Abstract
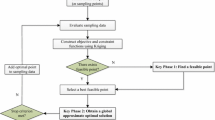
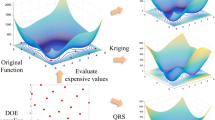
The Generalized Efficient Global Optimization (GEGO) algorithm assisted by Kriging model can solve black-box problem of complex computing. However, a single sampling point obtained in each iteration process may cause longer objective-evaluation time and slower convergence speed in contrast with multi-point sampling optimization methods. For this, a Kriging-based multi-point sequential sampling optimization (KMSSO) method is presented. The proposed method uses uncertainty estimate information of Kriging to construct the multiple-point generalized Expected Improvement (EI) criterion. In optimization cycle, this criterion is maximized to produce the Pareto front data, which will be further screened to obtain final expensive evaluation points. For numerical tests and an engineering case, KMSSO is compared to GEGO and HAM algorithm and is shown to deliver better results. It is also proves that when multiple points are added per cycle, the optimization accuracy and convergence property are both improved.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang M et al (2016) Transformation from business process models to BPEL with overlapped patterns involved. Int J High Perform Comput Netw 9(1–2):82–92
Li Y et al (2019) A Kriging-based bi-objective constrained optimization method for fuel economy of hydrogen fuel cell vehicle. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(56):29658–29670
Lu W et al (2016) A new method of QoS prediction based on probabilistic latent feature analysis and cloud similarity. Int J High Perform Comput Netw 9(1–2):52–60
Li Y et al (2019) A sequential Kriging method assisted by trust region strategy for proxy cache size optimization of the streaming media video data due to fragment popularity distribution. Multimed Tools Appl 78(20):28737–28756
Hu M-C et al (2019) Development of Kriging-approximation simulated annealing optimization algorithm for parameters calibration of porous media flow model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 33(2):395–406
Chang SE et al (2016) Cocktail: a service-oriented cloud storage architecture for enhancing service quality. Int J High Perform Comput Netw 9(1–2):19–30
Cassioli A, Schoen F (2013) Global optimization of expensive black box problems with a known lower bound. J Global Optim 57(1):177–190
Jones DR (2001) A taxonomy of global optimization methods based on response surfaces. J Global Optim 21(4):345–383
Müller J, Piché R (2011) Mixture surrogate models based on Dempster–Shafer theory for global optimization problems. J Global Optim 51(1):79–104
Duvigneau R, Chandrashekar P (2012) Kriging-based optimization applied to flow control. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 69(11):1701–1714
Regis RG (2014) Constrained optimization by radial basis function interpolation for high-dimensional expensive black-box problems with infeasible initial points. Eng Optim 46(2):218–243
Ller J, Shoemaker CA, Robert P (2013) SO-MI: a surrogate model algorithm for computationally expensive nonlinear mixed-integer black-box global optimization problems. Comput Oper Res 40(5):1383–1400
Chen L et al (2019) Comparative study of HDMRs and other popular metamodeling techniques for high dimensional problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59(1):21–42
Shi R et al (2019) Filter-based adaptive Kriging method for black-box optimization problems with expensive objective and constraints. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 347:782–805
Li Y, Wu Y, Huang Z (2014) An incremental Kriging method for sequential optimal experimental design. CMES Comput Model Eng Sci 97(4):323–357
Bouhlel MA, Martins JRRA (2019) Gradient-enhanced Kriging for high-dimensional problems. Eng Comput 35(1):157–173
Jones DR, Schonlau M, Welch WJ (1998) Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions. J Global Optim 13(4):455–492
Kanazaki M, Takagi H, Makino Y (2013) Mixed-fidelity efficient global optimization applied to design of supersonic wing. Proc Eng 67:85–99
Horowitz B et al (2010) A concurrent efficient global optimization algorithm applied to polymer injection strategies. J Pet Sci Eng 71(3–4):195–204
Zhang Y, Han Z-H, Zhang K-S (2018) Variable-fidelity expected improvement method for efficient global optimization of expensive functions. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 58(4):1431–1451
Sasena MJ, Papalambros P, Goovaerts P (2002) Exploration of metamodeling sampling criteria for constrained global optimization. Eng Optim 34(3):263–278
Li Y, Xuchang C (2016) A Kriging-based unconstrained global optimization algorithm. Int J Smart Sens Intell Syst 9(2):927–952
Li Y, Yizhong W, Shuting W (2015) Kriging-based sequence global optimization method for multiple sampling points. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Nat Sci Ed 43(12):7–11
Ginsbourger D, Le Riche R, Carraro L (2010) Kriging is well-suited to parallelize optimization, in Computational Intelligence in Expensive Optimization Problems. Springer, Berlin, pp 131–162
Parr JM et al (2012) Infill sampling criteria for surrogate-based optimization with constraint handling. Eng Optim 44(10):1147–1166
Dong H et al (2015) A kind of balance between exploitation and exploration on kriging for global optimization of expensive functions. J Mech Sci Technol 29(5):2121–2133
Cai X et al (2017) A multi-point sampling method based on kriging for global optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56(1):71–88
Yaohui L (2017) A Kriging-based global optimization method using multi-points infill search criterion. J Algorithms Comput Technol 11(4):366–377
Dong H et al (2018) Surrogate-based optimization with clustering-based space exploration for expensive multimodal problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(4):1553–1577
Dong H et al (2018) Multi-surrogate-based Differential Evolution with multi-start exploration (MDEME) for computationally expensive optimization. Adv Eng Softw 123:62–76
Gu J, Li GY, Dong Z (2012) Hybrid and adaptive meta-model-based global optimization. Eng Optim 44(1):87–104
Martin JD (2009) Computational improvements to estimating kriging metamodel parameters. J Mech Des 131:084501
Cressie N (1992) Statistics for spatial data. Terra Nova 4(5):613–617
Martin JD, Simpson TW (2005) Use of Kriging models to approximate deterministic computer models. AIAA J 43(4):853–863
Schonlau M, Welch WJ, Jones DR (1998) Global versus local search in constrained optimization of computer models. In: Flournoy N, Rosenberger WF, Wong WF (eds) New developments and applications in experimental design. Institute of Mathematical Statistics, Hayward, pp 11–25
Schonlau M (1998) Computer experiments and global optimization. University of Waterloo, Waterloo
Ye KQ, Li W, Sudjianto A (2000) Algorithmic construction of optimal symmetric Latin hypercube designs. J Stat Plan Inference 90(1):145–159
Jamil M, Yang X-S (2013) A literature survey of benchmark functions for global optimisation problems. Int J Math Model Numer Optim 4(2):150–194
Acknowledgements
Supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51775472).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y. A Kriging-based multi-point sequential sampling optimization method for complex black-box problem. Evol. Intel. 15, 2341–2350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00352-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00352-5