Abstract
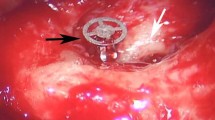
Stapedotomy with implantation of an alloplastic prosthesis is a well-established therapy for the treatment of otosclerosis. Since the middle of 2008, a new Nitinol prosthesis with memory function and superelastic properties has been available which is expected to make fixation on the long process of the incus much easier. The advantage of this prosthesis is that heat-induced wire crimping is no longer necessary and damage to the incus caused by heat is avoided. Since May 2008, laser-assisted stapedotomy with implantation of a Nitinol prosthesis was performed in 21 patients suffering from otosclerosis. The prostheses used for all patients had a size of 4.5 mm × 0.4 mm. The patient collective consisted of 14 women and 7 men with a mean age of 53.4 years. Pre- and postoperatively, an ENT examination was carried out followed by an audiological evaluation of the hearing result. In addition, the properties of the prosthesis (“proper fitt”, “handling”, and “overall rating”) were evaluated intraoperatively by means of a test protocol. The Nitinol prosthesis was implanted successfully in all 21 patients. The mean air-bone gap for the frequencies from 0.5 to 4 kHz was 9.83 dB postoperatively. Intraoperatively, the fit of the prosthesis was rated as “good to very good”, the handling as “good” and the overall rating of the system was “good to very good”. Our patient collective showed good postoperative hearing results. Due to simple intraoperative handling, especially placing the Nitinol prosthesis in position, the critical work step of crimping is no longer necessary.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shea JJ Jr (1958) Fenestration of the oval window. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 67(4):932–951
Shea JJ Jr (1998) A personal history of stapedectomy. Am J Otol 19(5 Suppl):S2–S12
Shea JJ Jr (1998) Forty years of stapes surgery. Am J Otol 19(1):52–55
House HP, Hansen MR, Al Dakhail AA, House JW (2002) Stapedectomy versus stapedotomy: comparison of results with long-term follow-up. Laryngoscope 112(11):2046–2050
Hausler R (2007) General history of stapedectomy. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 65:1–5
Jovanovic S, Schonfeld U, Scherer H (2006) “One shot” CO2 laser stapedotomy. HNO 54(11):842–850
Vincent R, Sperling NM, Oates J, Jindal M (2006) Surgical findings and long-term hearing results in 3,050 stapedotomies for primary otosclerosis: a prospective study with the otology-neurotology database. Otol Neurotol 27(8 Suppl 2):S25–S47
Tange RA, Grolman W, Dreschler WA (2004) Gold and titanium in the oval window: a comparison of two metal stapes prostheses. Otol Neurotol 25(2):102–105
Tange RA, de Bruijn AJ, Grolman W (1998) Experience with a new pure gold piston in stapedotomy for cases of otosclerosis. Auris Nasus Larynx 25(3):249–253
Causse JB, Causse JR, Parahy C (1985) Stapedotomy technique and results. Am J Otol 6(1):68–71
Jahnke K Dost P, Schrader M (1999) Biocompatibility studies of implants for reconstructive middle ear surgery. In: Yanagihara N, Suzuki JI (eds) Symposium on transplants in otology, Venice, Italy
Minovi A, Probst G, Dazert S (2009) Current concepts in the surgical management of otosclerosis. HNO 57(3):273–286
Kwok P, Fisch U, Strutz J, May J (2002) Stapes surgery: how precisely do different prostheses attach to the long process of the incus with different instruments and different surgeons? Otol Neurotol 23(3):289–295
Huettenbrink KB, Beutner D (2005) A new crimping device for stapedectomy prostheses. Laryngoscope 115(11):2065–2067
Bast F, Schrom T (2009) First experiences with the new soft-clip piston as an alloplastic prosthesis during stapedotomy. Laryngorhinootologie 88(5):304–308
Wengen DF (2007) A new self-retaining titanium clip stapes prosthesis. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 65:184–189
Stoeckel D, Pelton A, Duerig T (2004) Self-expanding nitinol stents: material and design considerations. Eur Radiol 14(2):292–301
Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Loewe C, Dick P, Amighi J, Mlekusch W et al (2006) Balloon angioplasty versus implantation of nitinol stents in the superficial femoral artery. N Engl J Med 354(18):1879–1888
Kasano F, Morimitsu T (1997) Utilization of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy for stapes prosthesis. Auris Nasus Larynx 24(2):137–142
Hornung J, Zenk J, Schick B, Wurm J, Iro H (2007) First experiences with a new nickel-titanium piston with a shape memory feature. HNO 55(2):104–108
Brown KD, Gantz BJ (2007) Hearing results after stapedotomy with a nitinol piston prosthesis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(8):758–762
Rajan GP, Diaz J, Blackham R, Eikelboom RH, Atlas MD, Shelton C et al (2007) Eliminating the limitations of manual crimping in stapes surgery: mid-term results of 90 patients in the Nitinol stapes piston multicenter trial. Laryngoscope 117(7):1236–1239
Knox GW, Reitan H (2005) Shape-memory stapes prosthesis for otosclerosis surgery. Laryngoscope 115(8):1340–1346
Hornung JA, Brase C, Bozzato A, Zenk J, Schick B, Iro H. (2009) Retrospective analysis of the results of implanting Nitinol pistons with heat-crimping piston loops in stapes surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:25–35
Babighian G, Fontana M, Caltran S, Ciccolella M, Amadori M, De Zen M (2007) The heat-activated stapes prosthesis ‘SMart’ Piston: technique and preliminary results. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 65:190–196
Tange RA, Grolman W (2008) An analysis of the air-bone gap closure obtained by a crimping and a non-crimping titanium stapes prosthesis in otosclerosis. Auris Nasus Larynx 35(2):181–184
Schobel H (2004) Realistic early and late results after otosclerosis surgery and presentation of a technique involving almost no complications. HNO 52(12):1049–1060
Schimanski G (1997) Erosion and necrosis of the long process of the incus after otosclerosis operation. HNO 45(9):682–689
Grolman W, Tange RA (2005) First experience with a new stapes clip piston in stapedotomy. Otol Neurotol 26(4):595–598
Zahnert T (2007) Nitinol as a memory-metal for the coupling of stapes prostheses. HNO 55(3):158–163
Shabalovskaya SA (1996) On the nature of the biocompatibility and on medical applications of NiTi shape memory and superelastic alloys. Biomed Mater Eng 6(4):267–289
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bast, F., Weikert, S. & Schrom, T. Treatment of Otosclerosis with a Superelastic Nitinol Piston: First Results. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63, 126–131 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0139-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0139-4