Abstract
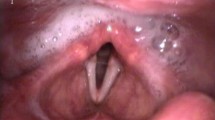
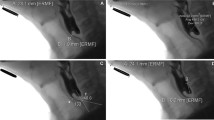
Dysphagia is a common symptom with diverse etiology in otolaryngology. In the present study clinicopathological, radiological and endoscopic evaluation of patients was done in a tertiary care hospital in patients presenting with dysphagia. A prospective nonrandomized observational study was carried out on total of 80 cases having dysphagia during March 2015 to August 2016. In the present study, out of 80 patients, youngest case was a three years old child while oldest case was an 85 years old female. The mean age was 48.3 ± 20.3 years. The majority of cases were in age group 41–59 years (35%). Male to female ratio was 2.33:1. The mean duration of illness was 15.44 weeks. 15% of patients had absolute dysphagia. For detecting the lesion, Barium swallow study (BSS) showed a total sensitivity of 49.05% (n = 53), Computerised Tomography (CT) showed a total sensitivity of 85.70% (n = 49), plain skiagram neck & chest showed a total sensitivity of 88.88% (n = 9) and endoscopy was the most sensitive test overall as it showed a total sensitivity of 98.75% (n = 80). No complications were reported with either rigid or flexible endoscopy. Dysphagia is a common presenting complaint in otolaryngology with cases coming directly or being referred from other specialities. Males are more commonly affected than females and incidence of malignancy increases with age. Endoscopy can become the first screening test in dysphagia due to its high sensitivity and low risk of complications, with radiological tests being done in an adjunct manner.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Gastroenterology Organisation Practice Guidelines (2007) Dysphagia : 01. http://almacen-gpc.dynalias.org/publico/Dysphagia%20WGO%202004%20Ingles.pdf
Tongper D, Naloh M, Hajong R (2015) Clinical and endoscopic study of dysphagia: a prospective cross-sectional study at a tertiary care centre at North-Eastern India. IOSR J Dent Med Sci (IOSR-JDMS) 14(2):9–11. http://journals.indexcopernicus.com/abstract.php?icid=1141591
Kishve SP, Aarif SMM, Kishve PS et al (2011) Clinico-pathological profile of oesophageal dysphagia. Indian Med Gaz 145(10):379–383 http://imsear.li.mahidol.ac.th/handle/123456789/157341
Nino-Murcia M, Vincent ME, Vaughan C (1990) Esophagography and esophagoscopy comparison in the examination of patients with head and carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116(8):917–919
Mazzeo S, Caramella D, Gennai A et al (2004) Multidetector CT and virtual endoscopy in the evaluation of the esophagus. Abdom Imaging 29:2
Gopalakrishnan S, Praveenkumar (2013) Epidemiological study on head and neck malignancies—a study of 150 cases. Otolaryngol Online J 3(1):1. ISSN: 2250–0359. http://www.jorl.net/abstract/epidemiological-study-on-head-and-neck-malignancies--a-study-of-150-cases-4033.html
Dabadghao VS, Kakrani AL (2015) A study of clinical and endoscopic findings in benign strictures of middle and lower thirds of esophagus. Indian J Basic Appl Med Res 5(1):752–756
Nanda V, Kochhar R (1986) Endoscopic dilatation of benign esophageal strictures. Indian J Gastroenterol 5(4):271–273
Desai DC, Swaroop VS (1992) Outpatient esophageal dilatation: an experience in 130 patients using Savary-Gilliard dilators. Indian J Gastroenterol 11(2):65–67
Wennervaldt K, Melchiors J (2012) Risk of perforation using rigid oesophagoscopy in the distal part of oesophagus. Dan Med J 59(11):01–04
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest is declared.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sachdeva, K., Kaul, V. Correlation of Radiological and Endoscopic Findings in Patients Presenting with Dysphagia. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69, 72–76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1047-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1047-4