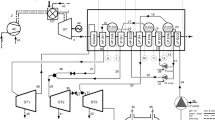
Abstract
Industrial energy conservation measures (ECMs) are important components of efforts to reduce global energy consumption and carbon emissions. To aid in assessing water conservation co-benefits of ECMs applied to industrial steam systems, this study proposes a combined energy-water conservation metric that captures the cost of conserved energy and water (CCEW) for common steam system-related ECMs. The proposed metric utilizes a fundamentals-based steam system model coupled with US industrial energy audit data to estimate potential water savings for 21 common ECMs in US industrial plants. At an average water cost of $0.71/kL ($2.66/1000 gal.), improvements to steam distribution, steam vents, de-aerator operation, steam traps, and steam leaks, which correlate to a reduction in steam generation requirements, are shown to have a CCEW that is 0.22 $/GJ lower than the conventional cost of conserved (CCE) for these ECMs. Furthermore, improvements to boiler system blowdown, which correlate to a reduction in liquid water purged from the system, are shown to have a CCEW that is 0.83 $/GJ lower than the CCE for this ECM. The study results demonstrate how broader consideration of water savings can improve the economic case for industrial ECMs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AI :
-
Annualized investment
- A p :
-
Assumed fraction of industry subset to which each energy conservation measure can be applied
- CCE:
-
Cost of conserved energy
- CCEW:
-
Cost of conserved energy and water
- CHP:
-
Combined heat and power
- C imp :
-
Capital purchase and implementation costs associated with each energy conservation measure
- CSC:
-
Conservation supply curve
- Δm MU /ΔQ fuel :
-
Change in mass of water consumed vs change in energy consumed
- ΔOM :
-
Change in annual operation and maintenance costs associated with each energy conservation measure
- ECM:
-
Energy conservation measure
- E pot :
-
Energy savings potential associated with each energy conservation measure
- ES :
-
Energy savings associated with each energy conservation measure
- Pn initial :
-
Assumed initial market penetration for each energy conservation measure
- Pn max :
-
Assumed max market penetration for each energy conservation measure
- P w :
-
Price of water
- Q boiler :
-
Energy consumed for steam generation in boiler systems for industry subset
- Q CHP :
-
Energy consumed by combined heat and power systems in industry subset
- Q fuel :
-
Total energy consumption baseline for steam generation in industry subset
- S p :
-
Average fractional energy savings associated with each energy conservation measure
References
American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, (2022). https://www.aceee.org. Accessed 17 December 2022.
Bertoldi, P., & Rezessy, S. (2007). Voluntary agreements for energy efficiency: Review and results of European experiences. Energy & Environment, 18(1), 37–73. https://doi.org/10.1260/095830507780157258
Boyd, G. A., & Pang, J. X. (2000). Estimating the linkage between energy efficiency and productivity. Energy Policy, 28, 289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(00)00016-1
Boyd, G., & Zhang, G. (2013). Measuring improvement in energy efficiency of the US cement industry with the ENERGY STAR energy performance indicator. Energy Efficiency, 6, 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-012-9160-z
Brown, H. L., Hamel, B. B., & Hedman, B. (1996). Energy analysis of 108 industrial processes. Prentice Hall.
CIBO energy efficiency handbook, (1997). Zeitz R, Ed. Council of Industrial Boiler Owners: Burke, VA.
Cornelis, E. (2019). History and prospect of voluntary agreements on industrial energy efficiency in Europe. Energy Policy, 132, 567–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.06.003
Demirel, Y., Simsek, E., Ozturk, E., et al. (2021). Selection of priority energy efficiency practices for industrial steam boilers by PROMETHEE decision model. Energy Efficiency, 14, 89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-021-10007-8
Einstein, D., Worrell, E., Khrushch, M. (2001). Steam systems in industry: Energy use and energy efficiency improvement potentials. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. 535–47.
European Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, (2022). https://www.eceee.org. Accessed 15 December 2022.
Harrel, G. (2002). Steam system survey guide. Oak Ridge National Laboratory 2002. ORNL/TM-2001/263.
Hasanbeigi, A., Menke, C., & Therdyothin, A. (2011). Technical and cost assessment of energy efficiency improvement and greenhouse gas emission reduction potentials in Thai cement industry. Energy Efficiency, 4, 93–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-010-9079-1
Hasanbeigi, A., Morrow, W., Sathaye, J., Masanet, E., & Xu, T. (2013). A bottom-up model to estimate the energy efficiency improvement and CO2 emission reduction potentials in the Chinese iron and steel industry. Energy, 50, 315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.10.062
Kaya, D., Yagmur, E. A., Yigit, K. S., Kilic, F. C., Eren, A. S., & Celik, C. (2008). Energy efficiency in pumps. Energy Conversion and Management, 49, 1662–1673.
Masanet, E., & Walker, M. E. (2013). Energy-water efficiency and U.S. industrial steam. AIChE Journal, 59, 2268–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.14148
Meier, A., Rosenfeld, A. H., & Wright, J. (1982). Supply curves of conserved energy for California’s residential sector. Energy, 7, 347–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-5442(82)90094-9
Michaela, M., Wright, A., Nimbalkar, S., Schoeneborn, F. (2011). From energy assessment to maximum implementation: Reducing the “implementation gap” for Save Energy Now LEADERS. ACEEE 2011.
