Abstract
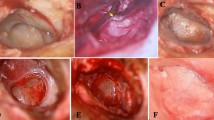
A theoretical risk of iatrogenic sensorineural hearing loss during surgery has induced a reluctance to perform bilateral tympanoplasty type I among some otosurgeons. This paper presents results of bilateral surgery in 14 patients (28 ears). Fourteen patients with bilateral, dry tympanic membrane perforations caused by chronic otitis media were selected prospectively for bilateral tympanoplasty type I (28 ears) at a tertiary referral center. All patients had a HL corresponding to the size and localization of the perforation (no suspicion of ossicular chain defect or other pathology). Mean age was 37.5 years. There were seven males and seven females in our study. All but five ears were operated through an endaural or endomeatal approach, and five ears operated by postaural approach. The Underlay technique was used in all cases. Total ten cases operated using Fascia Lata and four cases operated using Temporalis fascia as graft material. Follow-up examination and hearing tests (pure tone audiometry) were performed up to 20 months after surgery. The graft take rate was 96%, with no retraction pockets or displaced grafts observed during follow-up. One patient had small residual perforation which healed at the end of 3 months. Hearing improved significantly, and the air-bone gap was significantly reduced. The air-bone gap was closed to within 10 dB in 92% and within 20 dB in 100% of the ears. Surprisingly good hearing was found during postoperative, bilateral ear canal gauze packing. Iatrogenic sensorineural HL did not occur. We conclude that bilateral myringoplasty is safe, with good results, reduces costs, and leaves the patient satisfied. The hearing impairment during postoperative ear canal packing is surprisingly modest and readily acceptable by the patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Palva T, Kärjä J, Palva A (1973) High-tone sensorineural losses following chronic ear surgery. Arch Otolaryngol 98:176–178
Smyth GD (1977) Sensorineural hearing loss in chronic ear surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86:1–6
Tos M, Lau T, Plate S (1984) Sensorineural hearing loss following chronic ear surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:403–409
Mitchell RB, Pereira KD, Younis RT, Lazar RH (1996) Bilateral fat graft myringoplasty in children. Ear Nose Throat J 75:652–656
Katsura H, Sakagami M, Tsuji K et al (2005) Reevaluation of bilateral same-day surgery for bilateral perforated chronic otitis media. Otol Neurotol 26:842–845
Indorewala S et al (2004) Dimensional stability of the free fascia graft: a human study. The laryngoscope 114:543–547
Dhabolkar J et al (2007) Comparative study of underlay tympanoplasty with temporalis fascia and tragal perichondrium I. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 59:119–122
Tos M (1993) Manual of middle ear surgery, vol 1. Thieme, New York
Adkins WY, White B (1984) Type I tympanoplasty: influencing factors. Laryngoscope 94:916–918
Bajaj Y, Bais AS, Mukherjee B (1998) Tympanoplasty in children: a prospective study. J Laryngol Otol 112:1147–1149
Caylan R, Titiz A, Falcioni M et al (1998) Myringoplasty in children: factors influencing surgical outcome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:709–713 (Laryngoscope 117)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mane, R., Patil, B., Mohite, A. et al. Bilateral Type 1 Tympanoplasty in Chronic Otitis Media. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65, 293–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0294-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0294-7