Abstract
Introduction
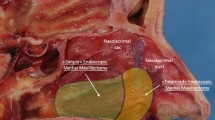
A medial maxillectomy (MM) consists of a complete resection of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus. Traditionally the surgery is performed via an open approach. With more familiarity and expertise in endoscopic sinus surgery the endonasal approach is feasible.
Objective
To expose the surgical technique and report the results of endonasal endoscopic MM in a series of 6 consecutive patients.
Materials and methods
Between August 2006 and October 2009, 6 patients were operated with this procedure. All were men. The mean age was 62-year-old (range: 43–83). In 5 cases, the surgery was performed for inverted papillomas confined to the maxillary sinus. In one case it was a primary surgery whereas it was a revision surgery for the others. The sixth patient was operated for a solitary extramedullary plasmocytoma inserted on the intersinonasal wall persistent after an external radiation therapy.
Results
All the patients are free of disease at the time of writing with a mean follow-up of 18,2 months (range: 9–38). This has been confirmed by a nasal endoscopy and CT scans. There were no major per or postoperative complications. Patients suffered from crusting for at least 6 months postoperatively necessitating daily nasal douches. One patient is still complaining of intermittent epiphora when he is exposed to wind.
Conclusion
Endoscopic MM can be successfully performed for the resection of expanding processes involving the maxillary sinus and/or the intersinonasal wall. Compared to open approaches, it seems to be as effective with less postoperative morbidity. An important technical point is to do the anterior osteotomy in front of the nasolacrimal duct in order to expose the prelacrimal recess that is typically an area for possible recurrence. Exact determination of the tumor attachment during the surgery is another key point for success.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanna N, Edwards JD, Aghdam H, Sadeghi N (2007) Maxillectomy as the initial oncologic approach to sinonasal neoplasms: the anatomic basis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(11):1139–1142
Kountakis Stilanos E, Önerci Metin (2007) Endoscopic medial maxillectomy. In: Rhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg 6: 119–124
Bielamowicz S, Calcaterra TC, Watson D (1993) Inverting papilloma of the head and neck: the UCLA update. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 109(1):71–76
Phillips PP, Gustafson RO, Facer GW (1990) The clinical behaviour of inverting papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses: report of 112 cases and review of the literature. Laryngoscope 100(5):463–469
Myers EN, Fernau JL, Johnson JT, Tabet JC, Barnes EL (1990) Management of inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 100:481–490
Han JK, Smith TL, Loehrl T, Toohill RJ, Smith MM (2001) An evolution in the management of sinonasal inverting papilloma. Laryngoscope 111(8):1395–1400
Wormald PJ, Ooi E, van Hasselt CA, Nair S (2003) Endoscopic removal of sinonasal inverted papilloma including medial maxillectomy. Laryngoscope 113(5): 867–873
Kraft M, Simmen D, Kaufmann T, Holzmann D (2003) Long-term results of endonasal sinus surgery in sinonasal papillomas. Laryngoscope 113(9):1541–1547
Sadeghi N, Al-Dhahri S, Manoukian JJ (2003) Transnasal endoscopic medial maxillectomy for inverting papilloma. Laryngoscope 113(4):749–753
Tomenzoli D, Castelnuovo P, Pagella F, Berlucchi M, Pianta L, Delù G, Maroldi R, Nicolai P (2004) Different endoscopic surgical strategies in the management of inverted papilloma of the sinonasal tract: experience with 47 patients. Laryngoscope 114(2):193–200
Krouse JH (2009) Evolution in the management of inverted papilloma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(3):336–337
Lane AP (2009) The role of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management osf sinonasal inverted Papilloma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 17(1):6–10
Lawson W, Patel ZM (2009) The evolution of management for inverted papilloma: an analysis of 200 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(3):330–335
Tsirbas A, Wormald PJ (2003) Mechanical endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy with mucosal flaps. Br J Ophthalmol 87(1):43–47
Booth JB, Cheesman AD, Vincenti NH (1973) Extramedullary plasmacytoma of the upper respiratory tract. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 82:709–715
Castro EB, Lewis JS, Strong EW (1973) Plasmocytoma of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity. Arch Otolaryngol 97:326–329
Kapadia SB, Desai U, Cheng VS (1982) Extramedullary plasmacytoma of head and neck. A clinicopathologic study of 20 cases. Medicine 6:317–329
Wax MK, Yun K J, Omar RA (1993) Extramedullary plasmacytomas of the head and neck. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 109:877–885
Liebross RH, Ha CS, Cox JD, Weber D, Delasalle K, Alexanian R (1999) Clinical course of extramedullary plasmacytoma. Radiother Oncol 52(3):245–249
Kaufman MR, Brandwein MS, Lawson W (2002) Sinonasal papillomas: clinicopathologic review of 40 patients with inverted and oncocytc schneiderian papillomas. Laryngoscope 112(8 Pt 1):1372–1377
Eloy P, Bachy V, Grulois V, Bertrand B (2008) Pyocele of the lachrymal sac — a late and unusual complication after surgery for a juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Clin Ophthalmol 2(1):211–215
Kalavagunta S, Roy D, Fish B, Jackson S (2002) Blindness following medial maxillectomy. Rhinology 40(4):223–225
Busquet JM, Hwang PH (2006) Endoscopic resection of sinonasal inverted papilloma: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(3):476–482
Bertrand B, Eloy P, Jorissen M, et al. (2000) Surgery of inverted papillomas under endoscopic control. Acta Otolaryngol Belg 542:139–150
Mortuaire G, Arzul E, Darras JA, Chevalier D (2007) Surgical management of sinonasal inverted papillomas through endoscopic approach. Eur Arch Otolaryngol 264(12):1419–1424
Sukenik MA, Casiano R (2000) Endoscopic medial maxillectomy for inverted papilloma of the paranasal sinuses: value of the intraoperative endocopic examination. Laryngocope 110:39–42
Lee TJ, Huang SF, Lee LA, Huang CC (2004) Endoscopic surgery for recurrent inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 114(1):106–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eloy, P., Mardyla, N., Bertrand, B. et al. Endoscopic endonasal medial maxillectomy: case series. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62, 252–257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-010-0076-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-010-0076-7