Abstract
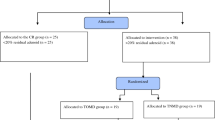
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of transoral or transnasal endoscopic-guided adenoidectomy compared with endoscopic nasopharyngeal inspection at the end of curettage adenoidectomy. A prospective case series of patients who had adenoidectomy. A total of 27 girls and 34 boys (age range 2.5–18 years) in whom adenoidectomy with or without tonsillectomy procedure was planned were included in the study. The cases were divided into three groups. Group 1 Transoral endoscopic-guided adenoidectomy performed patients. Group 2 Transnasal endoscopic-guided adenoidectomy performed patients. Group 3 Transnasal endoscopic nasopharyngeal exploration performed at the end of the conventional curettage adenoidectomy. The study was completed on 61 children. Mean age and sex frequency were not significant different between the groups. Mean operative time were 11.6 ± 2.9, 15.6 ± 4.4 and 9.7 ± 2 min, respectively (p > 0.05). On the other hand, significant differences were observed in operative time between group 1 and group 2 (p < 0.05), and between group 2 and group 3 (p < 0.05). Transnasal endoscopic examination at the end of curettage adenoidectomy is an appropriate method to assess the residual adenoid tissue after conventional curettage adenoidectomy. Also, operative time of this method is shorter than transoral or transnasal endoscopic-guided adenoidectomy. We recommend transnasal endoscopic inspection in all patients after conventional curettage adenoidectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon CR, Replogle WH, Schenk MP (1999) Endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:740–744
El-Badrawy A, Abdel-Aziz M (2009) Transoral endoscopic adenoidectomy. Int. J Otolaryngol 2009(2009):949315. doi:10.1155/2009/949315
Abdel-Aziz M (2012) Endoscopic nasopharyngeal exploration at the end of conventional curettage adenoidectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:1037–1040
Yıldırım YS, Apuhan T, Aksoy F, Veyseller B, Ozturan O (2014) Is Transnasal Endoscopic Examination Necessary Before and after adenoidectomy? Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 66:257–260
Wan YM, Wong KC, Ma KH (2005) Endoscopic-guided adenoidectomy using a classic adenoid curette: a simple way to improve adenoidectomy. Hong Kong Med J 11:42–44
Koltai PJ, Kalathia AS, Stanislaw P, Heras HA (1997) Power-assisted adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:685–688
Costantini F, Salamanca F, Amaina T, Zibordi F (2008) Videoendoscopic adenoidectomy with microdebrider. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 28:26–29
Stanislaw PJr, Koltai PJ, Feustel PJ (2000) Comparison of power-assisted adenoidectomy vs adenoid curette adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:845–849
Wynn R, Rosenfeld RM (2003) Outcomes in suction coagulator adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:182–185
Ark N, Kurtaran H, Ugur KS, Yilmaz T, Ozboduroglu AA, Mutlu C (2010) Comparison of adenoidectomy methods: examining with digital palpation versus visualizing the placement of the curette. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:649–651
Elnashar I, El-Anwar MW, Basha WM, AlShawadfy M (2014) Objective assessment of endoscopy assisted adenoidectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 May 14. pii: S0165–5876(14)00243-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.04.031. [Epub ahead of print]
Yanagisawa E, Weaver EM (1997) Endoscopic adenoidectomy with the microdebrider. Ear Nose Throat J 76:72–74
Öztürk Ö, Polat Ş (2012) Comparison of transoral power-assisted endoscopic adenoidectomy to curettage adenoidectomy. Adv Ther 29:708–721
Havas T, Lowinger D (2002) Obstructive adenoid tissue: an indication for powered-shaver adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:789–791
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaman, H., Memis, M. & Ilhan, E. Comparison of Transoral/Transnasal Endoscopic-Guided Adenoidectomy with Endoscopic Nasopharyngeal Inspection at the End of Curettage Adenoidectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67, 124–127 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0775-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0775-6