Abstract
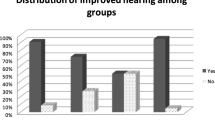
This study evaluates the outcome of type 1 tympanoplasty with and with out mastoidectomy. The comparative study comprises of 40 patients with CSOM safe type in dry ear. All cases were operated during a period of one and a half years. 20 of these cases were selected for tympanoplasty alone (Group A) and 20 cases were selected for Tympanoplasty with cortical mastoidectomy (Group B). Patients were reviewed after 3 weeks for inspection of the operated ear. The second and third postoperative reviews were done 6 and 12 weeks respectively for clinical assessment of the operated ear with respect to graft status, ear discharge and hearing improvement. The postoperative audiograms were recorded after 3 months. Type I tympanoplasty with cortical mastoidectomy has better graft uptake (100 %) as compared to without mastoidectomy (95 %). Post-operative A–B gap closure is better in tympano-mastoidectomy (20.48 dB) than tympanoplasty (15.75 dB) with p value <0.05. Post-operative hearing gain and graft uptake were both better with tympano-mastoidectomy and tympanoplasty.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chavan S, Deshmukh S, Pawar V, Kirpan V, Khobragade S, Sarvade K (2011) Tympanoplasty with and without cortical mastoidectomy for tubotympanic type of chronic suppurative otitis media. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 8(1):8–10
Browning GG, Merchant SN, Kelly G, Swan RC, Canter R, Mckerrow WS (2008) Chronic otitis media. In: Gleeson M, Browning GG, Burton MJ, Clarke RW, Hibbert J, Jones NS, Lund VJ, Luxon L, Watkinson JC (eds) Scott-Brown’s otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, vol 3, 7th edn. Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd, London, pp 3395–3401
Jackler S (1983) Myringoplasty with simple mastoidectomy: results in eighty two consecutive patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91:14–17
Holmquist J, Bergstorm B (1978) Mastoid air cell system in ear surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 104:127–129
Wullstein H (2003) Tympanoplasty. In: Glasscock ME, Shambaugh GE (eds) Surgery of the Ear, 5th edn. Elsevier, Hamilton, p 466
Browning GG, Merchant SN, Kelly G, Swan RC, Canter R, Mckerrow WS (2008) Chronic otitis media. In: Browning GG, Burton MJ, Clarke RW, Hibbert J, Jones NS, Lund VJ, Luxon L, Watkinson JC (eds) Scott-Brown’s otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, vol 3, 7th edn. Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd, London, pp 3424–3439
Glasscock ME (1976) Contraindications to tympanoplasty II: an exercise in clinical judgment. Laryngoscope 86:70–76
Awan Z, Bashin H, Hussain A (2008) Myringoplasty: a comparative study of different graft materials and various surgical procedures. Ann Pak Inst Med 4(4):209–211
Kontantinidis I, Malliari H, Tsakiropoulou E (2010) Fat myringoplasty as an office based procedure. Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 42:25–28
Kabdwal N, Varshney S, Bist SS, Bhagat S, Mishra S, Agarwal V (2013) Pre and post operative evaluation of hearing in chronic suppurative otitis media. Indian J Otol 19:164–168
Nayak DR, Balakrishnan R, Hazarika P, Mathew PT (2003) Role of cortical mastoidectomy in the results of myringoplasty for dry tubotympanic disease. Indian J Otol 9:11–15
Ashok KS, Munsi DM, Ghosh SN (2006) Evaluation of improvement of hearing in type 1 tympanoplasty and its influencing factors. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 58(3):253–257
Yasuo M, Masafumi S, Yoshifumi T, Kitahara T, Kajikawa H, Takeshi K (2001) Tympanoplasty with and without mastoidectomy for non-cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258(1):13–15
Goyal R (2010) Role of cortical mastoidectomy in type I tympanoplasty. Indian J Otol 16:8–12
Ruhl CM, Pensak ML (1999) Role of aerating mastoidectomy in non cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media. Laryngoscope 109(12):1924–1927
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest and there is no financial disclosure. Detailed written consent was taken from all the patients who have participated in the study pre-operatively.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Baisakhiya, N., Garg, L.N. et al. Evaluation of Role of Mastoid Surgery in the Management of Safe Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 68, 434–440 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0921-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0921-9