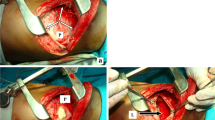
Abstract
Background
A retrospective study was conducted at Govt Medical College, Jammu in the pediatric patients who were referred to Cardio Thoracic and Vascular Surgery department with thoracic empyema and were taken up for thoracotomy and decortication Our experience showed that early intervention gave better results than in group with delayed intervention.
Material and methods
Between January 2003 and 2011, 76 patients underwent pleural decortication in pediatric age group presenting with thoracic empyema who did not respond to conservative management. 45 patients were male and 31 patients were female. They were initially evaluated with routine chest radio graphs and with Computed Tomography (CT) chest. Diagnosis of thoracic empyema was made in these cases with radio graphic evidence and was substantiated with pleural fluid cultures 62 underwent early intervention whereas 14 had delayed intervention.
Results
62 (84 %) patients underwent early decortication (within 4 weeks of Intercostaltube insertion) whereas 14 (16 %) cases were taken up for delayed decortication beyond 1 month due to unavoidable reasons like delayed referral, high grade fever or because of other co morbid diseases. In early group all patients responded well to early decortications. 6 (10 %) patients required secondary intervention that included 4 (6.4 %) patients due to recurrence of empyema or lung collapse after surgery & 2(3.2 %) patients required lung resection. and the mean hospital stay was 12 days In late intervention group, it was found that the operative time increased, the duration of chest drain also increased due to air leak/increased drainage leading to increased hospital stay (16 days) and 6 (42 %) patients required secondary intervention.
Conclusion
Early decortication is an effective surgical treatment for thoracic empyema as It facilitates early evacuation and mechanical decortication of pleural space with no additional morbidity and leads to reduced time for chest tube drainage and shortens hospital stay.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menon P, Kanoje RP, Rao KCN. Empyema thoracis: surgical management in children. J Ind Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:85–93.
Satish B, Bunker M, Sedson P. Management of thoracic empyema in childhood: does the plural thickening matter? Arch Dis Child. 2003;88:918–21.
Chonmaitree T, Powell KR. Parapneumonic pleural effusion and empyema in children. Review of a 19-year experience, 1962–1980. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1983;22:414–9.
Avansino JR, Goldman B, Sawin RS, Flum DR. Primary operative versus nonoperative therapy for pediatric empyema: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2005;115:1652–9.
Spencer D. Empyema thoracis: not time to put down the knife. Arch Dis Child. 2003;88:842–3.
Kosloske AM, Cartwright KC. The controversial role of decortication in the management of pediatric empyema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988;96:166–70.
Tiryaki T, Abbaso’Glu L, Bulut M. Management of thoracic empyema in childhood: A study of 160 cases. Pediatr Surg Int. 1995;10:534–6.
Cham CW, Haq SM, Rahamw J. Empyema thoracis: a problem with late referral? Thorax. 1993;48:925–7.
Foglia RP, Randolph JG. Current indications for decortication in the treatment of empyema in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1987;22:28–33.
Acknowledgments
Dr Rekha Harish, Dr Noor Ali, Dr Mohit Arora, Dr Puja Vimesh
Conflicts of interests
Nil
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandotra, V., Kohli, A. & Singh, G. Decortication in paediatric empyema, comparative study of early vs late intervention. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 29, 110–113 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-013-0209-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-013-0209-1