavioral issues? | ||
8 | Does the individual have any weakness or stiffness in the limbs/difficulty in walking or moving his limbs? | ||
9 | Did the individual have any history of fits, becoming rigid or lost consciousness in the last 6 months? | ||
10 | Did the individual have any neurological, metabolic or systemic illnesses? | ||
11 | Did the individual meet with any serious accidents/illness? | ||
12 | Compared with others of the same age, does the individual appear in any way backward, slow or dull? |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahul, K., Swapna, N., Resmitha, R. et al. Comparison Between Automatic and Volitional Swallow in Healthy Individuals Using Tongue Array and Cervical Auscultation Modules. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71, 520–530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01699-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01699-7