Abstract
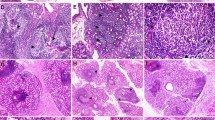
Lymphoepithelial salivary gland cysts are rarely seen in autoimmune diseases particularly Sjogren syndrome as well as in HIV for which medical management is advocated. To study the morphology of these cysts, correlate with the disease process and assess the final outcome. Case series. Fine needle aspiration clinic. HIV-infected and autoimmune disease patients with lymphoepithelial cysts. Antiretroviral therapy for HIV-patients and anti-inflammatory drugs for Sjogren syndrome. Three HIV-infected patients (two children and one adult) and three middle aged female patients presented with parotid and submandibular cysts, two of which were bilateral along with submandibular (one each in the HIV and the autoimmune group). In the adult HIV-patient, the cyst was found at the inception of the disease while the other pediatric HIV-patients just crossed a decade. Of the other three cases of Sjogren syndrome, two were primary and one, secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. All the cysts regressed completely with treatment of the respective diseases which was confirmed by ultrasonograms. Lymphoepithelial cysts are produced by release of serous secretion by the acinar and ductal cells within the epithelial islands in the process of their destruction. Possibly, antibody mediated increased secretion in the initial stages also plays a role. Lymphoepithelial cysts of HIV patients may occur in the course of treatment, not necessarily in the beginning, though it resolves spontaneously. Lymphoepithelial cysts of primary or secondary Sjogren syndrome may be repressed sufficiently by anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressant treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellis GL, Auclair PL (2007) Tumors of the salivary glands. Atlas of tumor pathology, 4th series, fascicle 9, 1st edn. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington
Craven DE, Duncan RA, Stram JR, O’Hara CJ, Steger KA, Jhamb K et al (1998) Response of lymphoepithelial parotid cysts to antiretroviral treatment in HIV-infected adults. Ann Intern Med 128:455–459
Greenspan D, Daniels TE, Talal N (1974) The histopathology of Sjogren’s syndrome in labial salivary gland biopsies. Oral Surg 37:217–229
http://www.naco.gov.in/ [home page on internet] Antiretroviral Therapy guidelines for HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents: updated May (2013) Department of AIDS control. National AIDS control organization (NACO), Ministry of health and family welfare, Government of India. http://www.naco.gov.in/upload/Policies%20&%20Guidelines/Antiretroviral%20Therapy%20Guidelines%20for%20HIV-Infected%20Adults%20and%20Adolescents.pdf
Harris NL (1999) Lymphoid proliferations of the salivary glands. Am J Clin Pathol 111:S94–S103
Ihrler S, Zietz C, Sendelhofert A, Riederer A, Lohrs U (1999) Lymphoepithelial duct lesions in Sjögren-type sialadenitis. Virchows Arch 434:315–324
Rosai J (2011) Major and minor salivary glands. In: Rosai J (ed) Rosai and Ackerman’s surgical pathology, 10th edn. Mosby Elsevier, Edinburgh, pp 817–856
Chetty R (1998) HIV-associated lymphoepithelial cysts and lesions: morphological and immunohistochemical study of the lymphoid cells. Histopathology 33:222–229
Ellis GL (2007) Lymphoid lesions of salivary glands: malignant and benign. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 12(7):E479–E485
Volpé R, Farid NR, Von Westarp C, Row VV (1974) The pathogenesis of Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin Endocrinol 3:239–261
Itescu S, Dalton J, Zhang HZ et al (1993) Tissue infiltration in a CD8 lymphocytosis syndrome associated with human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection has the phenotypic appearance of an antigenically driven response. J Clin Investig 91:2216–2225
Bahler DW, Swerdlow SH (1998) Clonal salivary gland infiltrates associated with myoepithelial sialadenitis (Sjögren’s syndrome) begin as nonmalignant antigen-selected expansions. Blood 91(6):1864–1872
Fox RI, Tornwall J, Michelson P (1999) Current issues in the diagnosis and treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 11:364–371
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan S (2002) Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis 61:554–558
Abdelghani KB, Mahmoud I, Chatelus E, Sordet C, Gottenberg JE, Sibilia J (2015) Br J Med Med Res 5:1287–1293
http://www.naco.gov.in/ [home page on internet] Pediatric antiretroviral therapy (ART) guidelines (2013) Department of AIDS control. National AIDS control organization (NACO). Ministry of health and family welfare. Government of India. http://naco.gov.in/upload/2014%20mslns/CST/Pediatric_14-03-2014.pdf
Author’s Contribution
Concepts: DS, RT; Design: DS, RT and MN; Definition of intellectual content: DS; Literature search: DS, RT, ND, MS and MN; Clinical studies: DS, RT and MN; Experimental studies: DS, FDL, ND and MS; Data acquisition: DS, RT and MN; Data analysis: DS, ND and MS; Manuscript preparation: DS; Manuscript editing: DS; Manuscript review: DS, RT, FDL, ND, MS and MN; Guarantor: DS, RT, FDL, ND, MS and MN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, D., Tapadia, R., Lobo, F.D. et al. Lymphoepithelial Sialadenitis Involving HIV-Infected and Sjogren Syndrome Patients: A Cytologic Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71, 176–181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1066-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1066-9