Abstract
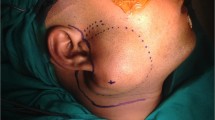
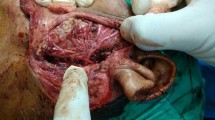
The anteriorly based partial thickness sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle flap is among the various methods described to correct parotidectomy defects, but its indications and limitations are not clearly demonstrated in several reports. This study was done to test the aesthetic outcome of this method, its indications and limitations. At Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Memorial hospital, Mumbai, 20 patients presenting with benign parotid tumors underwent parotidectomy. 16 underwent superficial parotidectomy and 3 underwent adequate parotidectomy, 1 had total parotidectomy. The anteriorly based partial thickness SCM muscle flap was used to correct the contour deformity and to prevent Frey syndrome. The aesthetic result was evaluated by assessing and scoring the overall appearance of the scar, the degree of symmetry of the reconstructed parotid region and the site of the donor muscle in comparison to their contralateral normal sides. The overall aesthetic appearance was good in 17 patients, and moderate in 3 patients. 17/20 patients had an overall deep satisfaction with the result. The residual hollowness following total parotidectomy defect and the poor quality of scars were the main reasons affecting the aesthetic outcome. Superficial parotidectomy through modified Blair’s incision with immediate reconstruction with anteriorly based partial thickness SCM flap allows a satisfactory aesthetic outcome and minimal donor site morbidity. Scores of the above two parameters were accessed. Patients’ satisfaction was assessed by patients questionnaire.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanabria A, Kowalski LP, Bradley PJ, Hartl DM, Bradford CR et al (2012) Sternocleidomastoid muscle flap in preventing Frey’s syndrome after parotidectomy: a systemic review. Head Neck 34(4):589–598
Appiani E, Delfino MC (1984) Plastic incisions for facial and neck tumors. Ann Plast Surg 13:335–352
Witt RL, Pribtikin EA (2013) How can Frey’s syndrome be prevented or treated following parotid surgery? Laryngoscope 123(7):1573–1574
Cesteleyn L, Helman J, King S, Van de Vyvere G (2002) Temporoparietal fascia flaps and superficial musculoaponeurotic system plication in parotid surgery reduces Frey’s syndrome. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1284–1297 (discussion 1297–1298)
Fee WE Jr, Tran LE (2004) Functional outcome after total parotidectomy reconstruction. Laryngoscope 114:223–226
Nouraei SA, Al-Yaghchi C, Ahmed J, Kirkpatrick N, MansuriS Singh A et al (2006) An anatomical comparison of Blair and facelift incisions for parotid surgery. Clin Otolaryngol 31:531–534
Hui Y, Wong DS, Wong LY, Ho WK, Wei WI (2003) A prospective controlled double-blind trial of great auricular nerve preservation at parotidectomy. Am J Surg 185:574–579
Meningaud JP, Bertolus C, Bertrand JC (2006) Parotidectomy; assessment of a surgical technique including facelift incision and SMAS advancement. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 34:34–37
Amin A, Moustafa A, Rihata M (2011) Parotidectomy for benign parotid tumors: an aesthetic approach. J Egypt Natl Cancer Inst 23:67–72
Ahmed OA, Kolhe PS (1999) Prevention of Frey’s syndrome and volume deficit after parotidectomy using the superficial temporal artery fascial flap. Br J Plast Surg 52:256–260
Bugis SP, Young JE, Archibald SD (1990) Sternocleidomastoid flap following parotidectomy. Head Neck 12:430–435
Chow TL, Lam CY, Chiu PW, Lim BH, Kwok SP (2001) Sternomastoid- muscle transposition improves the cosmetic outcome of superficial parotidectomy. Br J Plast Surg 54:409–411
Gooden EA, Gullane PJ, Irish J, Katz M, Carroll C (2001) Role of the sternocleidomastoid muscle flap preventing Frey’s syndrome and maintaining facial contour following superficial parotidectomy. J Otolaryngol 30:98–101
Hamilton J, Avitia S, Osborne RF (2006) Designing a bipedicled sternocleidomastoid muscle flap for parotidectomy contour deformities. Ear Nose Throat J 85:20–21
Kim SY, Mathog RH (1999) Platysma muscle-cervical fascia sternocleidomastoid muscle (PCS) flap for parotidectomy. Head Neck 21:428–433
Biglioli F, Autelitano L (2007) Reconstruction after total parotidectomy using a de-epithelialized free flap. J Craniomaxillofacial Surg 35:364–368
Kornblut AD, Westphal P, Miehlke A (1974) The effectiveness of a sterno-mastoid muscle flap in preventing postparotidectomy occurrence of the Frey syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol 77:368–373
Li C, Yang X, Pan J, Shi Z, Li L (2013) Graft for prevention of Frey syndrome after parotidectomy: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Oral Maxillofacial Surg 71(2):419–427
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalmia, D., Behera, S.K. & Bhatia, J.s.S. Anteriorly Based Partial Thickness Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Flap Following Parotidectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 68, 60–64 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0906-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0906-8