Abstract
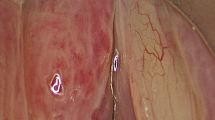
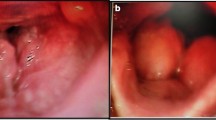
Tuberculosis is the most frequent granulomatous disease involving larynx. In most cases it is secondary to pulmonary tuberculosis. Incidence of tuberculosis is now on a rise due to increase in incidence of immune deficiency states. Here we present a report of clinical characteristic of laryngeal tuberculosis based on our experience of 10 cases. A detailed retrospective analysis of 10 patients of laryngeal tuberculosis was done at our tertiary care laryngology centre. Majority of patients had change of voice and dry cough. All the patients had hyperemia and edema of vocal cords. 80% patients had involvement of the arytenoids and ary-epiglottic folds. Frank granulomatous growth was seen in 70% of patients. In all patients histopathological report was consistent with tubercular granuloma. Two patients had associated pulmonary tuberculosis. Eight patients did not reveal any feature suggestive of previous or co-existent pulmonary tuberculosis. All patients responded to chemotherapy with complete resolution. Primary laryngeal tuberculosis is not as rare as generally considered. This series provides an insight towards clinical feature, growth pattern and management of tuberculosis of larynx.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulkarni NS, Gopal GS, Ghaisas SG, Guptel AN (2001) Epidemiological considerations and clinical features of ENT tuberculosis. J Laryngol Otol 115:555–558
Loehrl TA, Smith TL (2001) Inflammatory and granulomatous lesions of the larynx and pharynx. Am J Med 111:113–117
Rohwedder J (1974) Upper respiratory tract tuberculosis. Ann Intern Med 80:708–713
Zanaret M (2000) Tuberculose laríngea. In: Vercken S (ed) Encyclopédie médico-chirurgicale. Editions Scientifiques et Meédicales Elsevier SAS, Paris
Kandiloros DC, Nikopoulas TP, Ferekididis EA et al (1995) Laryngeal tuberculosis at the end of the 20th century. J Laryngol Otol 109:5–13
Harney M, Hone S, Timon C, Donnelly M (2000) Laryngeal tuberculosis: an important diagnosis. J Laryngol Otol 114:878–880
Galli J, Nardi C, Contucci AM et al (2002) Atypical isolated epiglottic tuberculosis: a case report and a review of the literature. Am J Otolaryngol 23:237–240
Soda A, Rub o H, Salazar M, Ganem J, Beilanga D, Sanchez A (1989) Tuberculosis of the larynx: clinical aspects in 19 patients. Laiıgosccpe 99:1147–1150
Ballenger JJ (1971) Diseases of the nose, throat and ear, 11th edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, p 366
Mehndiratta A, Bhat P et al (1997) Primary tuberculosis of larynx. Case Report Ind J Tub 44:211–212
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandhi, S., Kulkarni, S., Mishra, P. et al. Tuberculosis of Larynx Revisited: a Report on Clinical Characteristics in 10 Cases. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64, 244–247 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0333-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0333-4