Abstract
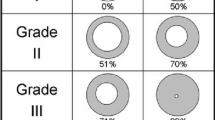
The aim of the study was to examine and analyze the epidemiology and outcome of treatment for paediatric acquired subglottic stenosis treated with endoscopic bougie dilatation and topical mitomycin C. There were 15 patients identified from 2008 until 2013. All of them had acquired subglottic stenosis due to history of intubation. Majority of the patients had grade III stenosis, with the total of seven. Three patients had grade IV; three were grade II and two were grade I. All of the patients with severe stenosis (grade III and IV) needed tracheostomy while only one in mild stenosis group (grade I and II) required it for prolonged ventilation rather than obstruction due to subglottic stenosis. All of them underwent direct laryngoscopy under general anesthesia followed by endoscopic dilatation with bougie and topical mitomycin C 0.4 mg/ml for 5 min. Aim of success in our study was decannulation of tracheostomy or absence of symptoms at exertion. We achieved 6 (60 %) successful decannulation out of 10 patients with tracheostomy (excluded the patient with tracheostomy in grade I stenosis due to prolonged ventilation). As for those without tracheostomy, 3 (75 %) out of 4 patients were asymptomatic even at exertion. Average number of dilatation was 3.1 times, with mean duration of 28 min. No complications were reported in our series. One patient with grade I stenosis passed away due to severe pneumonia unrelated to the stenosis or dilatation, and she did not have any dilatation before she passed away. Multiple related risk factors were identified such as intubation, prematurity, movement of endotracheal tube, respiratory infection, traumatic intubation and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Experience of open surgical method was very limited in our centre in Sabah in East Malaysia. Endoscopic technique plays an important role in treatment of subglottic stenosis with adjunct like mitomycin C possibly booster the successful rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotton RT, Evans JN (1981) Laryngotracheal reconstruction in children. 5 year follow up. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 90:516–520
Holinger PH, Kutnick SL, Schild JA, Holinger LD (1976) Subglottic stenosis in infants and children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 85:591–599
Sasaki CT, Horiuchi M, Koss N (1979) Tracheostomy related subglottic stenosis: bacteriologic pathogenesis. Laryngoscope 89:857
Noyek AM (1976) Xeroradiography in the assessment of the pediatric larynx and trachea. J Otolaryngol 5:468–474
Koufman JA (1991) The otolaryngologic manifestation of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24 hour pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Larungoscope 101(suppl 53):1
McDonald IH, Stocks JG (1965) Prolonged nasotracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth 37:161
Walner DI, Loewen MS, Kimura RE (2001) Neonatal subglottic stenosis—incidence and trends. Laryngoscope 111(1):48–51
Strong MS, Vaughan CW, Polanyi T, Wallace R (1974) Bronchoscopic carbon dioxide laser surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 83:769–776
Shapshay SM, Beamis JF, Hybels RL, Bohigian RK (1987) Endoscopic treatment of subglottic and tracheal stenosis by radial laser incision and dilation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 96:661–664
Ossolf RH, Tucker GF, Duncavage JA, Toohill RJ (1985) Efficacy of bronchoscopic carbon dioxide laser surgery for benign strictures of the trachea. Laryngoscope 95:1220–1223
Courey MS (1995) Airway obstruction: the problem and its causes. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 28(4):673–684
Eliashar R, Eliachar I, Esclamado R, Gramlich T, Strome M (1999) Can topical mitomycin prevent laryngotracheal stenosis? Laryngoscope 109(10):1594–1600
Doolin EJ, Strande LF, Tsuno K, Santos MC (1998) Pharmacologic inhibition of collagen in an experimental model of subglottic stenosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:275–279
Ingrams DR, Sukin SW, Ashton P et al (1998) Does Slow-release 5 flurouracil and nolone reduce subglottic stenosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:174–177
Palmer SS (1991) Mitomycin as adjunct chemotherapy with trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology 98:317–321
Jang CH, Song CH, Pak SC (2003) Effect of exposure to mitomycin C on cultured tympanic membrane fibroblasts. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 67:173–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liew, Y.T., Yong, D.J., Somasundran, M. et al. Management Experience of Subglottic Stenosis by Endoscopic Bougie Dilatation with Mitomycin C and Review of Literature: Case Series. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67 (Suppl 1), 129–133 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0801-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0801-8