Abstract
Introduction
Tubercular laryngitis is a known entity since a long time but it’s presentation, diagnosis and management has undergone a drastic makeover after the advent of chemotherapy in the form of ATT (Anti tubercular treatment), modernized diagnostic aids and early detection of lesions.
Materials and methods
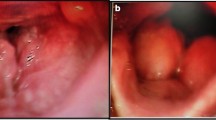
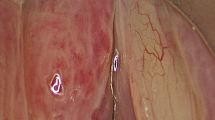
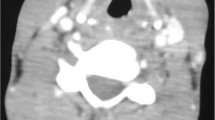
This prospective study was conducted on 180 patients. Each patient were subjected to detailed history and thorough ENT and head neck examination including laryngeal examination by visualization of the vocal cords, possibly using indirect laryngoscopy,. exible naso-laryngoscopy or rigid laryngoscopy Results Tubercular laryngitis was clinically diagnosed by laryngeal endoscopy and diagnosis con. rmed by laryngeal biopsy.
Conclusion
All patients showed remarkable improvement with anti-tubercular treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaelyn GC (1999) Hoarseness. Medical Clinics of North America 83:115–123
Orton HB (1941) Aetiology of hoarseness of voice. Laryngoscope 41:123–175
Varshney S, Hasan SA (1995) Clinico — Histopathological study of Laryngeal Biopsies. SDMH Journal 19:140–141
Kulkarni N, Gopal GS, Ghaisas SG (2001) Epidemiological considerations and clinical features of ENT Tuberculosis 115:555–558
Essad M (2001) Laryngeal tuberculosis: Apropos of 15 cases. Rev Laryngol Otol 122:125–128
Gaelyn GC (1999) Hoarseness; Medical Clinics of North America 83:115–123
Kleinsasser O (1982) Pathogenesis of vocal cord polyps. Annals of Otorhinolaryngol 91:378–381
Shin (2000) Changing trends in clinical manifestations of laryngeal tuberculosis. Laryngoscope 110(11):1950–1953
Farooq A (1994) The Larynx in Pulmonary Kocks. Indian Medical Gazette 361–362
Parikh Nimish P (1991) Aetiological study of 100 cases of hoarseness of voice. Indian Journal of Otolaryngolog 43: 71–73
Rupa V, Bhanu TS (1989) Laryngeal Tuberculosis in the eighties-An Indian Experience. J Laryngol Otol 103: 864–868
Galleti F, Freni F, Bucolo S, Spano F, Gambadoro O, Pispica L et al (2000) Laryngeal Tuberculosis: Considerations on the most recent clinical and epidemiological data and presentation of a case report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 20:196–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, R., Varshney, S., Bist, S.S. et al. Tubercular laryngitis: case series. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck S 60, 331–334 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-008-0111-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-008-0111-0