Abstract
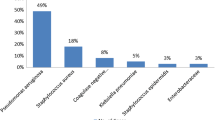
Inadequate antibiotic treatment, misuse/improper choice of antibiotic and poor compliance of patients have resulted in changes in susceptibility to antibiotics of the causative organisms and also development of resistance to commonly used antibiotics. Thus, this study aimed to identify the bacteriological profile and determine antibiotic susceptibility pattern in CSOM patients. This 1-year cross-sectional study was conducted on 120 clinically diagnosed cases of CSOM attending ear, nose, and throat outpatient department. Ear discharges obtained were processed for bacterial culture (aerobic and anaerobic). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was done by Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients were recorded. Of total 120 cases, pathogens were isolated from 116 cases. The commonest aerobic organism isolated was Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38.79%) followed by Staphylococcus aureus (32.75%). Staphylococcus aureus showed maximum sensitivity to erythromycin (71.05%), followed by cotrimoxazole (63.15%) and ampicillin (55.26%). Maximum resistance was observed for ciprofloxacin (78.9%), followed by amoxiclave (55.26%). Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed maximum sensitivity to piperacillin (91.11%) followed by gentamicin (71.11%), amikacin (71.11%), moderate sensitivity to ceftazidime (51.11%); however resistance to carbpenicillin (60%). Ciprofloxacin was the most prescribed topical agent showing an increase in resistance to common organisms of CSOM. Hence, it is mandatory to study each case of CSOM bacteriologically to formulate local antibiotic policy for appropriate use of antibiotics. This will certainly help in achieving a safe ear and to control the organisms developing resistance to prevalent antibiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Indudharan R, Haq JA, Aiyar S (1999) Antibiotics in chronic suppurative otitis media: a bacteriologic study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:440–445
Acuin J (2007) Chronic suppurative otitis media. BMJ Clin Evid 2007:0507
Adhikari P, Joshi S, Baral D, Kharel B (2009) Chronic suppurative otitis media in urban private school children of Nepal. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75:669–672
Varshney S, Nangia A, Bist S, Singh R, Gupta N, Bhagat S (2010) Ossicular chain status in chronic suppurative otitis media in adults. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62:421–426
Wasihun AG, Zemene Y (2015) Bacterial profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of otitis media in Ayder Teaching and Referral Hospital, Mekelle University, Northern Ethiopia. Springerplus 4:701
Sena RB, Gandham P (2016) Antibiotic susceptibility pattern among CSOM patients attending AIMSR. Natl J Integr Res Med 7:108–111
Okesola A, Fasina O (2012) Trends in the resistance pattern of bacterial pathogens of otitis media in Ibadan, Nigeria. Afr J Clin Exp Microbiol 13:416–450
Brook I, Frazier EH (1996) Microbial dynamics of persistent purulent otitis media in children. J Pediatr 128:237–240
Yogeesha B, Venkatesha B (2016) Study of bacteriological profile and antibiotic sensitivity pattern in chronic otitis media-mucosal type in tertiary care hospital. IOSR J Dent Med Sci 1:82–86
Smith JA, Danner CJ (2006) Complications of chronic otitis media and cholesteatoma. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 39:1237–1255
Mane PM, Basawraju A (2016) Clinical significance of microbial flora in middle ear infections and its implications. Trop J Med Res 19:128
Kumar D, Agarwal M, Prakash P (2016) Bacteriological profile of chronic suppurative otitis media in patients at a tertiary level hospital. Eastern J Med Sci 1:5–7
Poorey V, Lyer A (2002) Study of bacterial flora in CSOM and its clinical significance. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 54:91–95
Mohammad AH (2016) Chronic suppurative otitis media: microbial and antimicrobial findings. Int J Adv Res 4:1315–1320
Kumar R, Srivastava P, Sharma M, Rishi S, Nirwan S, Hemwaniand K (2013) Isolation and antimicrobial sensitivity profile of bacterial agents in chronic suppurative otitis media patients at NIMS Hospital. Int J Pharm Biol Sci 3:265–269
Deb T, Ray D (2012) A study of the bacteriological profile of chronic suppurative otitis media in agartala. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64:326–329
Saraswati JR, Venkatesh R, Jeya M (2013) Study of aerobic bacterial and fungal etiology of chronic suppurative otitis media in tertiary care hospital in out skirts of Chennai, India. Int J Health Sci Res 1:199–201
Vishwanath S, Mukhopadhyay C, Prakash R, Pillai S, Pujary K, Pujary P (2012) Chronic suppurative otitis media: optimizing initial antibiotic therapy in a tertiary care setup. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64:285–289
Loy A, Tan A, Lu P (2002) Microbiology of chronic suppurative otitis media in Singapore. Singapore Med J 43:296–299
Sharma K, Aggarwal A, Khurana PMS (2010) Comparison of bacteriology in bilaterally discharging ears in chronic suppurative otitis media. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62:153–157
Hiremath S, Kanta R, Yeshwanathrao M, Vasantha Kumar C (2001) Aerobic bacterial isolates of CSOM and their antibiotic sensitivity pattern. Indian Pract 54:486–489
Sharma V, Kaur G (2014) Microbiology and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of cases of chronic suppurative otitis media in a tertiary care teaching hospital. Int J Bioassays 3:3033–3035
Gulati SK (1997) Investigative profile in patients of chronic suppurative otitis media. Indian J Otol 3:59–62
Seid A, Deribe F, Ali K, Kibru G (2013) Bacterial otitis media in all age group of patients seen at Dessie referral hospital, North East Ethiopia. Egyptian J Ear, Nose, Throat Allied Sci 14:73–78
Pollock M (1996) Special role pseudomonas aeruginosa in CSOM: workshop on CSOM etiology and management. An Otorhinolaryngol 17:6
Prakash SK (2014) Aerobic bacteriology of chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) in a tertiary care hospital in North India. J Med Sci clin Res 2:395–398
Samarei R (2014) Comparison of local and systemic ciprofloxacin ototoxicity in the treatment of chronic media otitis. Glob J Health Sci 6:144
Ali SQ, Zehra A, Naqvi BS, Shah S, Bushra R (2010) Resistance pattern of ciprofloxacin against different pathogens. Oman Med J 25:294–298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiremath, B., Mudhol, R.S. & Vagrali, M.A. Bacteriological Profile and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A 1-Year Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 2), 1221–1226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1279-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1279-6