Abstract
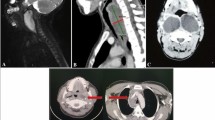
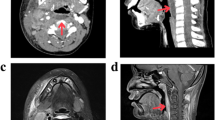
To discuss a case of suspected retropharyngeal abscess having important clinical and academic significance. This paper discusses an unusual presentation and evolution of a well known condition such as retropharyngeal abscess. Though the diagnosis in this case was initially a retropharyngeal abscess, several unusual findings were evident, which interfered with the optimal management of the patient. A literature review revealed rare causes and lesions mimicking a retropharyngeal abscess, such as retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis and Kawasaki disease, which are neither familiar to otolaryngologists nor other specialists such as orthopedicians. It is possible that this patient was both over treated and undertreated at the same time. Though the diagnosis in this case could not be established with certainty, several important pieces of information came up, especially unusual causes of retropharyngeal abscess and management of the same. Retropharyngeal abscess is a well-known condition with established modes of management. However, certain variations may occur and may pose challenges in diagnosis and management. These variations are little known and need to be highlighted so that optimal management is ensured.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pollak N, Wexler S (2013) Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis mimics retropharyngeal abscess. Case Rep Otolaryngol 2013:1–4
Hartley J (1964) Acute cervical pain associated with retropharyngeal calcium deposit. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg 46(8):1753–1754
Ring D, Vaccaro AR, Scuderi G, Pathria MN, Garfin SR (1994) Acute calcific retropharyngeal tendinitis. Clinical presentation and pathological characterization. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76(11):1636–1642
Kaplan MJ, Eavey RD (1984) Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93(3 Pt1):215–219
Paik NM, Lim CS, Jang HS (2012) Tendinitis of longus colli: computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and clinical spectra of 9 cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 36(6):755–761
Mihmanli I, Karaarslan E, Kanberoglu K (2001) Inflammation of vertebral bone associated with acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Neuroradiology 43:1098–1101
Razon RV, Nasir A, Wu GS, Soliman M, Trilling J (2009) Retropharyngeal calcific tendonitis: report of two cases. J Am Board Fam Med 22(1):84–88
Shin D, Ahn C, Choi J (2010) The acute calcific prevertebral tendinitis: report of two cases. Asian Spine J 4(2):123–127
Bettini N, Girardo M, Dema E, Cervellati S (2009) Evaluation of conservative treatment of non-specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J 18(1):143–150
Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ (2000) Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical managemen. Spine 25(13):1668–1679
Ansari S, Ashraf AN, Moutaery KA (2001) Spinal infections-A review. Neurosurg Q 11(2):112–123
Lai PL, Leu HS, Niu CC, Chen WJ, Chen LH (2005) Pyogenic spondylitis presenting with skip lesions. Chang Gung Med J 28(9):651–656
Doita M, Nabeshima Y, Nishida K, Fujioka H, Kurosaka M (2007) Septic arthritis of lumbar facet joints without predisposing infection. J Spinal Disord Tech 20(4):290–295
Stamos JK, Corydon K, Donaldson J, Shulman ST (1994) Lymphadenitis as the dominant manifestation of Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 93:525–528
Rowley AH, Shulman ST (2004) Kawasaki disease. In: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 17th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 793–834
Ganesh R, Srividhya VS, Vasanthi T, Shivbalan S (2010) Kawasaki disease mimicking retropharyngeal abscess. Yonsei Med J 51(5):784–786
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association Pediatrics 114:1708–33
Rothfield RE, Arriaga MA, Felder H (1990) Peritonsillar abscess in Kawasaki disease. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 20(1):73–79
Pontell J, Rosenfeld RM, Kohn B (1994) Kawasaki disease mimicking retropharyngeal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 110(4):428–430
Gross M, Eliashar R, Attal P, Sichel JY (2001) Radiology quiz case 2: Kawasaki disease (KD) mimicking a retropharyngeal abscess. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127(12):1507–1509
Falcini F (2006) Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:33–38
Rodrigue E, Costa J (2014) An unusual cause of neck pain: acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli. J Med Cases 5(3):171–173
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their heartfelt gratitude to the staff of the hospital to which the patient had been referred for further management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Consent of patient and family was obtained for publication of this report and confidentiality has been maintained.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1135-0.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, P.P., Poduval, J. & Divakaran, S. Review Article: Retropharyngeal Abscess—Mimickers and Masqueraders. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69, 269–273 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1105-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1105-6