Abstract
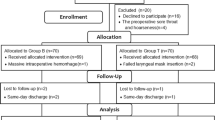
Impairment of laryngotracheal movement is a possible complication after total thyroidectomy. Here, we aimed to investigate the frequency and extent of impairment of laryngotracheal movement after total thyroidectomy and the effect of anti-adhesive barrier hyaluronic acid-carboxymethylcellulose membrane positioning between strap muscles and laryngotracheal complex on deglutition. The study design is prospective clinical study. Istanbul Training and Research Hospital, Laboratory of Electrophysiology, Istanbul Training and Research Hospital. The patients who underwent total thyroidectomy were selected and dichotomized according to use of seprafilm. Each group consisted of 8 female patients. All patients were assessed clinically and electrophysiologically in the pre/postop period. Electrophysiological investigations included cricopharyngeal muscle (CPM) electromyography (EMG), submental EMG, single bolus analysis [foreburst, reburst, swallowing (pause) patterns], laryngotracheal movement analysis and results were compared between two groups. CPM EMG was normal in both groups. Duration of submental muscle activity during dry and 15 cc water swallowing was similar between two groups (P = 0.751). Pause duration was shorter in group with seprafilm (P < 0.01). Dysphagia limit was 15 cc in both groups. The fore/rebound bursts duration, the time of laryngeal elevation, closure and suspension were similar (P = 0.954). We concluded that use of seprafilm between larynx and strap muscles during total thyroidectomy does not have any adverse effects on swallowing. Anti-adhesive barrier can be used safely during thyroid surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I (2003) Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2226–2244
Martin BJ, Logemann JA, Shaker R et al (1994) Coordination between respiration and swallowing: respiratory phase relationship and temporal integration. J Appl Physiol 76:714–723
Paydarfay D, Gilbert RJ, Poppel CS, Dodds WJ (1995) Respiratory phase resetting and airflow changes induced by swallowing in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 483:273–288
Yigit O, Coskun BU, Coskun H, Yilmaz B, Alkan S (2004) Efficacy of anti-adhesive barriers in secondary thyroidectomy: an experimental study. Laryngoscope 114:1668–1673
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yuceyar N (1996) Piecemeal deglutition and dysphagia limit in normal subjects and in patients with swallowing disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61:491–496
Ertekin C, Tarlaci S, Aydogdu I, Kıylıoglu N, Yuceyar N, Turman Bl (2002) Electrophysiological evaluation of pharyngeal phase of swallowing in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 17:942–949
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I (2002) Electromyography of human cricopharyngeal muscle of the upper esophageal sphincter—a review. Muscle Nerve 26:729–739
Dantas RO, IKern MK, Massev BT et al (1990) Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol 258:675–681
Hong KH, Kim YK (1997) Phonatory characteristics of patients undergoing thyroidectomy without laryngeal nerve injury. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 7:399–404
Akyildiz S, Ogut F, Akyildiz M, Engin EZ (2008) A multivariate analysis of objective voice changes after thyroidectomy without laryngeal nerve injury. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:596–602
Alfonsi E, Versino M, Merlo M et al (2007) Electrophysiologic patterns of oral-pharyngeal swallowing in Parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 68:583–589
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I (2002) Electromyography of human cricopharyngeal muscle of the upper esophageal sphincter—a review. Muscle Nerve 26:729–739
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yuceyar N et al (1997) Effects of bolus volumes on the oropharyngeal swallowing: an electrophysiological study in man. Am J Gastroenterol 11:2049–2053
Jones DV, Work CE (1961) Volume of swallow. Atl 7 Dis Child 102:427
Zeng Q, Yu Z, You J et al (2007) Efficacy and safety of seprafilm for preventing postoperative abdominal adhesion: systematic review and meta- analysis. World J Surg 31:2125–2131
Liakakos T, Thomakos N, Fine PM et al (2001) Peritoneal adhesions: etiology, pathophysiology and clinical significance. Dig Surg 18:260–273
Lombardi CP, Raffaelli M, D’alatri L et al (2008) Video-assisted thyroidectomy significantly reduces the risk of early postthyroidectomy voice and swallowing symptoms. World J Surg 32:693–700
Lombardi CP, Raffaelli M, D’Alatri L, Marchese MR (2006) Voice and swallowing changes after thyroidectomy in patients without inferior laryngeal nevre injuries. Surgery 140:1026–1032
Pereira JA, Girvent M, Sancho JJ, Parada C, Sitges-Serra A (2003) Prevalence of long term upper aero-digestive symptoms after uncomplicated bilateral thyroidectomy. Surgery 133:318–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkan, Z., Yigit, O., Adatepe, T. et al. Effect of Anti-Adhesive Barrier Use on Laryngotracheal Movement After Total Thyroidectomy: An Electrophysiological Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 66 (Suppl 1), 71–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0319-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0319-2