Abstract
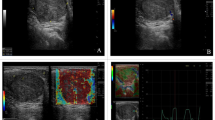
Cervical lymphadenopathy frequently poses a diagnostic challenge as neither clinical nor imaging assessment can reliably differentiate between benign and malignant lymphadenopathy. Non-invasive differentiation between the two may help to reduce the number of FNAC or biopsy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether the new ARFI technique (Virtual Touch Quantification), in conjunction with gray scale sonography and Doppler, can help in the characterization and differentiation of benign from malignant cervical lymphadenopathy. Fifty adult patients with cervical lymphadenopathy were included in the study and sonoelastography was done. Sonoelastographic findings were compared to the gold standard histopathology or cytopathology. ARFI measurements in benign and malignant enlarged lymph nodes were compared using the Student t test and ROC curve was used to arrive at the Youden index, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and diagnostic accuracy. Sonographic patterns indicative of malignancy includes heterogenous echopattern, short axis/long axis ratio > 0.5, absent echogenic fatty hilum and mixed vascular pattern. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy in differentiation between the benign and malignant lymph nodes using ARFI elastography was 79.17, 100, 100, 83.9 and 89.9% respectively. ROC curve analysis of SWVs for differentiation between the malignant and benign lymph nodes gave a cut-off value of 2.8 m/s with an area under curve of 0.892. ARFI imaging technique quantifies the tissue stiffness of the cervical lymph nodes non-invasively and aids in characterisation and differentiation of benign from malignant cervical lymphadenopathy in conjunction with conventional sonography.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang WT, Zhang ZH, Chen WH, Jiang Y, Tao JW, Zhou YZ (2003) Ultrasound surveillance of cervical lymph node metastasis in thoracic esophageal carcinoma. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 41(7):523–525
Mazaher H, Sharifkashani Sh, Sharifian H (2004) Triplex ultrasonographic assessment of cervical lymph nodes. Acta Med Iran 42(6):441–444
Dangore SB, Degwekar SS, Bhowate RR (2008) Evaluation of the efficacy of colour Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(4):205–212
Dayanand SM, Desai R, Reddy PB (2010) Efficiency of ultrasonography in assessing cervical lymphnode metastasis in oral carcinoma. Natl J Maxillofac Surg 1(2):117–122
Khanna R, Sharma AD, Khanna S, Kumar M, Shukla RC (2011) Usefulness of ultrasonography for the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy. World J Surg Oncol 9:29
Jayaraman V, Austin RD, Ramasamy R (2013) The efficacy of colour Doppler ultrasound in differentiating malignant and non-malignant head and neck lymph node enlargement. Int J Dent Sci Res 1(1):8–15
Naik RM, Pai A, Guruprasad Y, Singh R (2013) Efficacy of colour Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 12(2):123–129
Genes I, Mogoanta CA, Lostun G, Lostun A, Mozes H, Muhlfay G (2014) Ultrasonographic and histopathologic features of cervical lymph nodes metastases. Rom J Morphol Embryol 55(2):369–375
Raja Lakshmi C, Sudhakara Rao M, Ravikiran A, Sathish S, Bhavana SM (2014) Evaluation of reliability of ultrasonographic parameters in differentiating benign and metastatic cervical group of lymph nodes. ISRN Otolaryngol 2014:238740
Choi YJ, Lee JH, Lim HK, Kim SY, Han MW, Cho KJ, Baek JH (2013) Quantitative shear wave elastography in the evaluation of metastatic cervical lymph nodes. Ultrasound Med Biol 39(6):941–949
Meng W, Xing P, Chen Q, Wu C (2013) Initial experience of acoustic radiation force impulse ultrasound imaging of cervical lymph nodes. Eur J Radiol 82(10):1788–1792
Fujiwara T, Tomokuni J, Iwanaga K, Ooba S, Haji T (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for reactive and malignant/metastatic cervical lymph nodes. Ultrasound Med Biol 39(7):1178–1183
Cui XW, Jenssen C, Saftoiu A, Ignee A, Dietrich CF (2013) New ultrasound techniques for lymph node evaluation. World J Gastroenterol 19(30):4850–4860
Ying M, Bhatia KS, Lee YP, Yuen HY, Ahuja AT (2014) Review of ultrasonography of malignant neck nodes: grey scale, Doppler, contrast enhancement and elastography. Cancer Imaging 13(4):658–669
Ahuja AT, Ying M, Yuen HY, Metreweli C (2001) ‘Pseudocystic’ appearance of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomatous nodes: an infrequent finding with high-resolution transducers. Clin Radiol 56(2):111–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinayagamani, S., Prakash, A., Chowdhury, V. et al. Is Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Ultrasound Elastography Valuable in the Assessment of Cervical Lymphadenopathy?. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 70, 597–603 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1306-7