Abstract
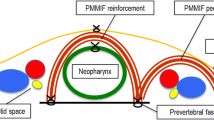
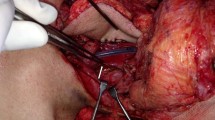
To evaluate our results of post laryngectomy pharyngeal defect reconstruction by pectoralis major myocutaneous (PMMC) flap. Retrospective analysis of 48 patients who underwent laryngectomy and PMMC patch pharyngeal reconstruction from year 2009 to 2013 was done. Patient and tumor characteristics were noted, CT scan and histopathology reports were reviewed. 46 (95.8 %) patients were male and 2 (4.2 %) were female. Mean age was 57.2 ± 8.5 years and mean postoperative stay was 22.6 ± 12.0 days. Most common complication was pharyngocutaneous fistula, seen in 13 (27.1 %) cases. Postoperative mortality was low (2.1 %). Post surgery rehabilitation in respect to swallowing and tolerance to radiotherapy was satisfactory in most patients. PMMC patch pharnygoplasty is a reliable option for pharyngeal reconstruction with acceptable complication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welkoborsky HJ, Deichmüller C, Bauer L, Hinni ML (2013) Reconstruction of large pharyngeal defects with microvascular free flaps and myocutaneous pedicled flaps. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21(4):318–327
Clark JR, Gilbert R, Irish J, Brown D, Neligan P, Gullane PJ (2009) Morbidity after flap reconstruction of hypopharyngeal defects. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 21(1):23–32
Ariyan S (1979) The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. A versatile flap for reconstruction in the head and neck. Plast Reconstr Surg 63:73–81
Okamura H, Inaki S, Mori T (1991) Swallowing function following hypopharyngeal reconstruction with the pectoralis major musculocutaneous flap. Auris Nasus Larynx 18(4):383–389
Spriano G, Pellini R, Roselli R (2002) Pectoralis major myocutaneous flap for hypopharyngeal reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1408–1413 discussion 1414–1416
Piazza C, Taglietti V, Nicolai P (2012) Reconstructive options after total laryngectomy with subtotal or circumferential hypopharyngectomy and cervical esophagectomy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20(2):77–88
Carlson GW, Schusterman MA, Guillamondegui OM (1992) Total reconstruction of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: a 20-year experience. Ann Plast Surg 29:408–412
Triboulet JP, Mariette C, Chevalier D, Amrouni H (2001) Surgical management of carcinoma of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: analysis of 209 cases. Arch Surg 136:1164–1170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhera, K.K., Shenoy, A.M., Chavan, P. et al. PMMC Patch Pharyngoplasty Reconstruction After Laryngectomy: Our Experience at a Regional Cancer Institute. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67, 170–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0833-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0833-8