Mills, E., & Rosenfeld, A. (1996). Consumer non-energy benefits as a motivation for making energy-efficiency improvements. Energy, 21, 707–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-5442(96)00005-9
Morrow, W. R., Marano, J., Hasanbeigi, A., Masanet, E., & Sathaye, J. (2015). Efficiency improvement and CO2 emission reduction potentials in the United States petroleum refining industry. Energy, 93, 95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.08.097
National Association of Manufacturers, (2014) Efficiency and innovation in U.S. manufacturing energy use, https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2014/05/f15/energy-nam.pdf. Accessed 30 January 2019.
Pardo Martínez, C. I., & Silveira, S. (2013). Energy efficiency and CO2 emissions in Swedish manufacturing industries. Energy Efficiency, 6, 117–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-012-9159-5
Rao, P., Sholes, D., & Cresko, J. (2019). Evaluation of US manufacturing subsectors at risk of physical water shortages. Environmental Science & Technology, 53, 2295–2303. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04896
Sathitbun-anan, S., Fungtammasan, B., Barz, M., et al. (2015). An analysis of the cost-effectiveness of energy efficiency measures and factors affecting their implementation: A case study of Thai sugar industry. Energy Efficiency, 8, 141–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-014-9281-7
Seiler, D., Donovan, D., & O’Donnell, G. (2019). Industrial steam systems: Strategic framework with proxy measurements to evaluate the total cost of steam. Journal of Cleaner Production, 231, 1307–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.285
Tanaka, K. (2011). Review of policies and measures for energy efficiency in industry sector. Energy Policy, 39(10), 6532–6550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.058
Trubetskaya, A., Horan, W., Conheady, P., et al. (2021). A methodology for industrial water footprint assessment using energy-water-carbon nexus. Processes, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020393
United States Census Bureau, (2017). North American industry classification system. http://www.census.gov/eos/www/naics/. Accessed 30 January 2019.
United States Department of Energy (DOE), (2002). Steam system opportunity assessment for the pulp and paper, chemical manufacturing, and petroleum refining industries. U.S. DOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy 87. DOE/GO-102002–1639.
United States Department of Energy (DOE), (2014). Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. U.S. manufacturing energy use and greenhouse gas emissions analysis. https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo/downloads/us-manufacturing-energy-use-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-analysis. 3311–2. Accessed 30 January 2019.
United States Department of Energy (DOE) (n. d.) Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. U.S. DOE Industrial Assessment Centers. Energy and cost saving assessments for small and medium-sized U.S. manufacturers. https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo/industrial-assessment-centers-iacs. Accessed September 2020
United States Department of Energy (DOE), (2002). Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Steam system opportunity assessment for the pulp and paper, chemical manufacturing, and petroleum refining industries: Main report; DOE/GO-102002–1639; Washington, DC.
United States Department of Energy (DOE), (2014). Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. U.S. DOE combined heat and power installation database, https://doe.icfwebservices.com/chpdb/. Accessed 30 January 2014.
United States Department of Energy (DOE), (2017). Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. DOE water wastewater industrial prices report. DOE/EE-1670.
United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), (2020). Natural gas annual – Natural gas gross withdrawals and production. https://www.eia.gov/naturalgas/annual/. Accessed September 2020.
United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), (2020). Natural gas annual – Natural gas prices. https://www.eia.gov/naturalgas/annual/. Accessed September 2020.
United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), (2021). Manufacturing Energy Consumption Survey (MECS), https://www.eia.gov/consumption/manufacturing/data/2018/. Accessed 8 July 2021.
Villoria-Siegert, R., Brodrick, P., Hallinan, K., et al. (2015). Cost-availability curves for hierarchical implementation of residential energy-efficiency measures. Energy Efficiency, 8, 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-014-9291-5
Walker, M. E., Lv, Z., & Masanet, E. (2013). Industrial steam systems and the energy-water nexus. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 13060–13067. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403715z
Wang, F., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., et al. (2021). Integrated graphical approach for selecting industrial water conservation projects. Journal of Cleaner Production, 287, 125503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125503
Worrell, E., Martin, N., & Price, L. (2001). Energy efficiency and carbon dioxide emissions reduction opportunities in the U.S. iron and steel sector. Energy, 26, 513–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(01)00017-2
Worrell, E., Laitner, J. A., Ruth, M., & Finman, H. (2003). Productivity benefits of industrial energy efficiency measures. Energy, 28, 1081–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(03)00091-4
Yue, H., Worrell, E., Crijns-Graus, W., et al. (2021). Saving energy in China’s industry with a focus on electricity: A review of opportunities, potentials and environmental benefits. Energy Efficiency, 14, 60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-021-09979-4
Zuberi, M. J. S., Hasanbeigi, A., & Morrow, W. (2022). Electrification of industrial boilers in the USA: Potentials, challenges, and policy implications. Energy Efficiency, 15, 70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-022-10079-0
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Abigail Hawley for her contributions assessing industrial water prices, as well as Randall Waymire for their contributions assessing energy conservation measures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niemeyer, E., Walker, M.E., Lema, G. et al. Impact of water consumption on the economic viability of energy efficiency improvements for industrial steam systems. Energy Efficiency 16, 89 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-023-10167-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-023-10167-9