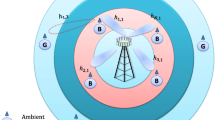
Abstract
Automatic toll collection systems have been known to operate with a backscatter mechanism. Such systems are highly prone to eavesdropping despite the security measures implemented, as the data can be stored and processed later for the transaction. In this paper, we analyse the probability that secrecy is compromised in the automatic toll collection systems using the physical layer security principles. We perform simulations to corroborate the analytical results in the proposed fading channel environment. The results are obtained for different distances between the tag and the reader and that between the tag and the eavesdropper. The analytical and simulation results are found to be in close agreement.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inserra D, Hu W and Wen G 2018 Antenna array synthesis for RFID-based electronic toll collection. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66(9): 4596–4605
Wyner A D 1975 The wire-tap channel. The Bell System Technical Journal 54(8): 1355–1387
Bloch M, Barros J, Rodrigues M R D and McLaughlin S W 2008 Wireless information-theoretic security. IEEE Trans. on Inf. Theory 54(6): 2515–2534
Liu X 2013 Probability of strictly positive secrecy capacity of the Rician-Rician fading channel. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 2(1): 50–53
Sun X, Wang J, Xu W and Zhao C 2012 Performance of secure communications over correlated fading channels. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(8): 479–482
Shukla M K and Nguyen H H 2021 Ergodic secrecy sumrate analysis of a two-way relay NOMA system. IEEE Syst J 15(2): 2222–2225
He F, Man H and Wang W 2011 Maximal ratio diversity combining enhanced security. IEEE Commun. Lett. 15(5): 509–511
Yang N, Yeoh P L, Elkashlan M, Schober R and Collings I B 2013 Transmit antenna selection for security enhancement in MIMO wiretap channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 61(1): 144–154
Liu Z, Ye Y, Chu X and Sun H 2022 Secrecy performance of backscatter communications with multiple self-powered tags. IEEE Commun. Lett. 26(12): 2875–2879
Liu Y, Ye Y and Hu R Q 2021 Secrecy outage probability in backscatter communication systems with tag selection. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 10(10): 2190–2194
Gradshteyn I S and Ryzhik I M 2007 Table of Integrals, Series, and Products, 7th ed. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H.K., Kumbhani, B. Ergodic secrecy capacity of backscatter communication based automatic toll collection systems. Sādhanā 48, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-023-02143-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-023-02143-x